Anti-ror1/Anti-cd3 bispecific binding molecules
A molecular-binding, bispecific technology for anti-receptor/cell surface antigen/cell surface determinant immunoglobulins, anti-animal/human immunoglobulins, antibodies, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0671] Example 1: Design and expression of anti-ROR1 / anti-CD3 bispecific binding molecules
[0672] Multiple variables affect the in vivo potency of bispecific binding molecules, including PK, epitope, relative affinities of the binding components, and the valence and steric configuration of the paratope. Currently, there is no reliable way to a priori design a single molecule that optimizes all these parameters. Therefore, multiple anti-ROR1 / anti-CD3 bispecific constructs were designed, fabricated and tested to systematically assess the impact of many of these parameters.
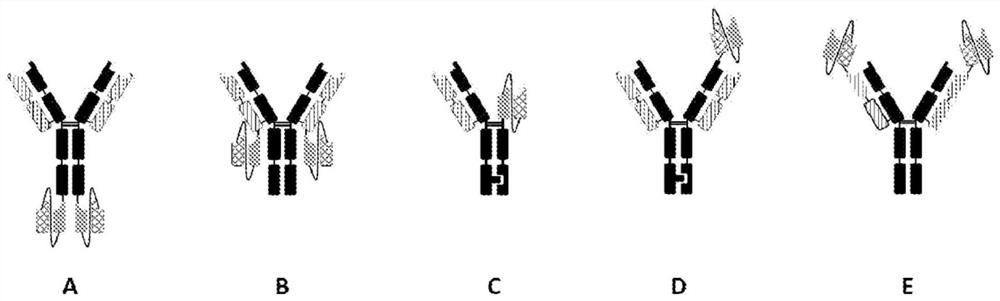
[0673] To identify the structure that provides the optimal conformation, in particular the most active relative spatial position of the ROR1 and CD3 binding components, various constructs were designed, such as figure 1 summed up. Although various bispecific formats have been described (see e.g. Brinkmann and Kontermann, MABS 9:182-212 (2017)), current efforts are focused on formats comprising the Fc com...
Embodiment 2
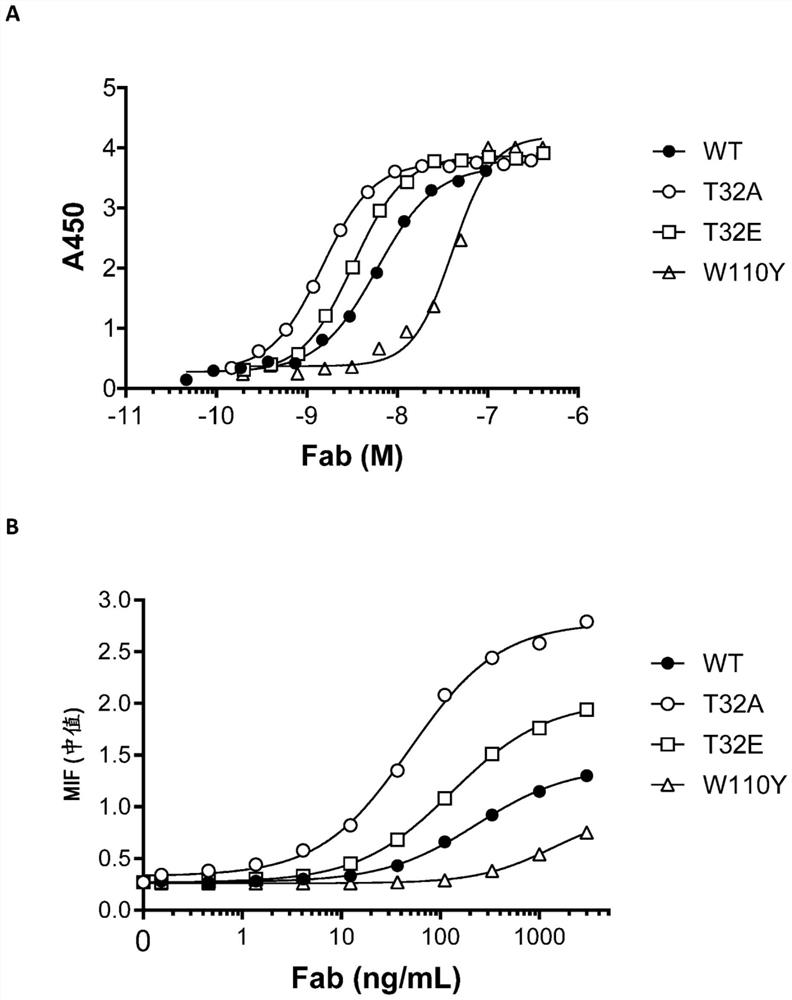
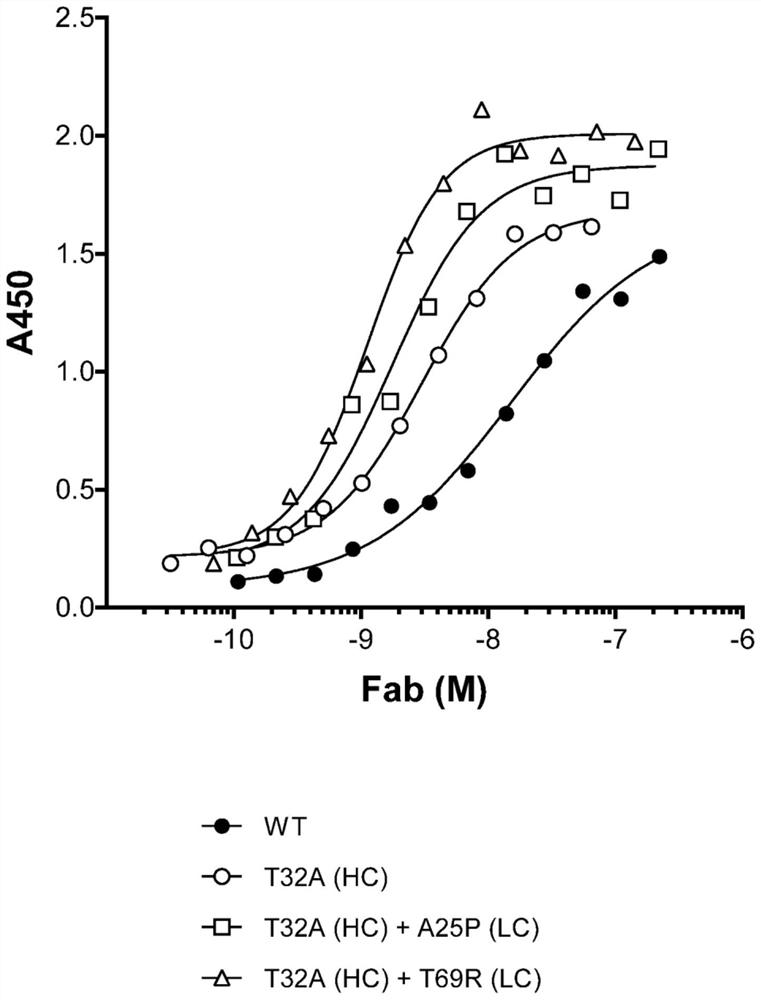
[0694] Example 2: Binding of anti-ROR1 / anti-CD3 bispecific binding molecules to ROR1
[0695] Bispecific binding molecules with different configurations, ROR1 affinities and ROR1 potencies were evaluated for binding to human ROR1 to determine the effect of these parameters on cytotoxicity. Binding of bispecific constructs 1-20 to human ROR1 was characterized using ROR1 transfected MEC cells, JeKo-1 cells and recombinant ROR1 extracellular domain (ECD).
