Control method based on leg and arm multiplexing hexapod robot and robot
A technology of a hexapod robot and a control method, which is applied to the control method and robot field of a hexapod robot based on leg-arm multiplexing, can solve the problem of difficult control technology, occupation of robot hardware and structural resources, and lack of flexible gait motion and operation. Ability and other issues to achieve the effect of flexible mobile job control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
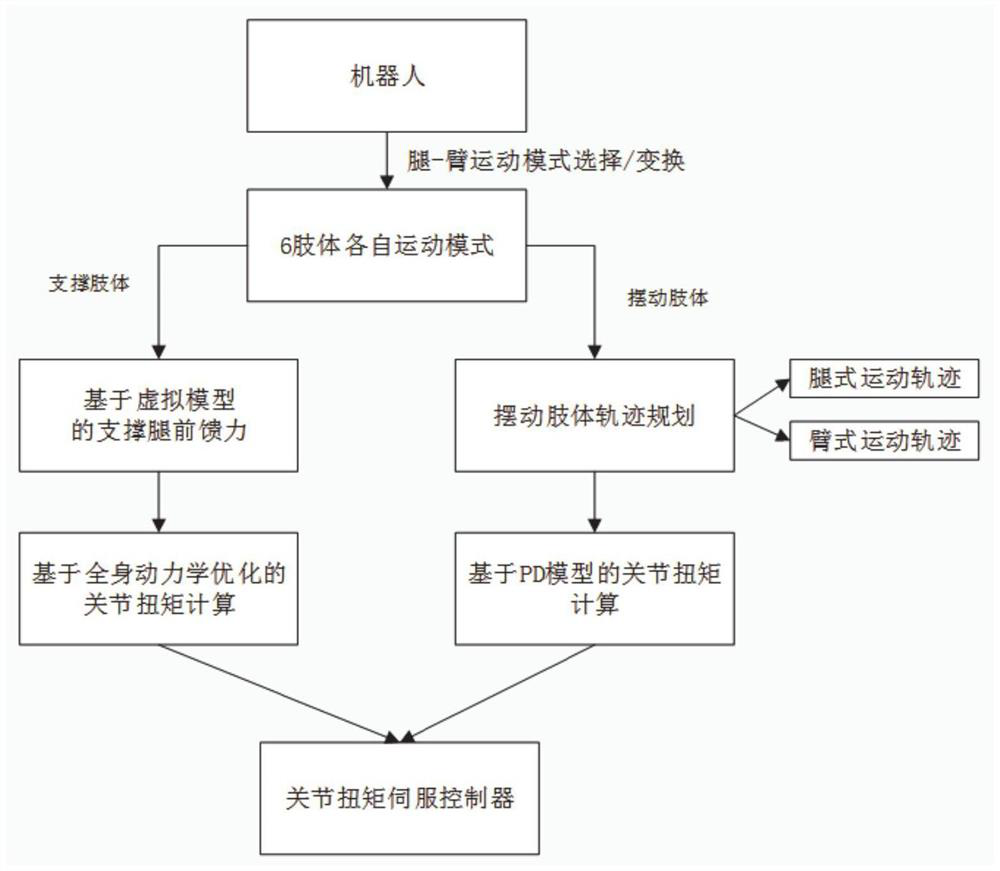
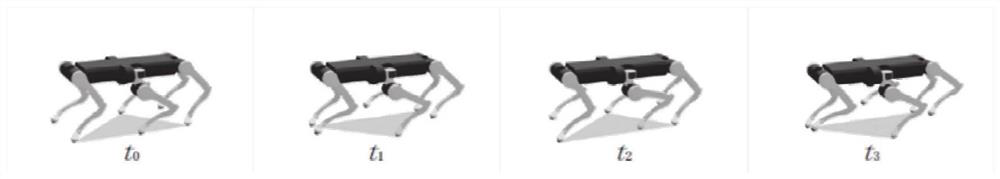
[0047] Such as figure 2 As shown, the purpose of this embodiment is to provide a control method based on leg-arm multiplexing hexapod robot, including the following steps:
[0048] The model is constructed with the center of mass of the torso of the leg-arm multiplexing hexapod robot as the origin, and the feedforward force of each supporting leg of the robot is obtained by using the position vector of the support point of the robot's legs relative to the center of mass and the virtual force at the center of mass of the torso;
[0049] Using the floating degrees of freedom of the robot torso, the motion degrees of freedom of the robot joints and the obtained feedforward force of each supporting leg, construct a full-body dynamics model of the robot, and obtain the joint torque of each supporting leg of the robot;
[0050] Using the change of robot position coordinates, obtain the joint angle and joint torque in the swing trajectory of the non-supporting leg of the robot;
[...
Embodiment 2
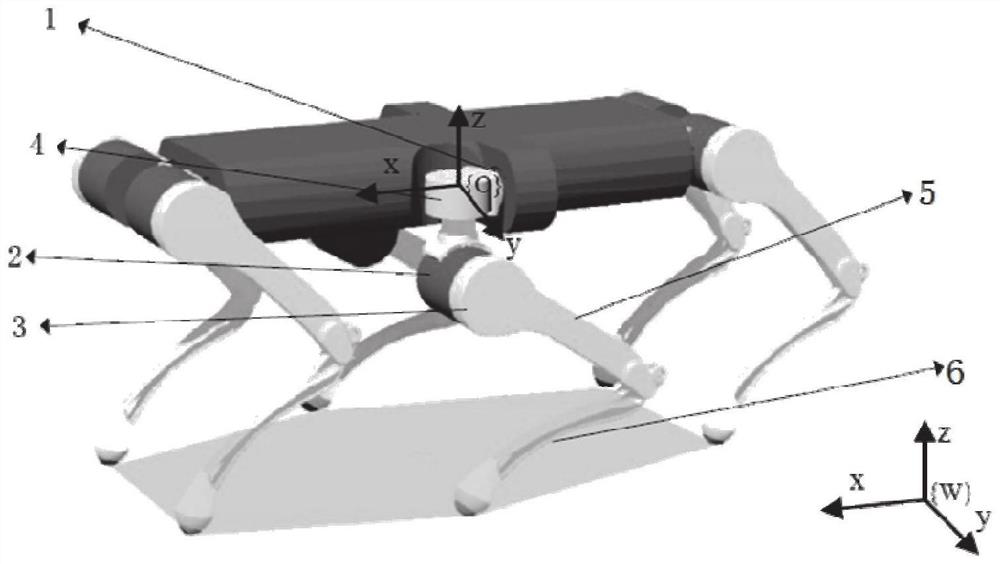
[0115] The robot that implements the above control method includes: a robot trunk and six sets of leg mechanisms connected to the trunk and arranged in pairs, four sets of leg mechanisms located at the front and rear of the robot trunk are movably connected with the robot trunk, and located at two The first kinematic joint 1 is arranged on each side, the first kinematic joint 1 is connected with the fourth kinematic joint 4 , the fourth kinematic joint 4 is connected with the second kinematic joint 2 , and the second kinematic joint 2 is connected with the third kinematic joint 3 .
[0116] The thigh link 5 and the calf link 6 form a leg mechanism, the second kinematic joint 2 is connected with the thigh link 5 to drive the movement of the thigh link, and the third kinematic joint 3 realizes the movement of the shank link 6 through the transmission of the link; the first kinematic joint 1 moves around the moving direction of the robot, drives the leg mechanism to move in and ou...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com