Bragg reflector and light emitting diode with Bragg reflector
A technology of Bragg mirrors and light-emitting diodes, applied in semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of low machine utilization rate and inability to reflect various light types
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
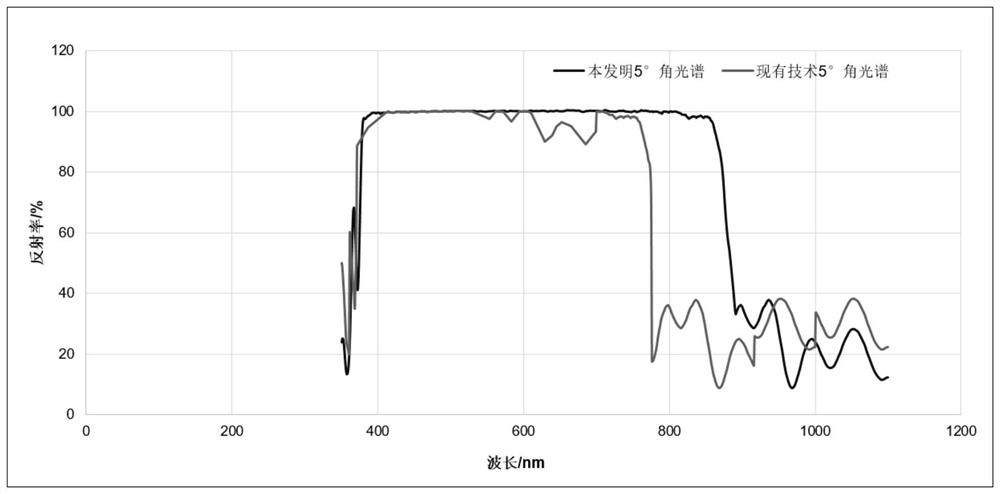
[0041] The principle of Bragg mirror reflection is that Fresnel reflection occurs at each interface of the two materials of the Bragg mirror. At the working wavelength, the optical path difference of the reflected light at two adjacent interfaces is half the wavelength, and the sign of the reflection coefficient at the interface also changes. Therefore, all reflected light at the interface interferes destructively, resulting in a strong reflection. The reflectivity is determined by the number of layers of the material and the difference in refractive index between the materials. The reflection bandwidth is mainly determined by the refractive index difference.
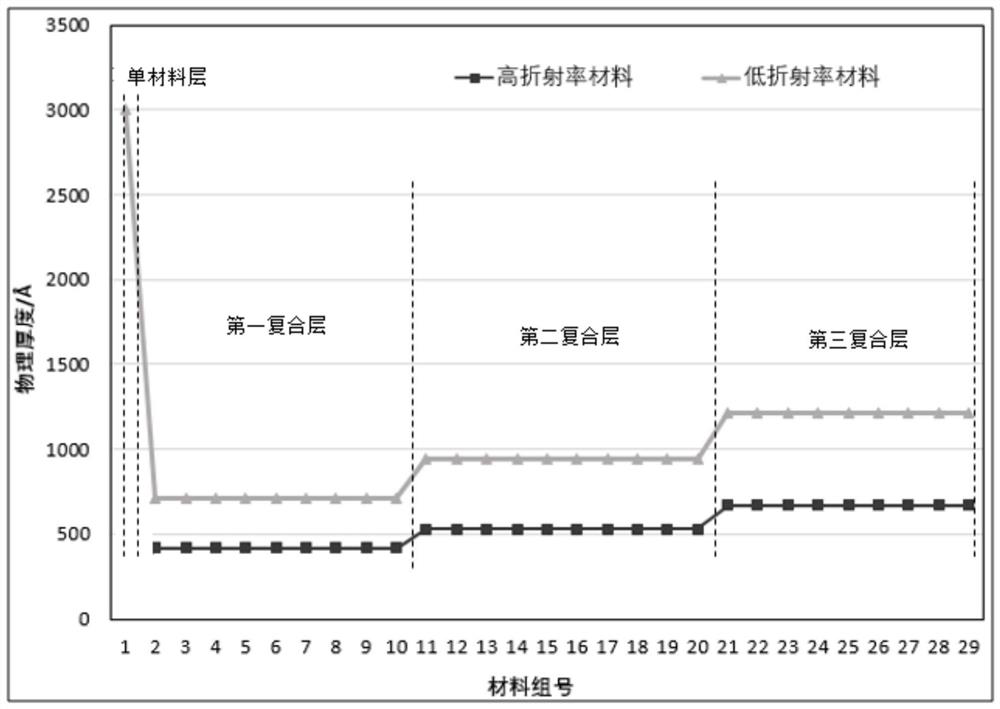
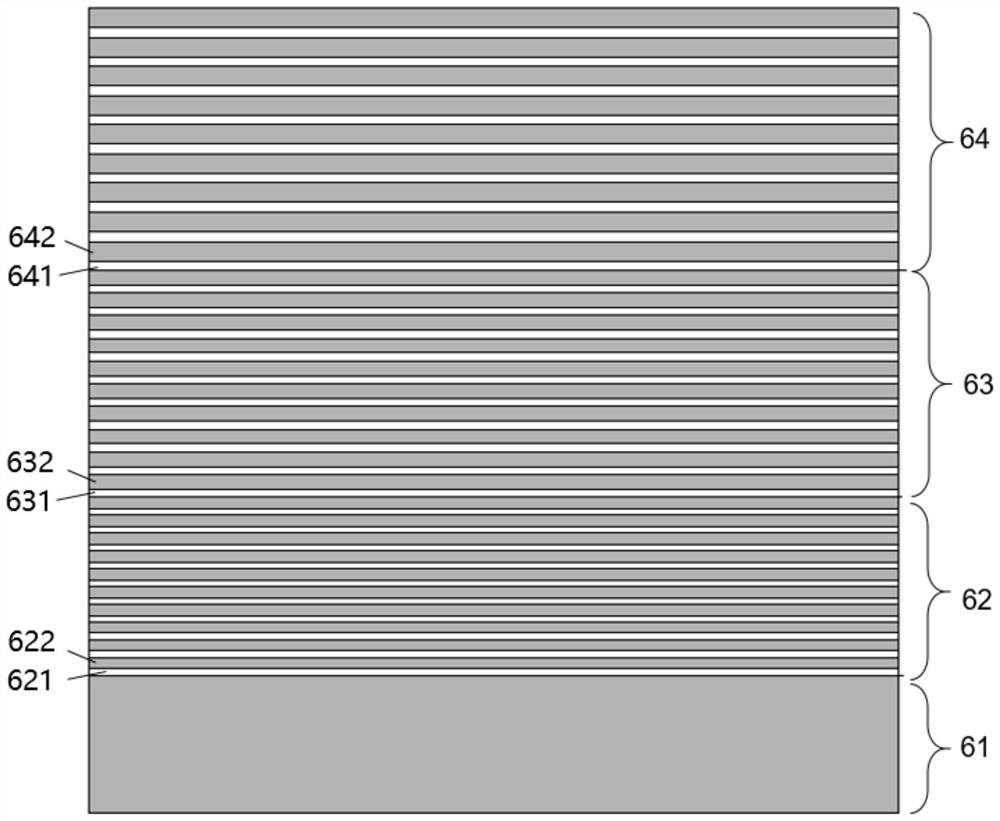
[0042] see figure 2 , shows a schematic cross-sectional view of the Bragg mirror in this embodiment, including a Bragg mirror single-material layer 61, a Bragg mirror first composite layer 62, a Bragg mirror second composite layer 63, and a Bragg mirror third composite layer 64 , wherein, the first composite layer 6...
Embodiment 2
