Variable-grid core particle arrangement optimization algorithm
An optimization algorithm and grid technology, applied to the photoplate-making process of the pattern surface, microlithography exposure equipment, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of inaccurate results, large amount of calculation, time-consuming and other problems, and achieve the goal of overcoming the problem of seeking Optimize the effect of large amount of calculation, ensure accuracy, and shorten calculation time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] This embodiment provides a Die arrangement optimization algorithm with variable grid, specifically as follows:
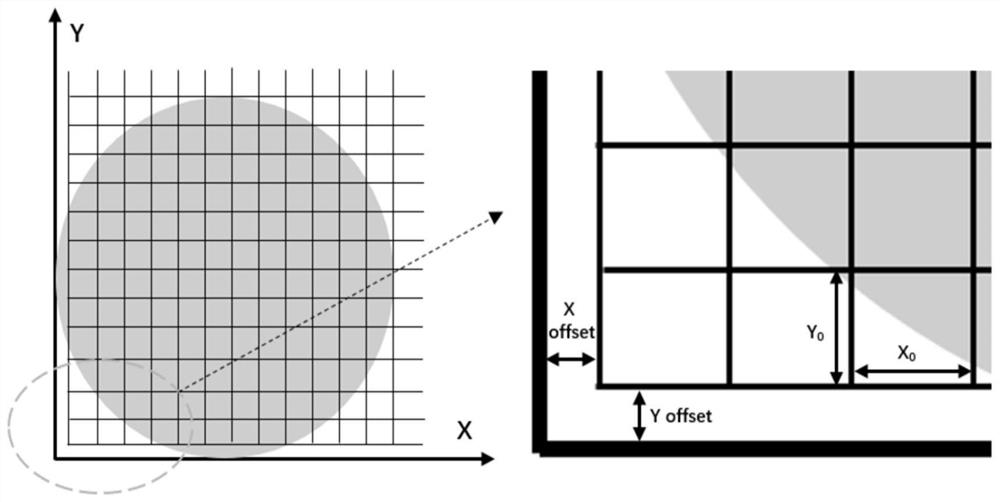
[0042] S1: Establish a rectangular coordinate system, the X and Y axes of the rectangular coordinate system are tangent to the edge of the wafer.
[0043] S2: Taking the origin of the coordinates as the starting point, using the dichotomy method to find the optimal combination of offsets X offset and Y offset, so that the number of Dies divided on the wafer is the largest, and an array arrangement of Dies is obtained.
[0044] The step S2 specifically includes the following steps:
[0045] S2-1: Die length and width X 0 , Y 0 Divide them into 10 equal parts, and the length and width of each part are X 0 / 10, Y 0 / 10;
[0046] S2-2: Set the X-direction offset X offset of Die arrangement to X in turn 0 / 10, 2X 0 / 10,...,X 0 ;Set the Y-direction offset Y offset of Die arrangement to Y in sequence 0 / 10, 2Y 0 / 10,...,Y 0 . A total of 10*10=100 combina...
Embodiment 2
[0051] This embodiment also provides a calculation method for the arrangement of Die arrays on a wafer, and the similarities with Embodiment 1 will not be repeated, and the difference lies in:
