Long non-coding RNA and application thereof in diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
A non-coding technology for the treatment of liver cancer, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of low surgical resection rate, poor overall prognosis of HCC patients, and incomplete understanding of the pathogenesis of liver cancer.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
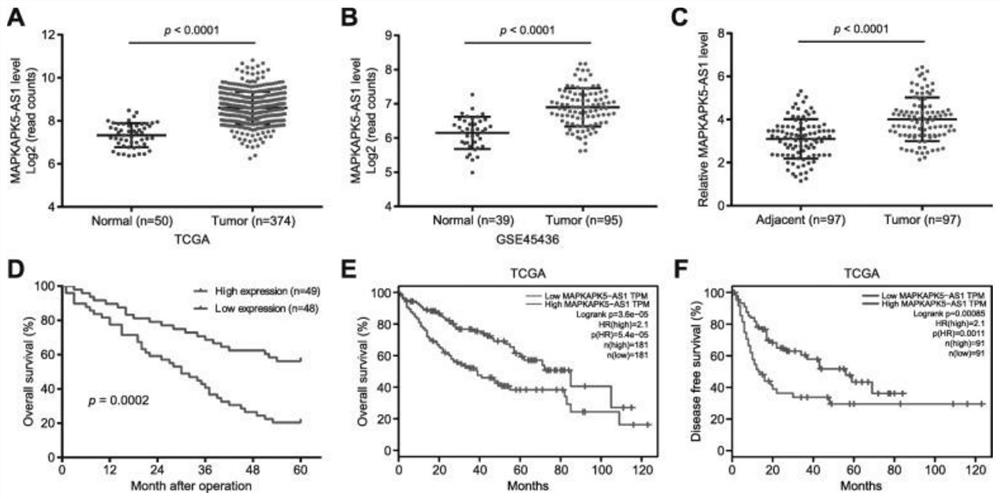
[0064] Example 1: Differential expression and clinical significance of MAPKAPK5-AS1 in liver cancer
[0065] GEO and TCGA public databases were analyzed to identify lncRNAs that may play important biological functions in liver cancer progression, and found that lncRNA MAPKAPK5-AS1 (SEQ ID NO.1) was consistently elevated in liver cancer, and subsequently, our qRT- PCR results confirmed high expression of MAPKAPK5-AS1 in HCC tissues compared with adjacent non-tumor tissues,
[0066] The primer sequences are: MAPKAPK5-AS1-F (Seq ID NO.2): GGCGTCGTGAGGTATGGATGTTC, MAPKAPK5-AS1-R (Seq ID NO.3): GCTTGACCACTTCTCGGCTGTG.
[0067] In addition, Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of 97 HCC patients and patient data in the TCGA database showed that HCC patients with high MAPKAPK5-AS1 expression exhibited significantly worse overall survival. Taken together, these results suggest that MAPKAPK5-AS1 is upregulated in HCC, which is associated with poor clinical features and prognosis in HCC pati...
Embodiment 2
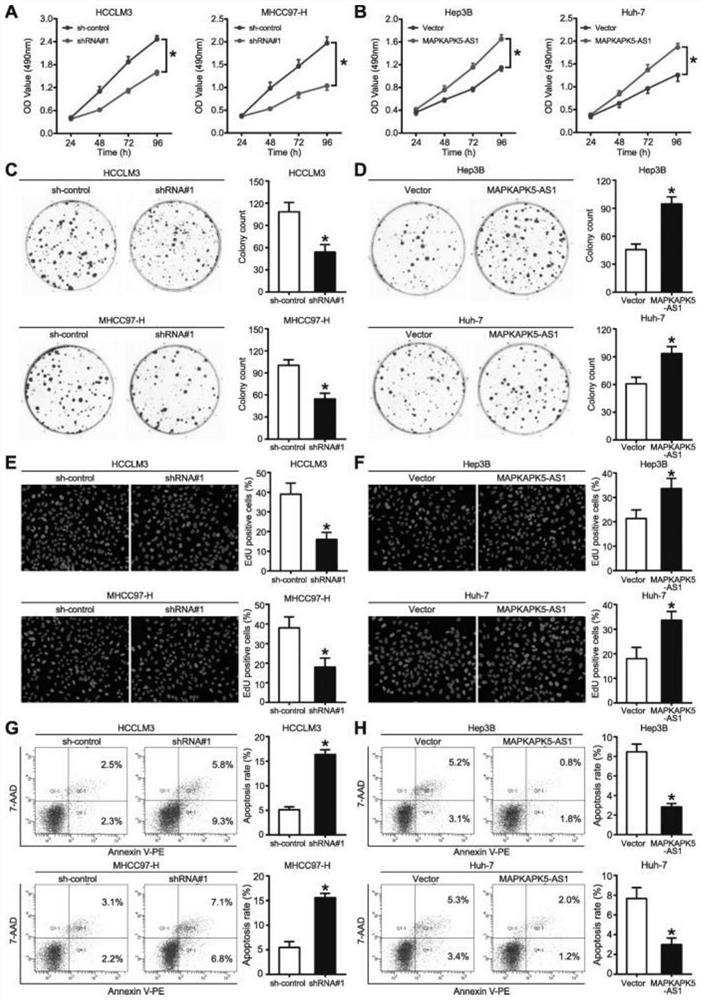
[0068] Example 2: MAPKAPK5-AS1 promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of HCC cells in vitro
[0069] To investigate the biological function of MAPKAPK5-AS1, we stably knocked down MAPKAPK5-AS1 in HCCLM3 and MHCC97-H cells, and overexpressed MAPKAPK5-AS1 in Hep3B and Huh-7 cells. MAPKAPK5-AS1 knockdown significantly inhibited the viability and proliferation of HCCLM3 and MHCC97-H cells in MTT, colony formation and EdU assays. While MAPKAPK5-AS1 overexpression significantly enhanced the viability and proliferation of Hep3B and Huh-7 cells, in addition, flow cytometry analysis showed that knockdown of MAPKAPK5-AS1 in HCCLM3 and MHCC97-H cells significantly induced apoptosis, While overexpression of MAPKAPK5-AS1 in Hep3B and Huh-7 cells strongly inhibited apoptosis. These results above indicate that MAPKAPK5-AS1 promotes the proliferation of HCC cells by inhibiting apoptosis (eg figure 2 ).
