Ultrasonic guided wave imaging method and system for anisotropic structure
An anisotropic, ultrasonic guided wave technology, applied in the analysis of solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic waves, material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic waves, and processing response signals of detection, etc. The problems of complex signals and poor imaging robustness can achieve the effect of accurate positioning imaging detection, avoiding the analytical solution process, and good robustness.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
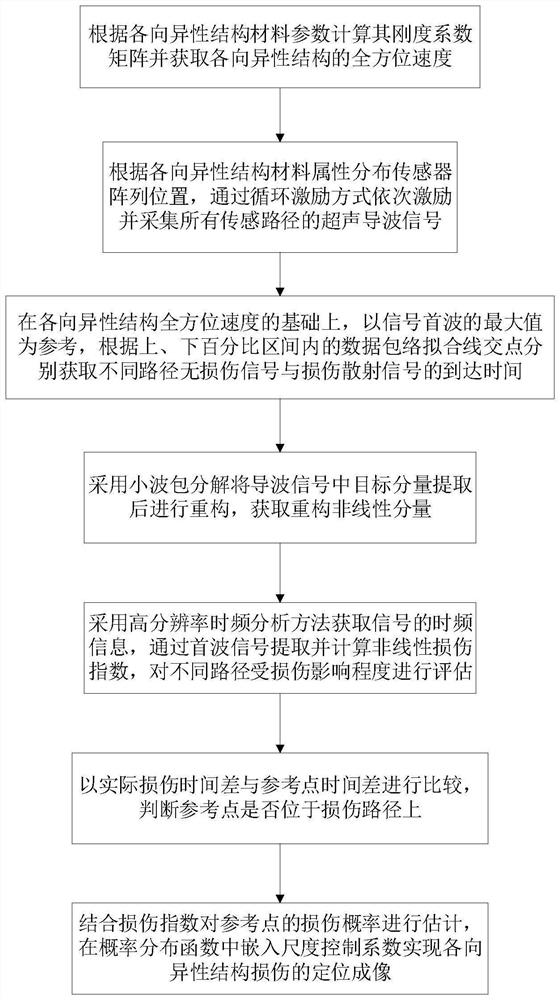
[0053] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment provides an ultrasonic guided wave imaging method for anisotropic structures, including the following steps:
[0054] S1: Calculate the stiffness coefficient matrix according to the material parameters of the anisotropic structure and obtain the omni-directional velocity of the anisotropic structure;
[0055] In this embodiment, the omni-directional velocity of the anisotropic structure is obtained at one time by finite element simulation. In the simulation, the number of receiving sensors is N, and the number of receiving sensors is evenly distributed on a circle at the same distance from the exciting sensor as the center of the circle. According to the symmetry Receiving sensors can be reduced accordingly.
[0056] In this embodiment, the omni-directional velocity of the anisotropic structure is obtained by performing polynomial fitting on the guided wave velocity of each sensing path, and the degree of fitting polynomial is...
Embodiment 2
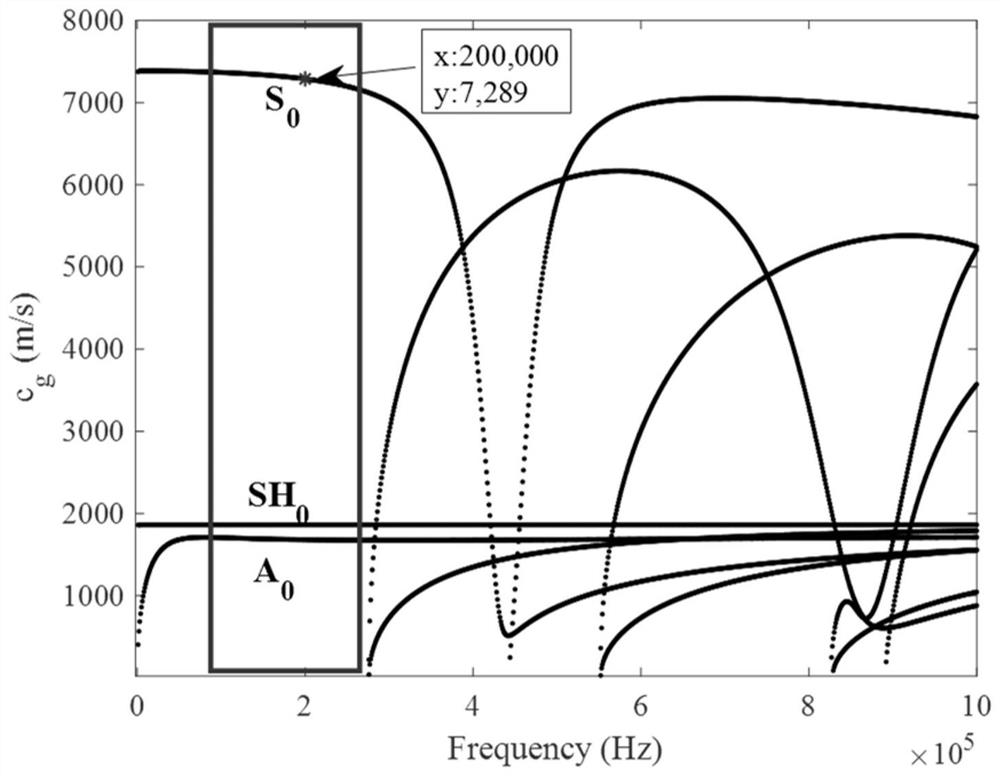
[0082] This embodiment selects the anisotropic CFRP structure with the ply direction [0 / 90 / 0] as a specific example based on the content of embodiment 1, and draws its dispersion curve according to the material parameters, such as figure 2 As shown, according to the dispersion curve, the excitation frequency is determined to be 200kHz. At this time, there are fewer guided wave modes and the speed is relatively stable.
