Methods of detecting analytes and compositions thereof
A technology for analytes and compositions, applied in the field of detecting analytes and compositions thereof, can solve problems such as inaccurate reading counts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
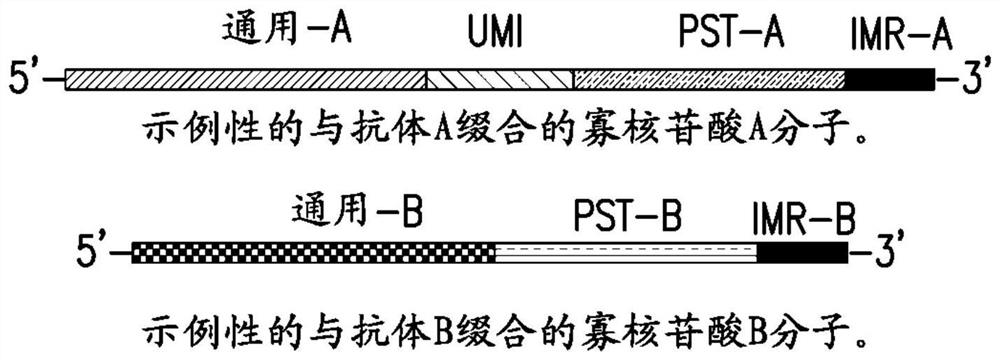
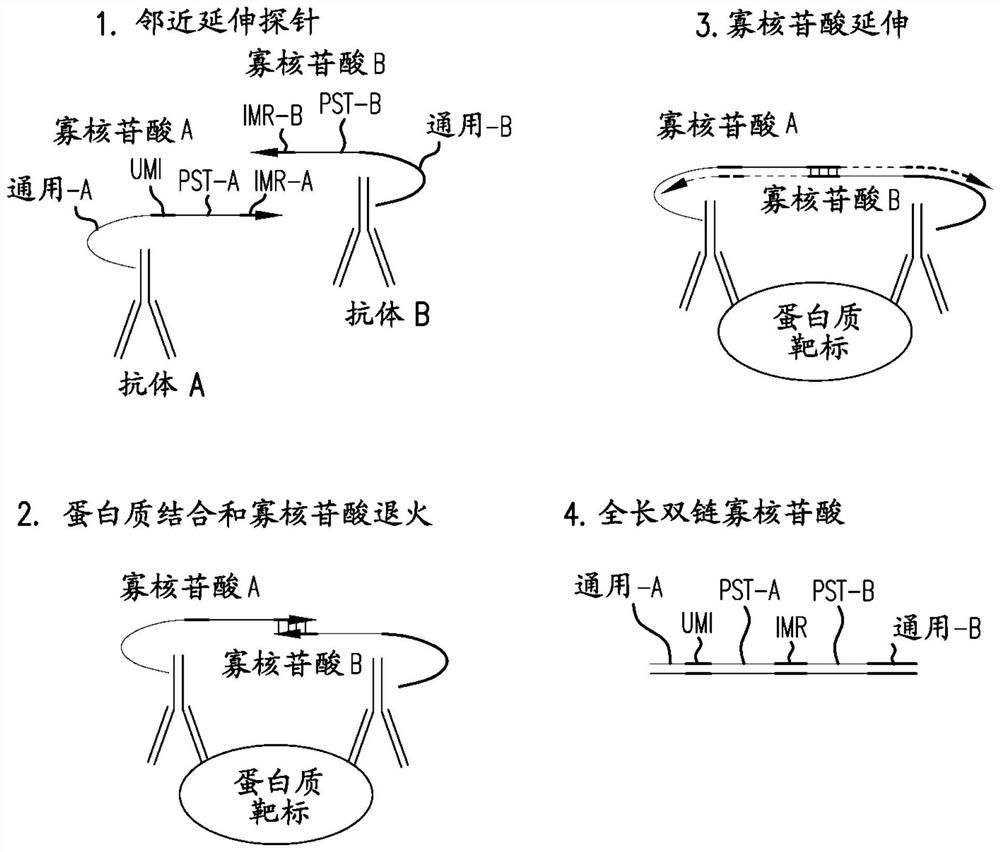
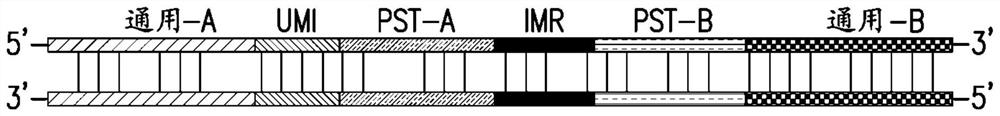
[0159] The following is an illustrative example showing how the methods described herein can be used for protein analysis. In total, 96 pairs of probes were designed to detect 96 different protein targets. Four of these are controls for data normalization purposes. Control 1 and Control 2 were used for exogenous protein targets that were not in the test sample. The 5' ends of all oligonucleotides were conjugated to their respective antibodies. Control 3 is an extension control in which both oligo A and oligo B are conjugated to the same antibody, so extension is not related to antigen binding. Control 4 is an assay control used to monitor changes in PCR amplification, where the intact full-length oligonucleotide was incorporated directly into the reaction.
Embodiment 2
[0161] sample:
[0162] 1. Human serum samples
[0163] 2. Human serum sample + protein targets #1 and #2 spiked at 5ng / ml
[0164] 3. PBS (negative control)
[0165] Antibody Binding:
[0166]
[0167] Incubate overnight (16 hr) at 4°C.
[0168] extend:
[0169]
[0170] Incubate at 50°C for 20 min → 95°C for 5 min → 17 cycles (95°C for 30 sec → 54°C for 1 min → 60°C for 1 min) → hold at 4°C in a thermal cycler with a heating lid.
[0171] Library amplification:
[0172]
[0173] Incubate in a thermal cycler with a heated lid at 95 °C for 13 min → 98 °C for 2 min → 20 cycles (98 °C for 15 sec → 60 °C for 2 min) → 72 °C for 5 min → 4 °C hold.
[0174] Purification: 75uL of ice-cold water was added to each of the 25uL samples from the previous step for a total of 100uL. One round of 1.2x Ampure XP bead purification (eluted in 20 uL of water) was performed.
[0175] Library quantification using Agilent Bioanalyzer High Sensitivity DNA chip: Dilute the purified lib...
Embodiment 3
[0177] Starting material: purified genomic DNA and total RNA. For example, 50ng gDNA and 50ng total RNA were purified from THP-1 cell line. Ideally, the relative amounts of gDNA and RNA should be representative of the amount in the sample.
[0178] DNA / RNA Fragmentation:
[0179]
[0180] RNA polyadenylation
[0181]
[0182]
[0183] DNA connection:
[0184]
[0185] Purification: Add 50uL of ice-cold water to 50uL of the sample from the previous step, making a total of 100uL. 2 rounds of 1.2×Ampure XP bead purification were performed following the manufacturer's manual with the following exceptions: the first round was eluted in 52 uL of water; and the second round was eluted in 13 uL of water.
[0186] reverse transcription:
[0187]
[0188]
[0189] Purification: 75uL of ice-cold water was added to 25uL of the sample from the previous step for a total of 100uL. Follow the manufacturer's manual for 1 round of 1.2x Ampure XP bead purification and elu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com