Floating switch driving circuit and method
A floating switch and drive circuit technology, applied in electronic switches, electrical components, pulse technology, etc., can solve problems such as complex structure, complex and difficult gate drive circuit design
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
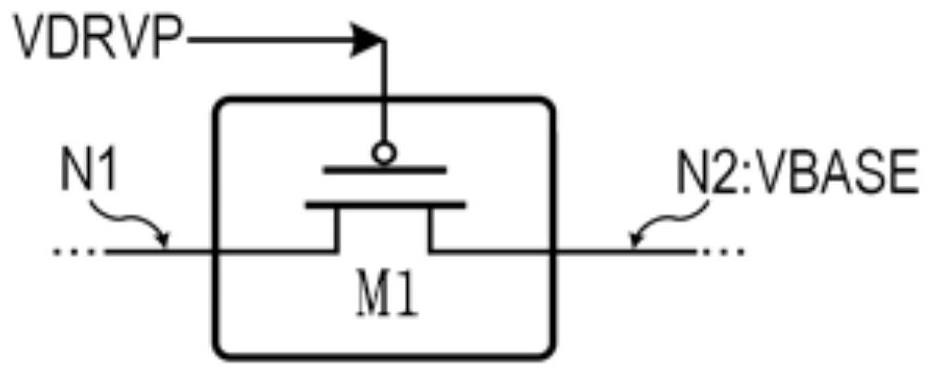
[0072] see figure 1 , figure 1 A schematic structural diagram of a PMOS transistor floating switch M1 provided in an embodiment of the present application. Floating switches are usually MOS transistors, and are usually used in power transmission stages of some power converters to connect different power components in switch mode. Its characteristic is that the relative magnitude of the voltage across the source and drain of the floating switch will change dynamically. Generally, the turn-on and turn-off of the MOS transistor is controlled by controlling the voltage between the gate and the source. For the PMOS tube, the gate-source voltage Ugs<0 means it is turned on, and the gate-source voltage Ugs≥0 means it is turned off. However, since the source and drain of the floating switch are prone to dynamic high and low potential changes, that is, low and high voltages appear alternately at both ends of the switch, making it difficult to control the voltage between the gate and...
Embodiment 2
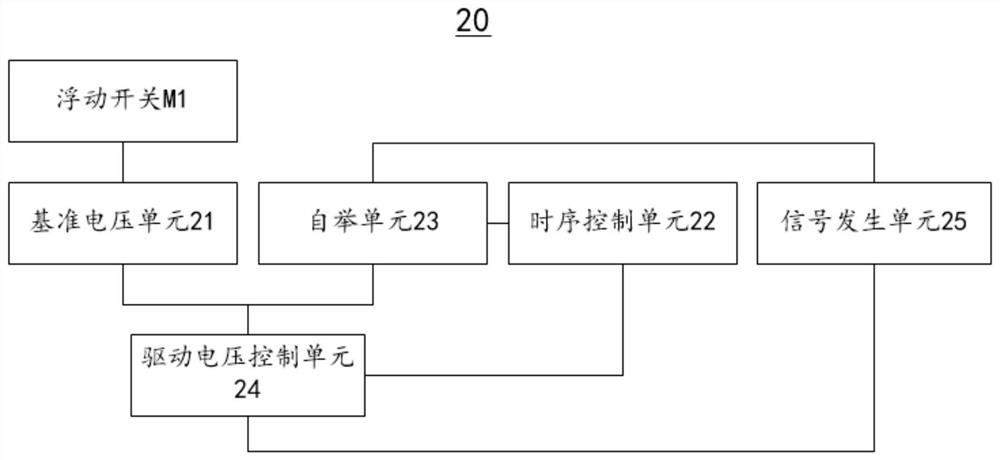
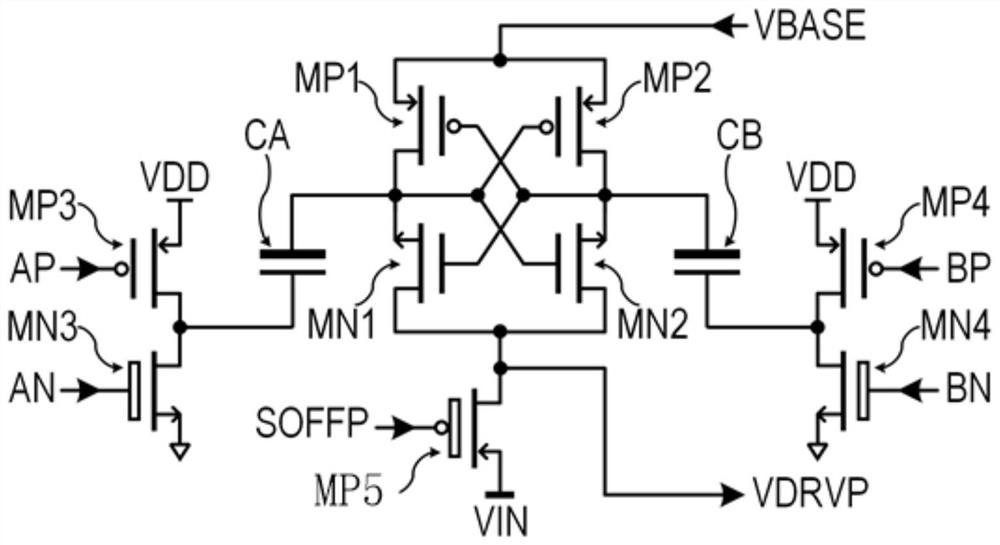
[0111] In order to solve the above technical problems, the present application also provides a driving circuit corresponding to the floating switch of the NMOS transistor. see Figure 7 , Figure 7 A schematic structural diagram of an NMOS transistor floating switch M2 provided in an embodiment of the present application. For NMOS transistors, the gate-source voltage Ugs>0 means it is turned on, and the gate-source voltage Ugs≤0 means it is turned off. see figure 2 The floating switch driving circuit applied to NMOS transistors also includes a reference voltage unit 21 , a timing control unit 22 , a bootstrap unit 23 and a driving voltage control unit 24 . One end of the reference voltage unit 21 is used to connect any one of the source or drain of the floating switch, and the other end of the reference voltage unit 21 is connected to the drive voltage control unit 24; the bootstrap unit 23 is respectively The timing control unit 22 is connected to the driving voltage con...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com