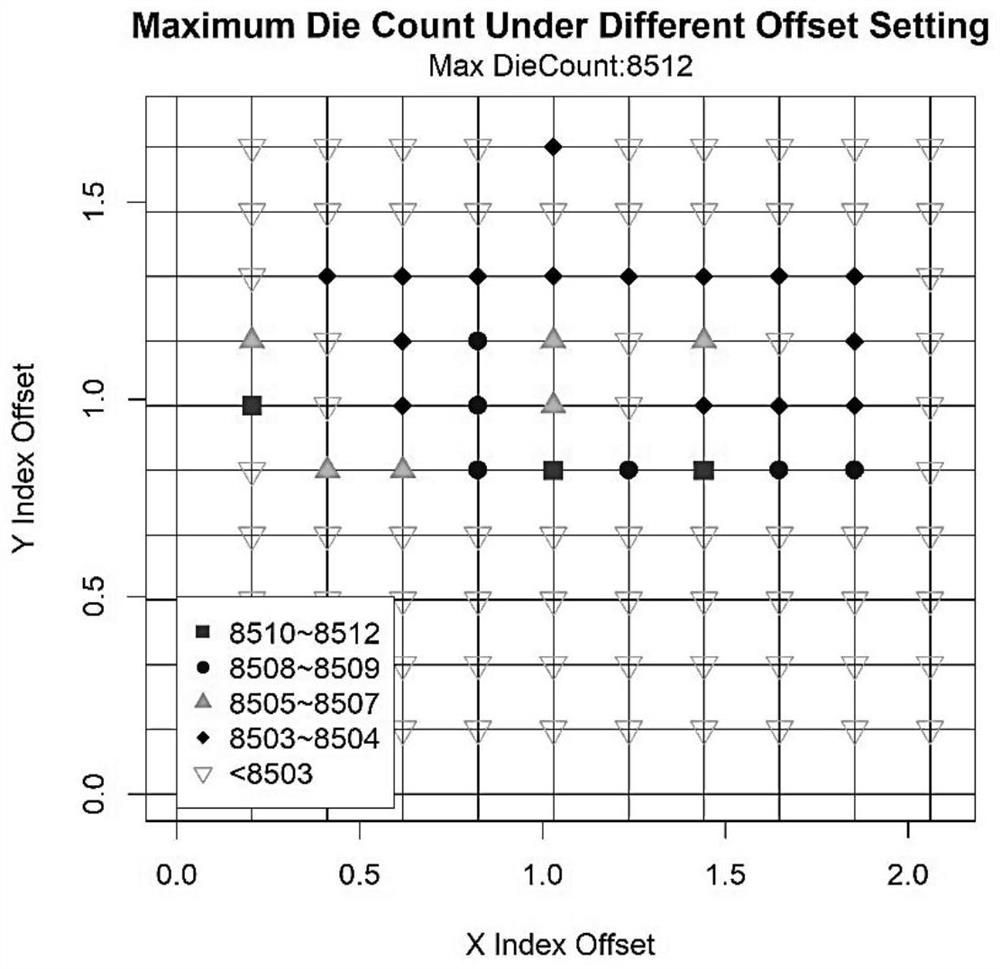
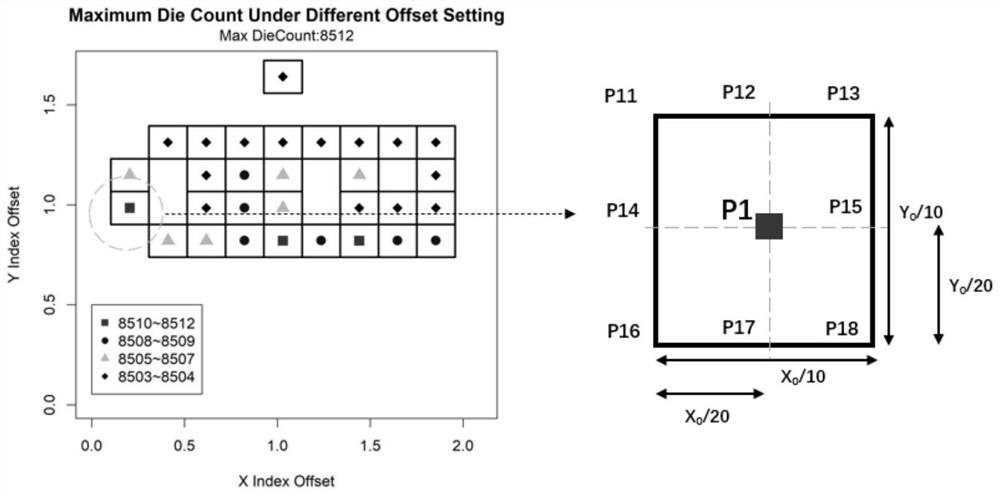
[0052] After finding the suspected points at all levels in Embodiment 1, cluster analysis is carried out to the suspected points at all levels respectively, as Image 6 As shown, the suspected points are classified, and each closed curve in the figure represents a class. The method of using cluster analysis to classify suspected points is as follows: calculate the spatial distance between each suspected point, set the threshold of the class, and classify the suspected points with the spatial distance smaller than this threshold and the corresponding Die Count value into one class. The threshold of the class is determined according to the series of suspected points. For example, the distance between the class I suspected points is far away, and the threshold of the class is relatively l...
Embodiment 3
[0056] This embodiment provides a method for calculating the Die array arrangement on a wafer. The method mainly performs Die array arrangement for wafers with unusable areas such as defects, flags, and engraved codes. The similarity with Embodiment 2 will not be described in detail, the difference is:
[0057] Before executing S2, it is necessary to divide the unusable area of the wafer, such as Figure 9 As shown, these unusable areas are first accurately positioned on the wafer, and these areas are classified as invalid areas when performing array layout calculations, and these invalid areas are excluded when calculating Die Count, so that through the embodiment The optimal point obtained by the algorithm in 2 is the real optimal point, and it is also the most in line with the actual situation.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com