EEG time-sharing frequency spectrum Riemannian-based semantic visual image classification method and device
A visual image and classification method technology, applied in the field of semantic visual image classification, can solve the problems of less research on semantic visual observation, less useful features of EEG signals, and lower classification accuracy, achieving considerable social and economic benefits, and improving Classification accuracy, effect of reducing burden
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
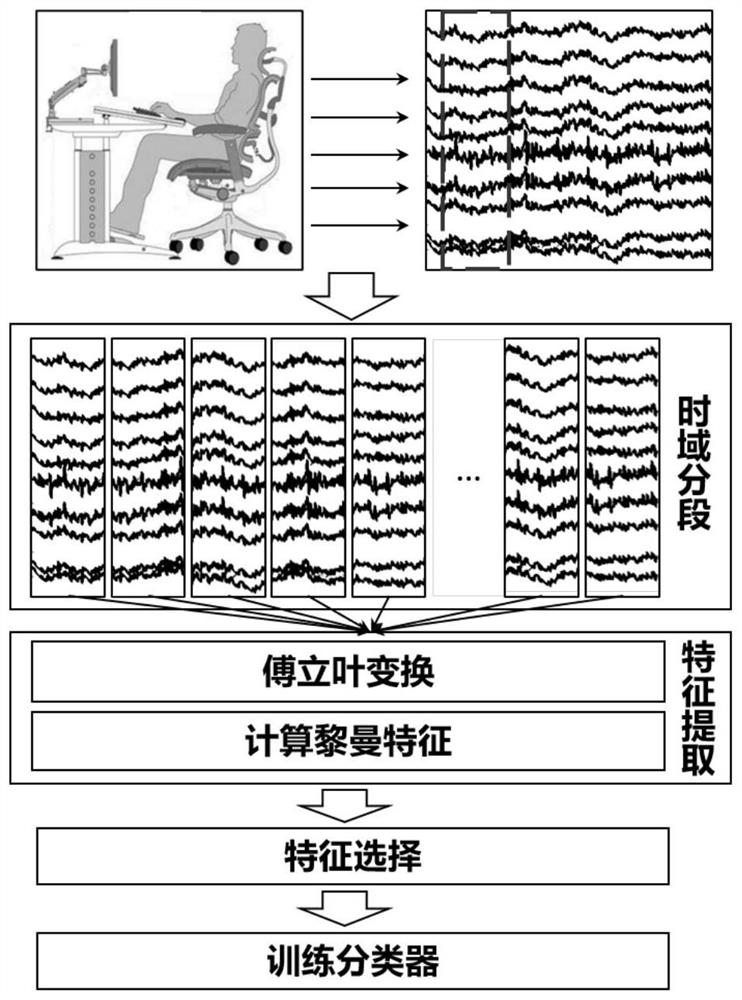
[0032] The embodiment of the present invention designs an EEG-based time-sharing spectral Riemannian semantic visual image classification method. This method can distinguish the EEG response of the brain when observing different semantic visual images. Semantic Visual Observe (SVO) is a new paradigm of Brain-Computer Interface (BCI). When people observe visual images with different semantics, due to different cognitions and emotions, they will change the neuron activity state in different regions of the brain, thereby changing the energy of different frequency bands and the energy distribution in different spaces, and the visual images with different semantics Images also respond differently in the temporal domain. The embodiment of the present invention combines the features of time domain, frequency domain and space domain, and can improve the accuracy of classification of different semantic visual images. Its technical process is as follows:
[0033] 101: Collect the EEG ...
Embodiment 2
[0038] The scheme in embodiment 1 is further introduced below in conjunction with specific examples and calculation formulas, see the following description for details:
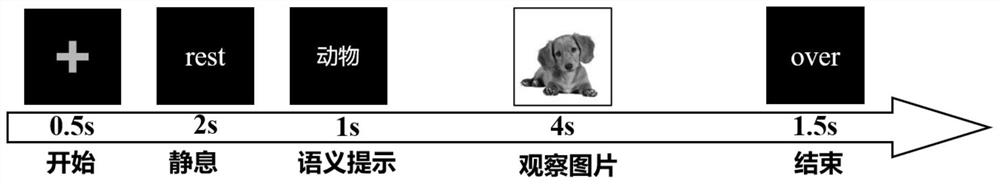
[0039] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of a paradigm design of an embodiment of the present invention. The design mainly includes: stimulation interface, EEG acquisition module and signal processing module. The stimulation interface was written using the Matlab Psychtoolbox toolkit. The EEG acquisition module selected NeuroScan’s EEG cap and amplifier, and the signal processing module implemented data processing, feature extraction, and classification steps through python.
[0040] The experimental paradigm uses the "+" sign to indicate the beginning of the experiment, and the subjects need to rest for 2 seconds at the beginning of the experiment. After resting, the stimulus interface will remind the subject of the semantic category of the upcoming picture, and the semantic prompt lasts for 1 second. Af...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Combine below figure 1 with figure 2 , experimental data, table 1 and table 2, the scheme in embodiment 1 and 2 is further introduced, see the following description for details:
[0061] 1. Experimental process:
[0062] subjects according to figure 1 Schematic diagram of the paradigm design. At the beginning of the experiment, it is necessary to rest for 2 seconds. After resting, the stimulus interface will remind the subject of the semantic category of the upcoming picture, and the semantic prompt lasts for 1 second. After that, the subjects will observe the pictures for 4 seconds, and judge the semantic categories of the pictures while observing. There are three types of pictures in the experiment, the experiment is divided into 12 groups, each group has 24 trials (8 trials for each type of pictures), a total of 288 samples, 96 samples for each type of pictures.
[0063] Collect the EEG data of 12 subjects according to the above process. The EEG acquisition mod...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com