Embodiment 3
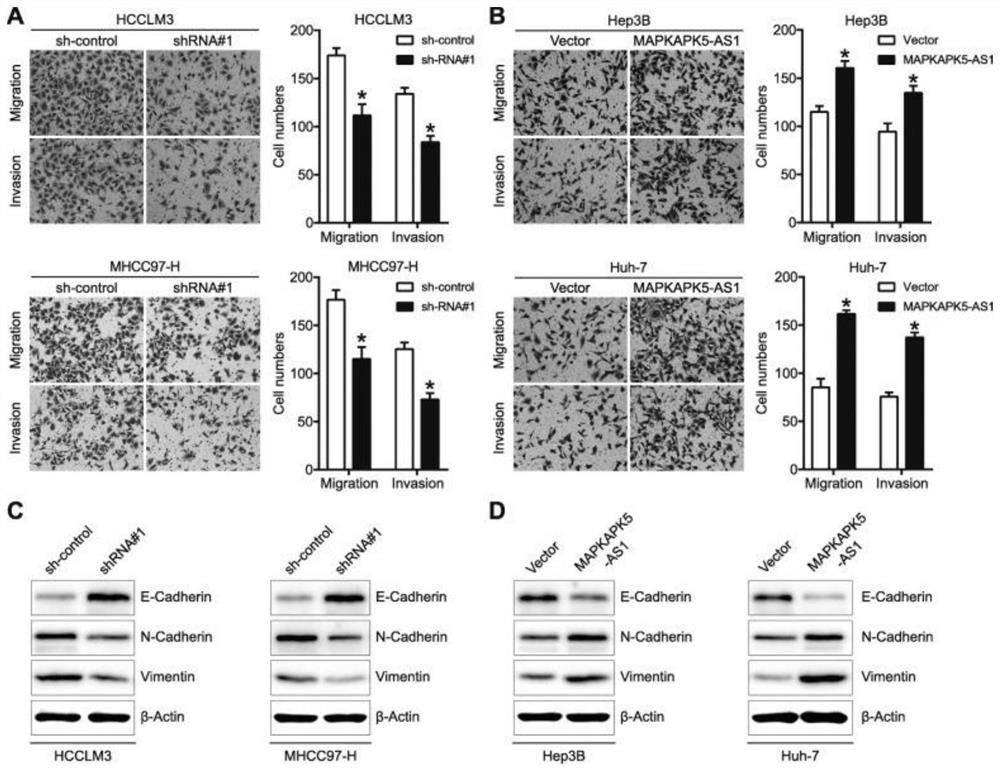
[0070] Example 3: MAPKAPK5-AS1 promotes the migration and EMT process of HCC cells in vitro
[0071] Transwell migration and invasion experiments were performed to explore the effect of MAPKAPK5-AS1 on cell migration, and the results showed that knockdown of MAPKAPK5-AS1 in HCCLM3 and MHCC97-H significantly inhibited the migration and invasion of tumor cells, while overexpression of MAPKAPK5-AS1 Significantly enhanced the migration of Hep3B and Huh-7 cells. Considering that EMT is a key mechanism mediating cancer metastasis, the effect of MAPKAPK5-AS1 on the EMT process of tumor cells was further investigated. Western blot analysis showed that MAPKAPK5-AS1 knockdown in HCCLM3 and MHCC97-H significantly increased the expression of E-cadherin and decreased the levels of N-cadherin and vimentin. Opposite regulation of EMT marker expression was observed after overexpression of MAPKAPK5-AS1 in Hep3B and Huh-7 cells. Therefore, our above results suggest that MAPKAPK5-AS1 promotes ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com