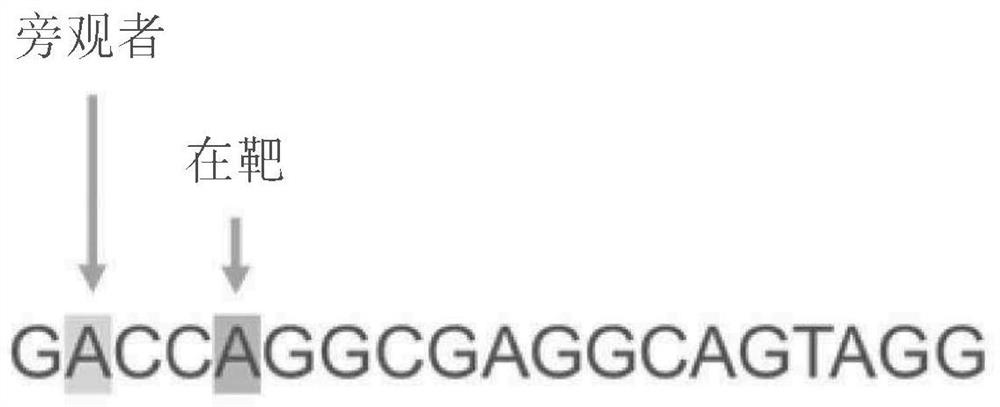Compositions and methods for treating glycogen storage disease type 1a
A glycogen storage disease, glucose technology, used in the treatment of type 1a glycogen storage disease, and adenosine deaminase domain, related to GSD1a, can solve problems such as no approved therapy yet
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
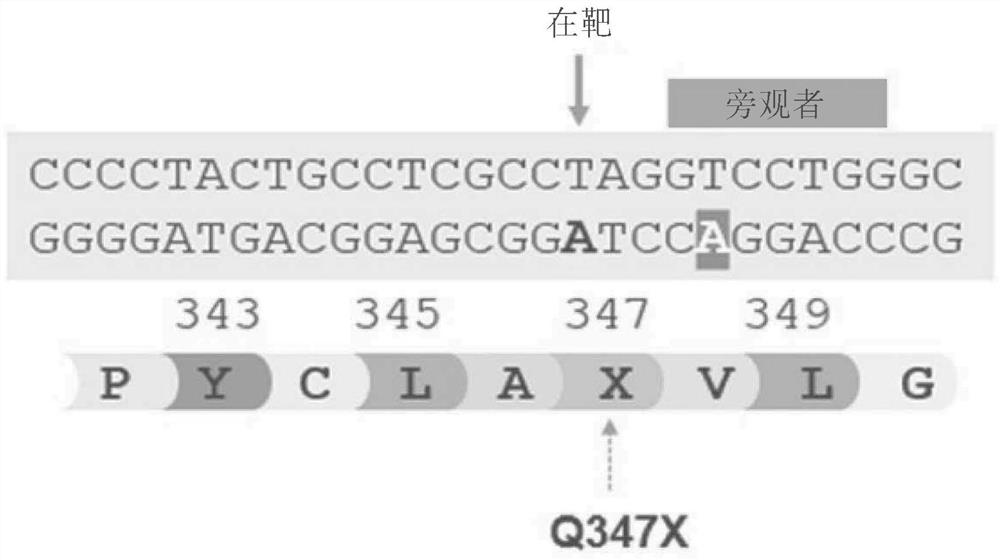
[1307] Example 1. Gene Editing to Correct the Q347X Mutation of Glycogen Storage Disease Type 1A (Von Gilke Disease) in HEK293T Cells
[1308] Example 1. Base editing strategy for 1Q347X mutation correction.
[1309] GSD1a is caused by mutations in the glucose 6-phosphatase (G6PC) gene, which affects approximately 80 percent of people with GSD1. The Q347X mutation affects approximately 500 US patients diagnosed with GSD1a each year. This mutation is a single base substitution that introduces a stop codon that terminates prematurely at position 347 (Q347X) of the G6PC protein. Precise correction of Q347X may restore G6PC expression and normalize glucose metabolism.
[1310] Adenosine base editors (ABEs) employing Cas9 moieties and validated protospacer-adjacent motif (PAM) sequence preferences were evaluated for their ability to correct the Q347X mutation by efficiently switching A>G at the target site. Representative G6PC nucleotide target sequences and corresponding amino ...
