Integrated lens antenna and communication equipment
A technology that integrates lenses and antennas. It is applied in the directions of antennas, antenna arrays, and antenna arrays that are energized separately. It can solve problems such as the inability to achieve continuous angular scanning.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
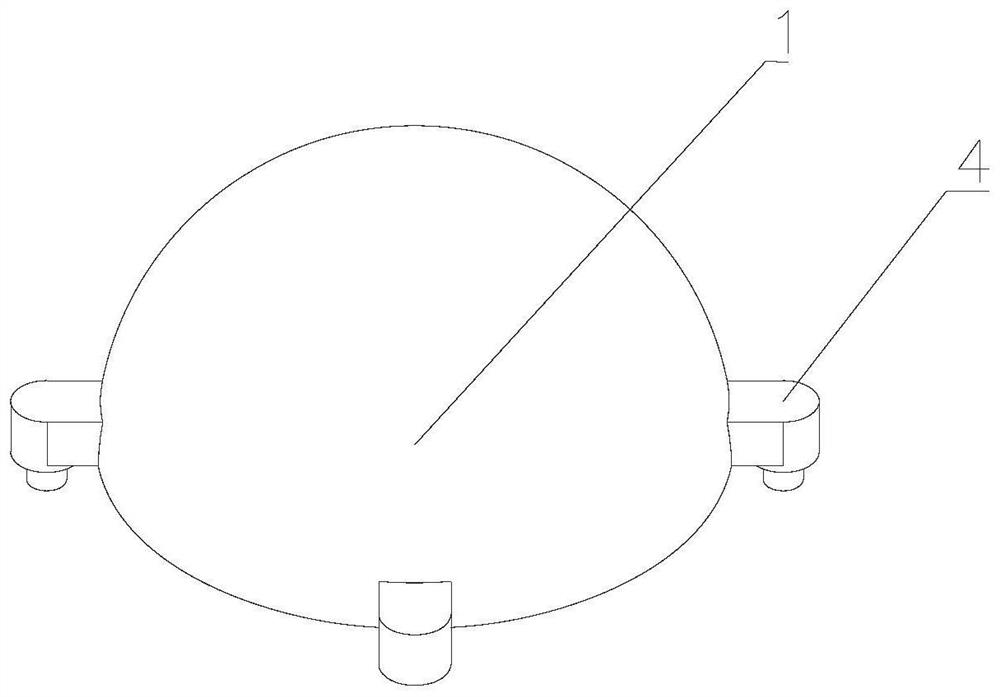
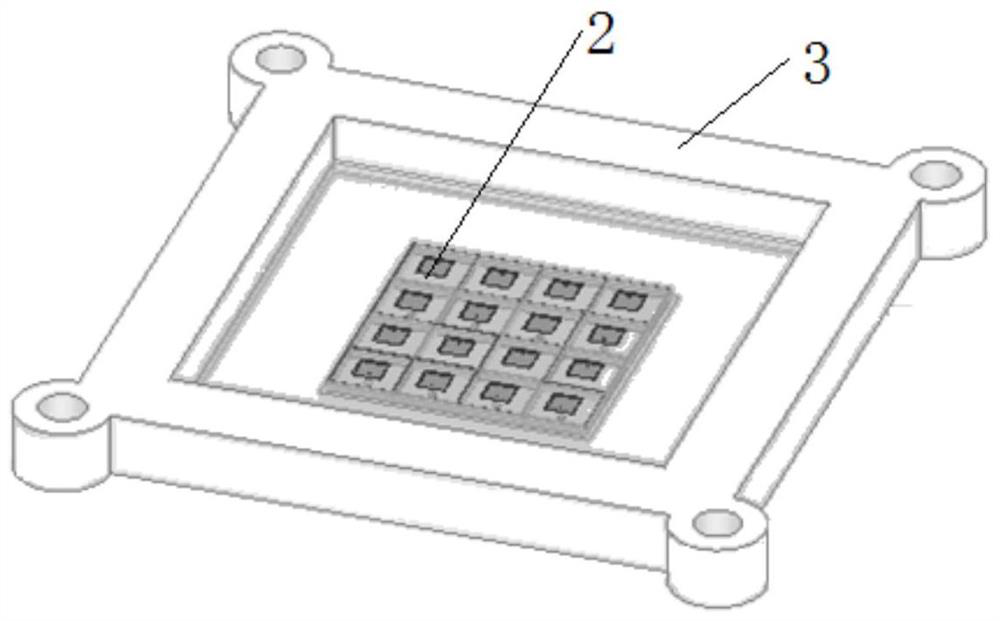
[0051] Please refer to figure 1 as well as figure 2 , an integrated lens antenna, comprising a first dielectric lens 1, a microstrip radiation unit 2 and a base 3;
[0052] The microstrip radiation unit 2 is arranged on one side of the base 3 and is located in the base 3; the base 3 is rectangular and has a rectangular groove inside, and the microstrip radiation unit 2 is arranged on the base 3. In the rectangular groove, there is a height difference between the microstrip radiation unit 2 and the base 3;
[0053]The first dielectric lens 1 is a rotationally symmetrical structure, and the main body of the first dielectric lens 1 is hemispherical; the surface of the hemispherical medium can obtain parallel beams by calculating Snell's law, and by adjusting the first medium The distance between the lens 1 and the microstrip radiation unit 2 enables the first dielectric lens 1 to emit parallel beams; the first dielectric lens 1 can be made of a single dielectric constant mater...
