Sign function-based dynamic positioning fixed time control method
A dynamic positioning and symbolic function technology, applied in two-dimensional position/channel control, non-electric variable control, vehicle position/route/height control, etc., can solve the problem that dynamic positioning ships cannot achieve synchronous convergence and achieve optimal motion path, avoiding anomalies, and reducing energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
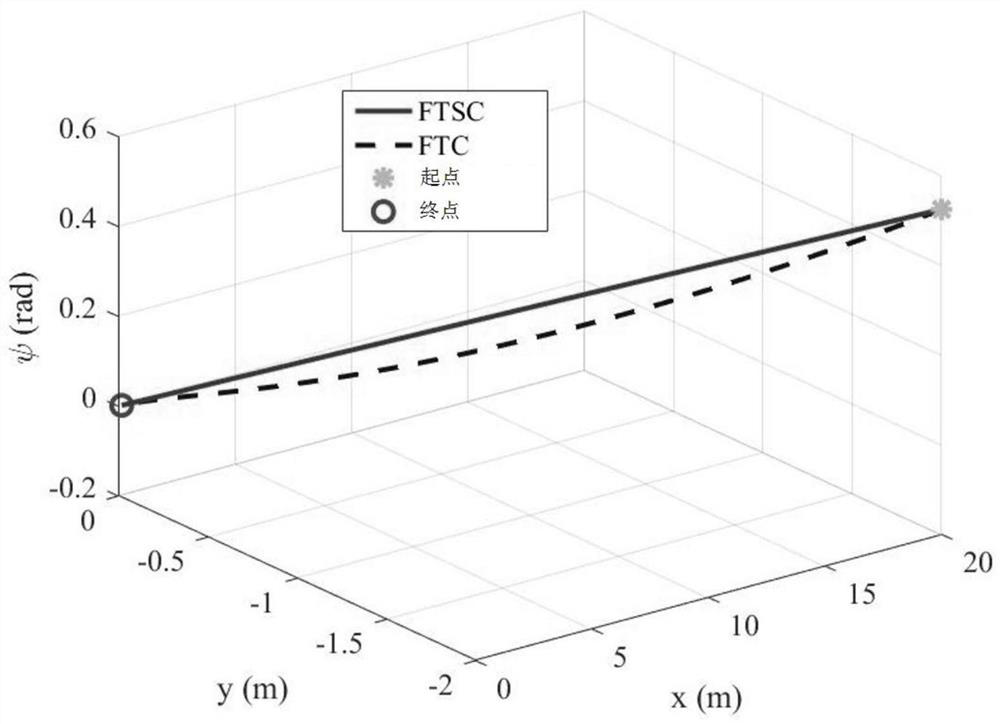
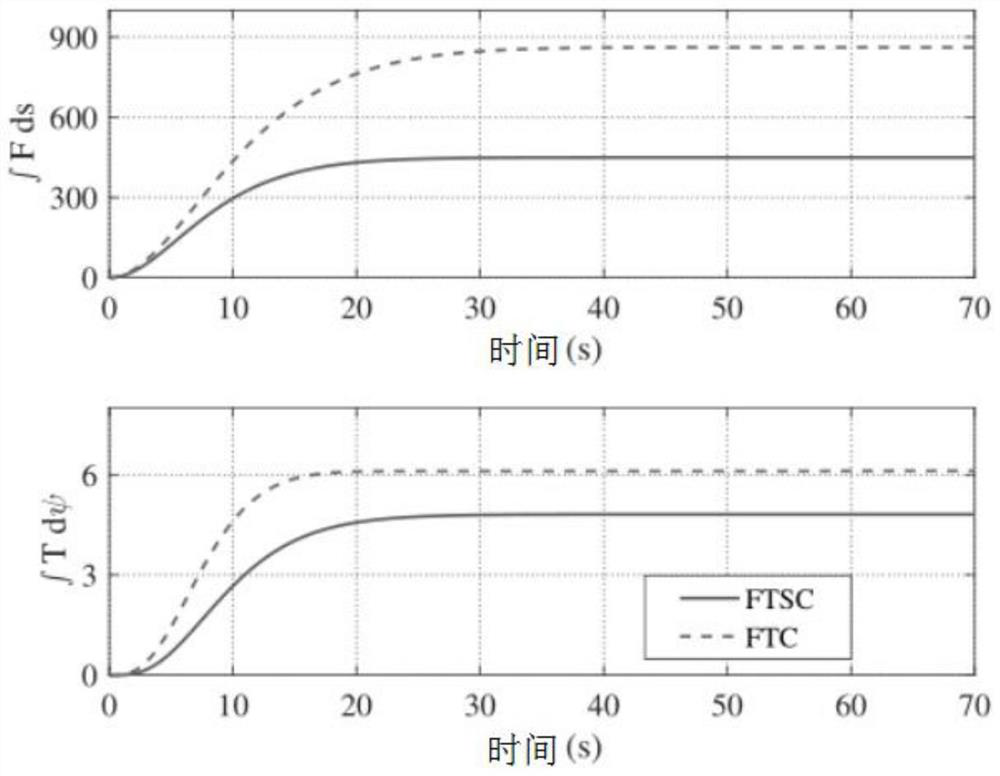
Examples
Embodiment
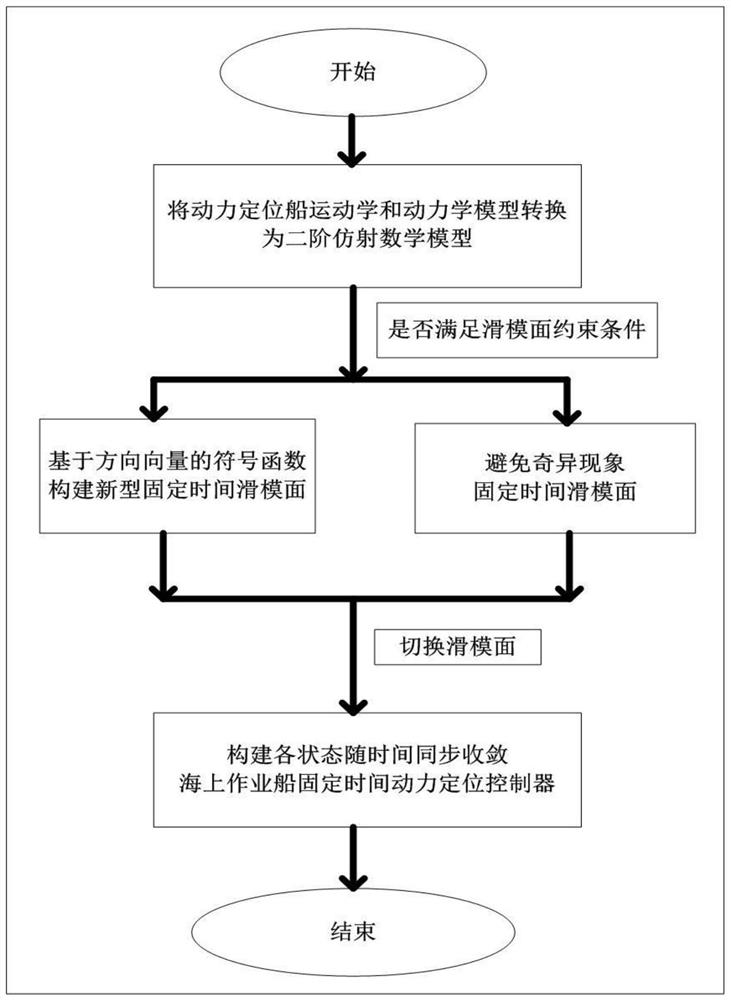
[0064] Step 1: Establish the kinematics and dynamics model of the dynamic positioning vessel:
[0065]
[0066]
[0067] Where: R(η(t)) represents the coordinate system transformation matrix, η=[x,y,ψ] T Indicates the position and heading angle of the dynamically positioned ship; υ=[u,v,r] T Indicates the velocity and angular velocity of the dynamically positioned ship; M 0 Indicates the mass and moment of inertia of the dynamic positioning ship; C 0 (ν) represents the Coriolis centripetal force matrix, D 0 (ν) represents the damping coefficient matrix; τ represents the control force and control torque. The initial values of the position and velocity vectors are set to
[0068] Then combine the system (1) and (2) to establish a second-order mathematical model:
[0069]
[0070] in,
[0071]
[0072]
[0073]
[0074] In the formula,
[0075] M(η(t))=R(η(t))M 0 R -1 (η(t)) (7)
[0076] The second step is to design a new type of direction sign f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com