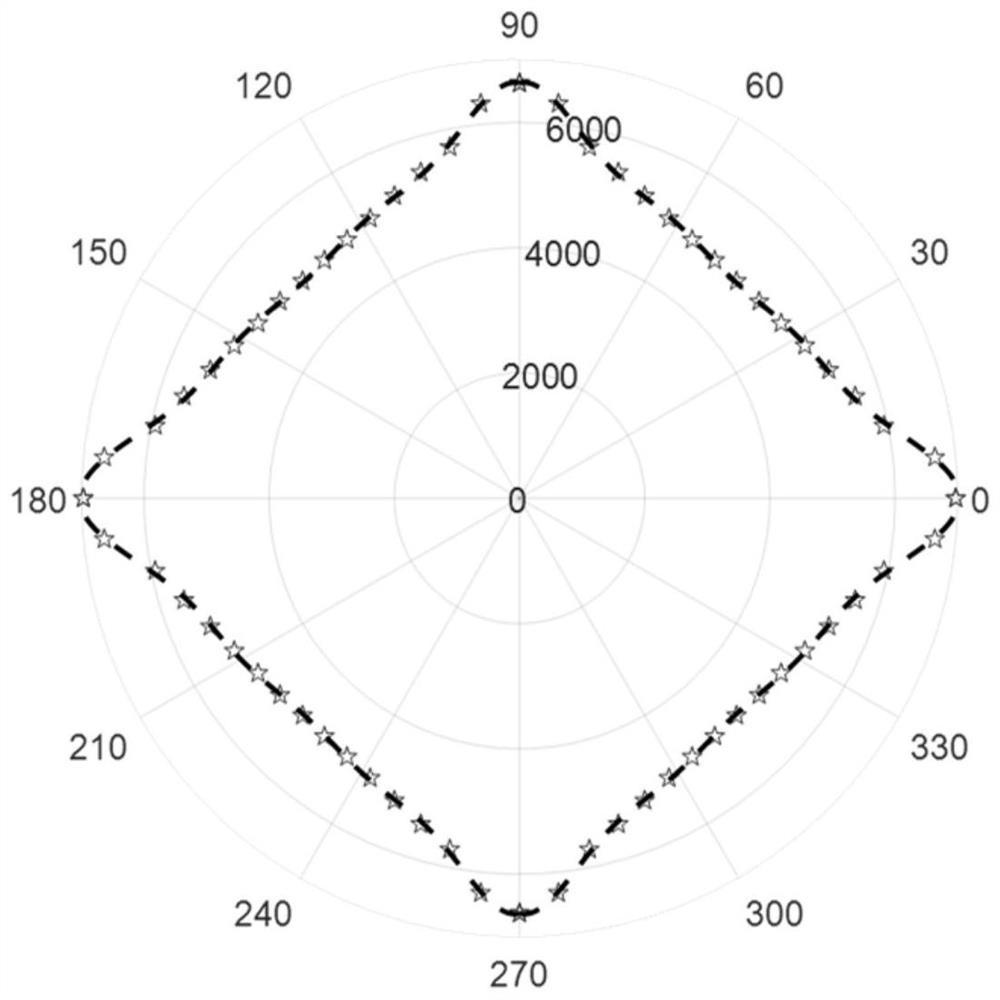
[0083] In this embodiment, an anisotropic CFRP structure simulation model is established, and 17 receiving sensors are evenly distributed on a circle 200 mm away from the exciting sensor with the exciting sensor as the center of the circle, and the guided wave velocities at different angles are obtained by using the threshold method. Such as image 3 As shown, the omni-directional velocity of the anisotropic CFRP structure is obtained by an 8th degree polynomial fitting.
[0084] In this embodiment, a circular array layout is adopted, and all sensors are cycl...
Embodiment 3
[0107] This embodiment provides an ultrasonic guided wave imaging system for anisotropic structures, including: a stiffness coefficient matrix calculation module, an omni-directional velocity acquisition module, an ultrasonic guided wave signal acquisition module, a signal arrival time acquisition module, and nonlinear component reconstruction Module, time-frequency information analysis module, nonlinear damage index acquisition module, damage path determination module, damage location imaging module;
[0108] In this embodiment, the stiffness coefficient matrix calculation module is used to calculate the stiffness coefficient matrix according to the anisotropic structural material parameters;
[0109] In this embodiment, the omnidirectional velocity acquisition module is used to acquire the omnidirectional velocity of the anisotropic structure;
[0110] In this embodiment, the ultrasonic guided wave signal acquisition module is used to distribute the position of the sensor ar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com