Causal correlation analysis method for fine positioning of whole genome pathogenic SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism)
A genome-wide and association analysis technology, applied in the fields of genomics, proteomics, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as easy deletion of pathogenic SNPs, affecting analysis results, etc., to break through limitations, reduce false positive rates, and improve true The effect of positive rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
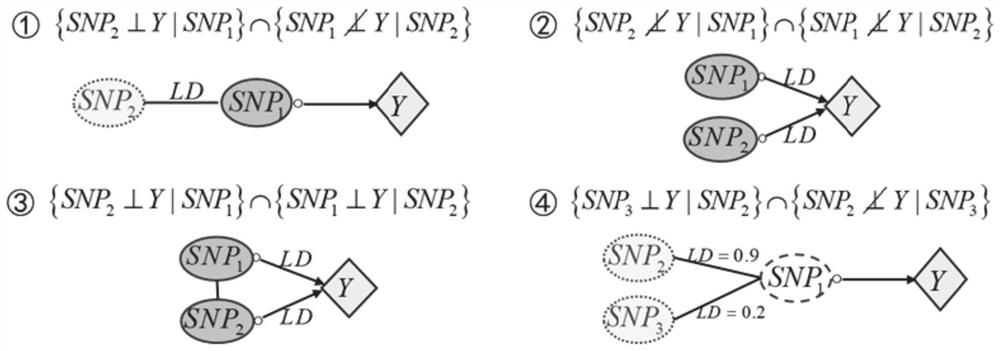
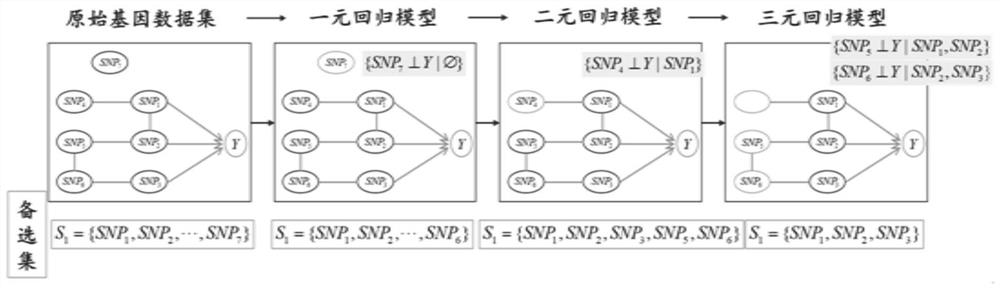
[0055] Take a small data set as an example, assuming that the real causal relationship between SNP and Y in the data is as follows figure 2 shown in . Assuming that there are 7 SNPs in the original data set, in order to screen the causative locus of outcome Y, first use the unary regression model to judge whether each SNP is marginally independent from Y, and remove the SNP 7 ; In the binary regression model due to a given SNP 1 Post-SNP 4 Independent of Y condition, remove SNP 4 ; Similarly, the triple regression model can be used to remove SNPs 5 and SNP 6 ; At this time, the number of remaining SNPs in the candidate set is less than 4, and the quaternary regression model cannot be constructed, and the operation is terminated. then {SNP 1 , SNP 2 , SNP 3} is the pathogenic site selected.
Embodiment 2
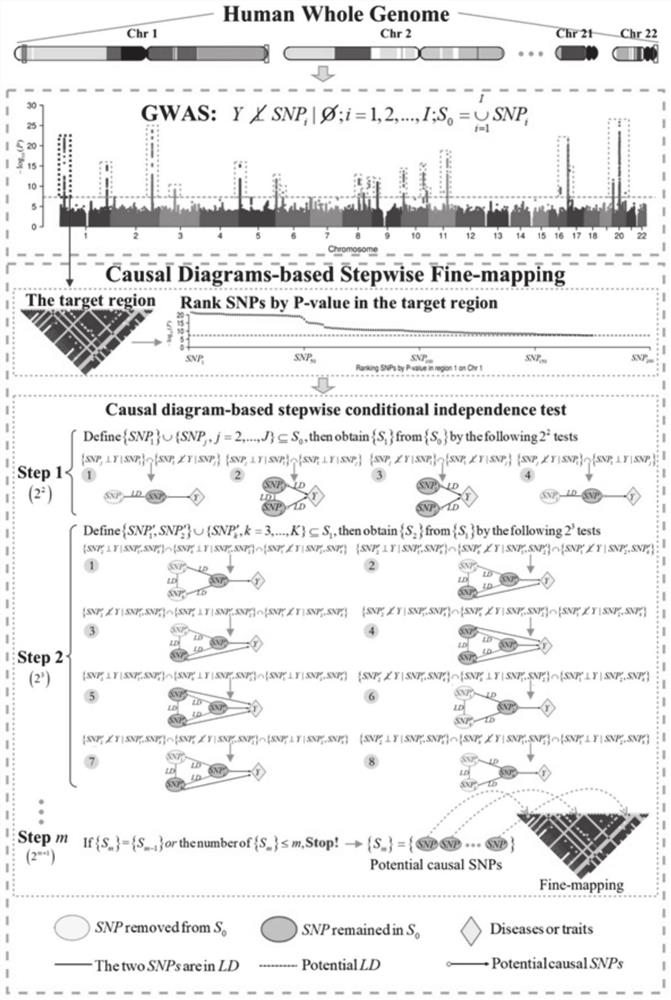
[0057] Such as image 3 As shown, Example 2 of the present invention provides a causal GWAS method for fine mapping of pathogenic SNPs oriented to the whole genome, comprising the following steps:
[0058] (1) First determine whether each SNP in the genome is independent of the outcome Y. In this model, a univariate regression model (such as linear regression or logistic regression model) is used to conduct genome-wide association analysis on samples, and based on the analysis results, the P value is screened below a certain threshold (such as P–8 ), and define the selected SNP as the candidate gene set S 0 ,which is:
[0059]
[0060] gene set S 0 The SNPs in are sorted according to the P value from small to large.
[0061] (2) Fixed S 0 The SNP with the smallest P value in 01 , the remaining SNPs constitute S 0 subset SNP 0j (j=2, . . . , J).
[0062] SNPs 01 with SNP 0j (j=J, . . . , 2) Simultaneously perform regression analysis on the outcome Y (for example, u...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Embodiment 3 of the present invention provides a causal association analysis system for fine mapping of pathogenic SNPs in the whole genome, including:
[0069] The data acquisition module is configured to: acquire genome data to be analyzed;
[0070] The causal GWAS module, configured as:
[0071] Genome-wide association analysis was performed on genomic data using a single factor regression model, and significant SNPs with P values lower than the preset threshold were screened, and the selected SNPs were defined as the first candidate gene set (i.e. S 0 ), sort the SNPs in the first candidate gene set according to the P value from small to large;
[0072] Fix the SNP with the smallest P value in the first candidate gene set 01 , the remaining SNPs constitute the first candidate gene subset, SNP 01 Perform binary regression analysis on the outcome in turn with the SNPs in the first candidate gene subset, calculate the conditional independence between the two SNPs ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com