Metabolism-related fatty liver disease in-vitro cell model and construction method thereof
A fatty liver disease and cell model technology, applied in the field of metabolic-related fatty liver disease in vitro cell model and its construction, can solve the problems of lack of MAFLD cell model, cell damage, fibrosis and inflammation that are not fully described.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0064] Example: Saturated fatty acid induces liver cell line to establish metabolic fatty liver disease injury and fibrosis model
[0065] 1. Overview of the invention
[0066] 1.1 Purpose of the invention
[0067] Select appropriate induction reagents and liver cell lines to establish an in vitro cell model of advanced metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) with severe cell damage and fibrosis.
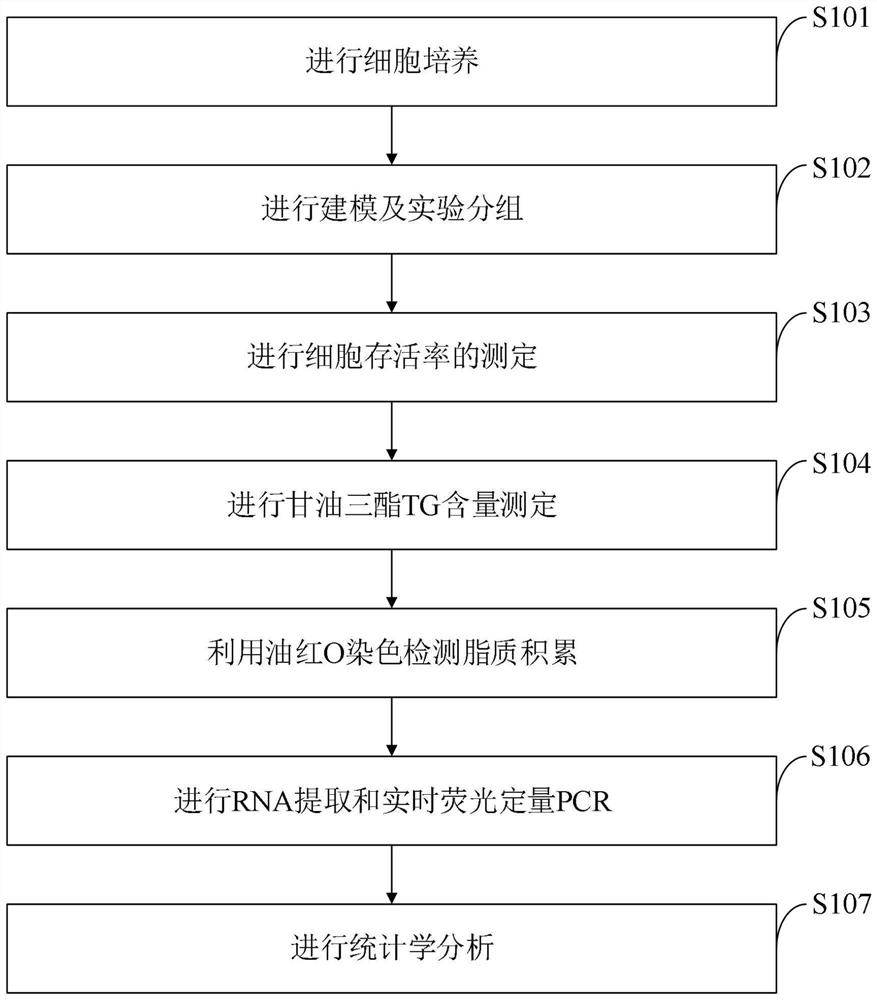
[0068] 1.2 Invention method
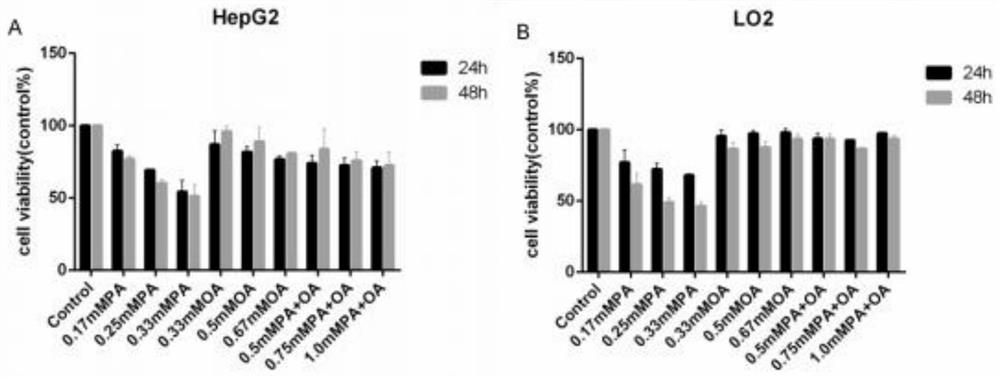
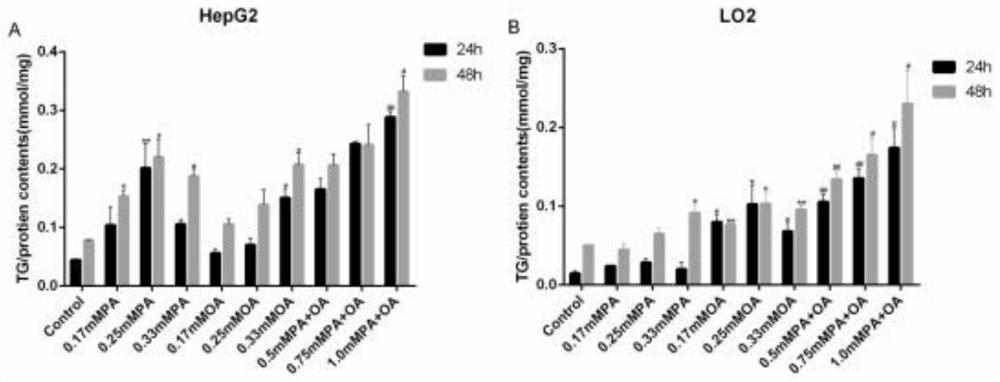
[0069] HepG2 and LO2 cells were treated with OA or PA or their mixture, and the cell viability was detected by CCK8; the degree of lipid accumulation was detected by oil red O staining and triglyceride enzyme method; apoptosis-related proteins (Bax , Bcl2, Cleaved caspase-3), fibrosis-related proteins (α-SMA, Col.I), autophagy-related proteins (LC3-II, P62 / SQSTM1, Beclin-1), inflammatory factors (NLRP3, TNF-α) level of expression.
[0070] 1.3 Results
[0071] Compared with the blank control group, treatment of HepG2 cells with...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com