Embodiment 2
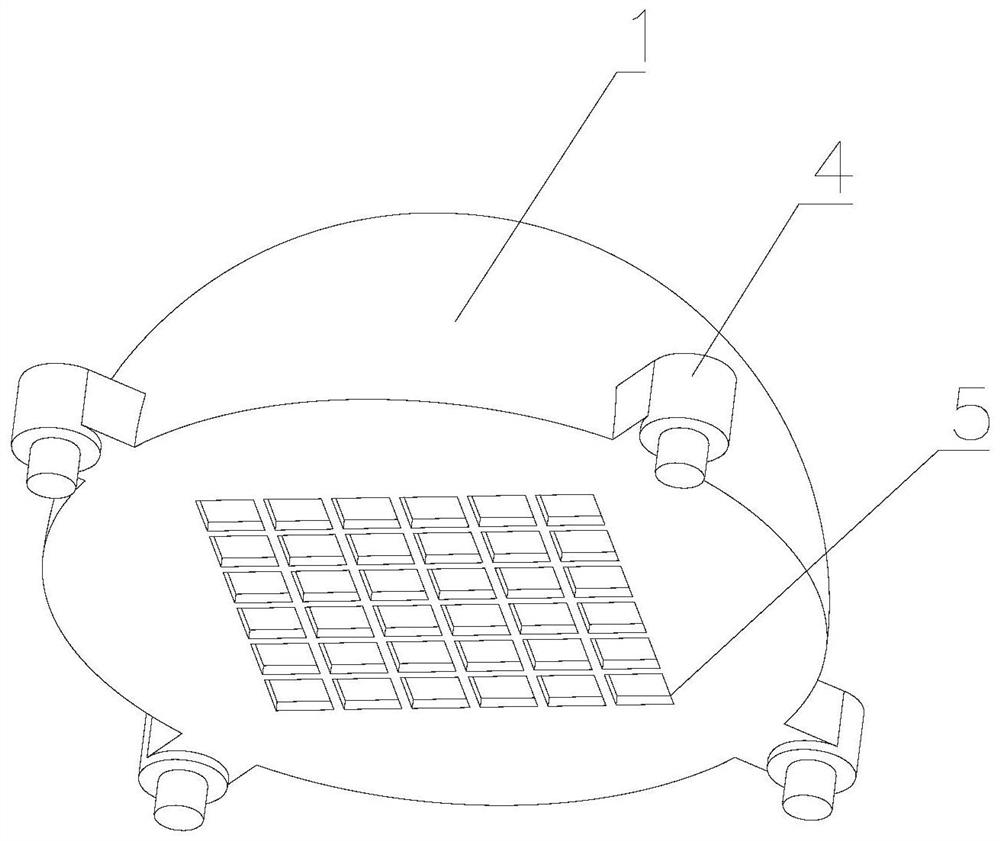
[0058] The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that a dielectric constant buffer layer 5 is also provided;
[0059] The plane side of the first dielectric lens 1 is provided with a dielectric constant buffer layer 5;
[0060] Please refer to image 3 , the dielectric constant buffer layer 5 is an array of recessed grooves; the array of recessed grooves corresponds to the position of the microstrip radiation unit 2; the array of recessed grooves is distributed in a grid; the array of recessed grooves is rectangular;
[0061] Specifically, according to the area of the plane side of the first dielectric lens 1, an array of concave grooves of a corresponding size is set; the array of concave grooves is a 6×6 square array of concave grooves; two sides are respectively parallel to the four sides of the rectangle formed by the microstrip radiation unit 2;
[0062] Wherein, the dielectric constant buffer layer 5 is not limited to an array of recessed gro...
Embodiment 3
[0064] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that it also includes a second dielectric lens 6;
[0065] Please refer to Figure 4 , the second dielectric lens 6 is a rotationally symmetrical structure, the main body of the second dielectric lens 6 is cylindrical, and its shape is adapted to the first dielectric lens 1; one side of the second dielectric lens 6 It is connected to the plane side of the first dielectric lens 1, and the other side is connected to the base 3;
[0066] Specifically, the dielectric constant and material of the second dielectric lens 6 are the same as those of the first dielectric lens 1, and the hemi-warp is the same as the hemi-warp of the first dielectric lens 1; the first dielectric lens 1 After being connected with the second dielectric lens 6, it can be equivalent to an ellipsoidal dielectric lens; according to the ray tracing theory, when the electromagnetic wave radiated by the microstrip radiation unit 2 passes throu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com