Homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) detection method and reagent set thereof
A homologous recombination and state-of-the-art technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, genomics, proteomics, etc., can solve problems such as lethality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
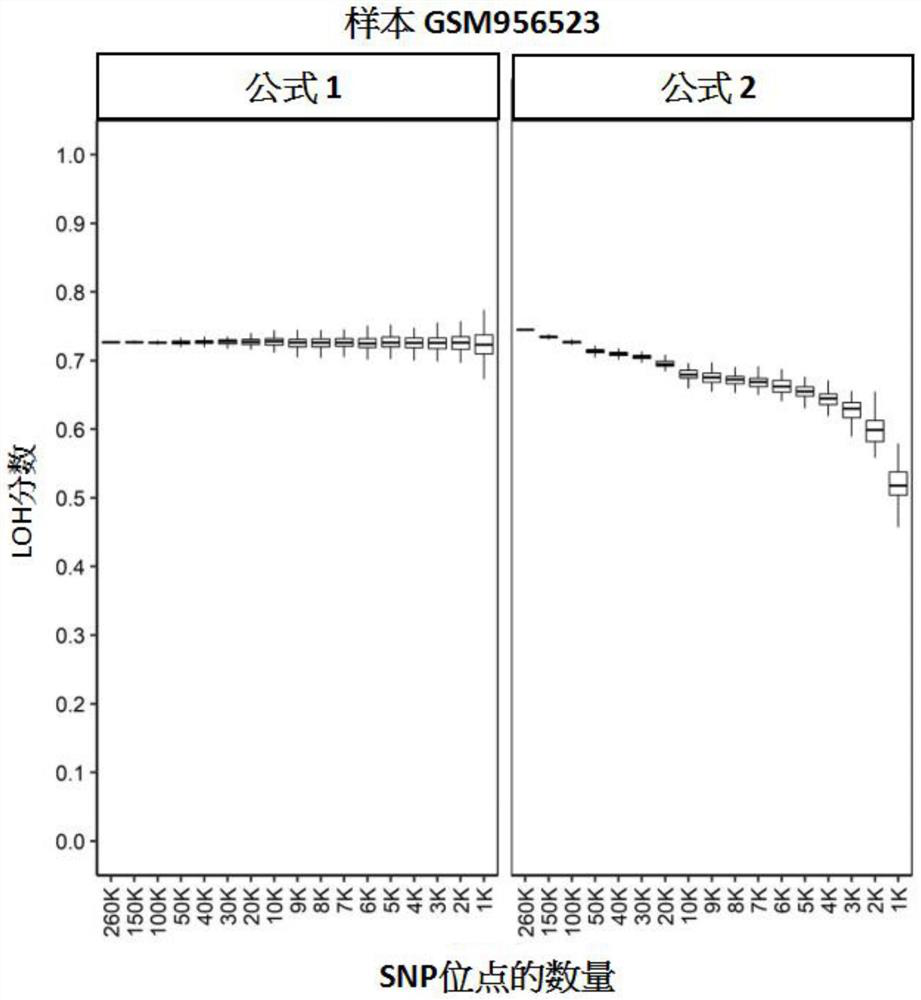
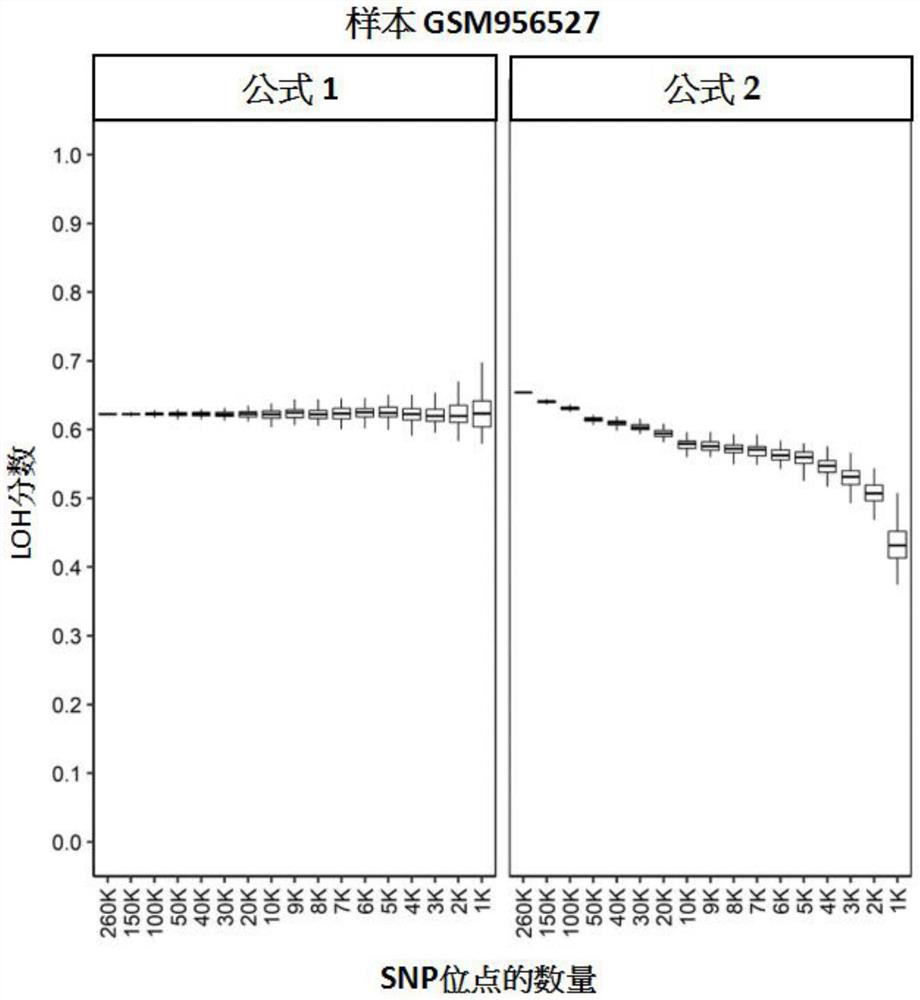
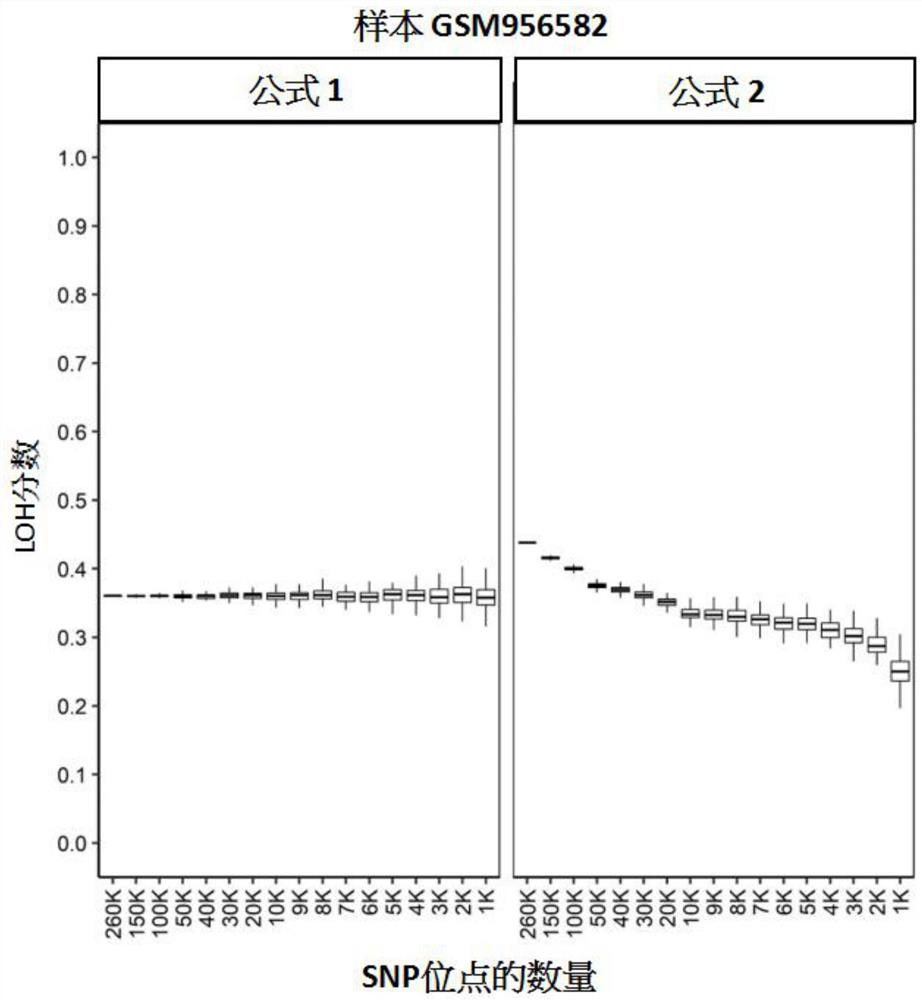
[0128] The stability test of embodiment 1LOH scoring algorithm
[0129] This study aimed to evaluate the stability of LOH scores derived by different algorithms.
[0130] 260,000 (260K), 150,000 (150K), 100,000 (100K), 50,000 (50K), 40,000 (40K), 3 Ten thousand (30K), twenty thousand (20K), ten thousand (10K), nine thousand (9K), eight thousand (8K), seven thousand (7K), six thousand (6K), five thousand (5K), four thousand ( 4K), 3 thousand (3K), 2 thousand (2K) or 1 thousand (1K) SNP loci were subjected to in silico downsampling. The aforementioned data were published in the high-throughput gene expression database GEO (Gene Expression Omnibus), and its GEO number is GSE39130 (Wang, Birkbak, et al., 2012). We