Embodiment 16
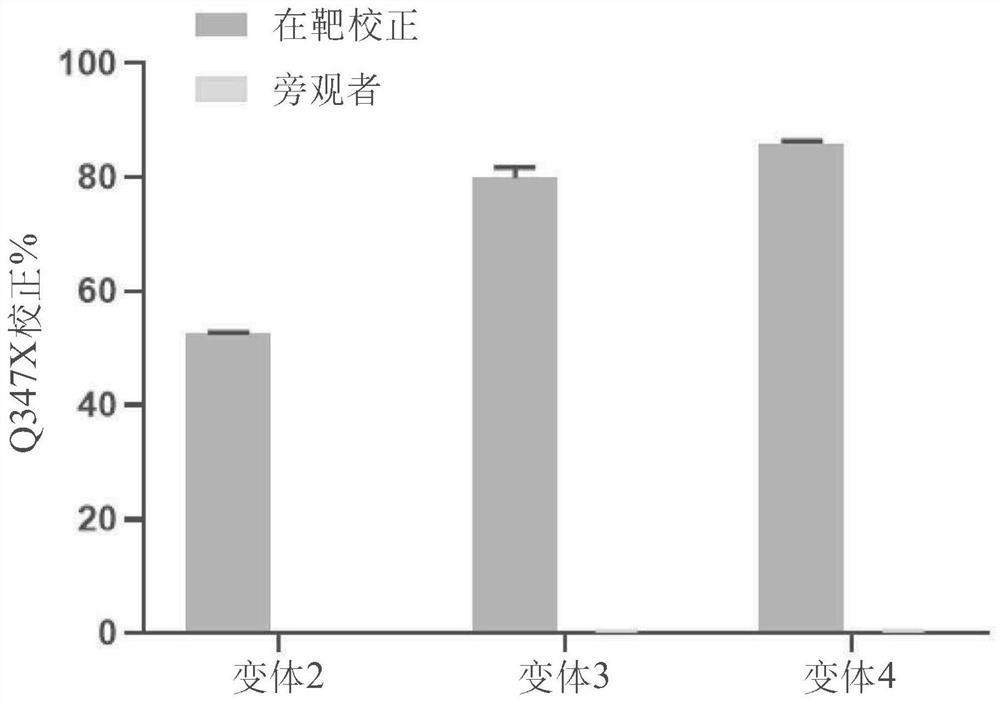
[1346] Example 1.6 Accurate correction in heterozygous patient iPSc-derived Q347X hepatocytes.
[1347] Precise on-target base editing was tested using heterozygous patient iPSc-derived human hepatocytes (Definigen, Hep GSD1a lots 493, 507 and 518). The GSD1a iPSc-derived hepatocytes were compound heterozygous (Q347X / G222R) and carried the Q347X mutation.
[1348] The target / spacer sequence of the Q347X mutation is shown in Figure 6A . The target / spacer sequence is shown at target and bystander "a" nucleobases. The Q347X mutation can be targeted using NGA PAM variants such as GGA.
[1349] The gRNA sequence hybridizes to the complement of the G6PC DNA target sequence as follows:
[1350] GACCTAGGCGAGGCAGTAGG GGA
[1351] The NGA PAM sequence (i.e. SpCas9) is underlined.
[1352] The gRNA scaffold sequence is as follows:
[1353] GUUUUAGAGCUAGAAAUAGCAAGUUAAAAUAAGGCUAGUCCGUUAUUCAACUUGAAAAAGUGGCACCGAGUCGGUGCUUUU
[1354] Percentage of on-target and bystander A>G base e...
Embodiment 2
[1365] Example 2. In vitro transduction of GSD1A mutant primary hepatocyte co-culture system Example 2.1 Co-culture system and transduction method.
[1366]Base editing was tested using an in vitro transduction approach in a primary hepatocyte co-culture system. To generate a co-culture system, primary human hepatocytes (PHH) (BioIVT) were seeded at 350k cells per well in type I collagen-coated 24-well plates (Corning, 354408) and incubated at 37°C in 5% A monolayer of adherent cells was produced under carbon dioxide. Four hours after plating, the plated hepatocytes were washed with CP medium (BioIVT) to remove any non-adherent cells. 3T3-J2 mouse embryonic fibroblasts (Kerafast (distributed from Howard Green (Harvard), Boston)) were seeded at a ratio of 95% hepatocytes:5% fibroblasts / well and re-cultured at 37°C, 5% CO2 12 hours to form a co-culture. Change the medium (500 μL per well) every 2 days for continuous maintenance. Figure 8B Shown are images of transduced prima...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com