[0696] Materials and methods
[0697] ROR1 Binding Assay Using Cells and Flow Cytometry
[0698] ROR1 binding was quantified using ROR1-transfected MEC cells and JeKo-1 cells. For each condition, 2.5E5 cells were used. Place cells in 50 μL of PBS with 2% FBS. Cells were then diluted with an equal volume of a 2X stock solution of the test bispecific binding molecule. Co-incubate cells and antibodies on ice for 20 minutes, then wash cells 3 times with 300 μL FACS buffer, resuspend in 100 μL anti-human Fc-PE conjugated ant...
Embodiment 3
[0719] Example 3: Internalization of ROR1 by anti-ROR1 / anti-CD3 bispecific binding molecules
[0720] Internalization and recycling of ROR1 and bispecific binding molecules that recognize ROR1 may affect therapeutic efficacy in vivo. For example, ROR1 binding, internalization, and degradation prior to integration with T cells may reduce cytotoxicity. Anti-ROR1 / anti-CD3 bispecific binding molecules with five different configurations were characterized for binding and internalization.
[0721] While characterizing the internalization of the various bispecific constructs, cell surface expression of ROR1 was detected using two different ROR1 antibodies. One antibody (UC961) recognized the same ROR1 epitope as the bispecific binding molecule, while the other (4A5) recognized a non-overlapping ROR1 epitope.
[0722] In addition, cell surface binding of the bispecific binding molecules was assessed after 24 h incubation at 37°C to determine whether prolonged exposure affected cell ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com