first assigned chromosome arm information to each SNP site in the data set, and defined the allele frequency ranges for homozygous, heterozygous, and loss of heterozygous (LOH) SNP sites. This computational downsampling is performed by stratified sampling at the chrom...
Embodiment 2
[0134] Embodiment 2 Verification of LOH scoring algorithm
[0135] This study chose an algorithm for estimating the LOH score, which has a significant difference between the tumor group and the normal group when the number of SNP sites is different.
[0136] All samples used in the aforementioned studies were included in the analysis (Wang, Birkbak, et al., 2012). Tumor samples with BRCA2 LOH were classified as gene body high instability group (GI-H), in contrast to gene body low instability group (GI-L) tumor samples without BRCA2 LOH. Since cells with BRCA2 LOH exhibit gene body instability and exhibit high susceptibility to DNA damaging agents, the GI-H group in this study could represent the drug-sensitive group, while the GI-L group could represent the drug-resistant group Group. There were 12, 11 and 18 samples in GI-H group, GI-L group and normal group, respectively. The number of SNP sites is 260,000 (260K), 50,000 (50K), 10,000 (10K), 7,000 (7K), 5,000 (5K), 3,000 ...
Embodiment 3
[0138] Example 3 LOH scoring of samples with different tumor contents with or without consideration of chromosome arm imbalance factors
[0139] The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of chromosome arm imbalance on the calculation of LOH scores.
[0140] A cancer cell line sample (NCL-H1395) with a copy number variation was mixed with a match-normal sample (match-normal sample) to simulate different tumor contents. The experimental procedure includes DNA extraction, sequence library construction and NGS sequencing, all of which are consistent with Example 5. The LOH scores of mixed samples with different tumor contents were estimated by three different algorithms. The first algorithm calculates the LOH score without considering the effect of chromosome arm imbalance (Equation 1). The second and third algorithms take into account the chromosome arm imbalance, which excludes SNPs located on the imbalanced chromosome arm (Equation 3). Unbalanced chromosome arms are c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com