[0055] See Figure 5 , which is a schematic cross-sectional view of the light-emitting diode in this embodiment, and the light-emitting diode in this embodiment includes the Bragg reflector in the above-mentioned first embodiment.
[0056] The light-emitting diode in this embodiment is a front-mounted diode, including a Bragg mirror third composite layer 64, a Bragg mirror second composite layer 63, a Bragg mirror first composite layer 62, a Bragg mirror single-material layer 61, a substrate 71. Epitaxial layer 72, current blocking layer 73, current spreading layer 74, PAD conductive layer 75; epitaxial layer 61 includes N-type semiconductor layer 721, active light-emitting layer 722, P-type semiconductor layer 723.
[0057] The Bragg reflector single-material layer 61 is located on the side of the substrate 71 away from the active light-emitting region 722 in the epitaxial layer 61, the Bragg reflector first composite layer 62 is located on the side of the Bragg reflector sin...
Embodiment 3
[0060] refer to Image 6 , is a schematic cross-sectional view of the light-emitting diode in this embodiment, and the light-emitting diode in this embodiment includes the Bragg reflector in the above-mentioned first embodiment.
[0061] The light-emitting diode in this embodiment is a flip-chip light-emitting diode, including a substrate 71, an epitaxial layer 72, a current blocking layer 73, a current spreading layer 74, a PAD conductive layer 75, a Bragg mirror single-material layer 61, a Bragg mirror first The composite layer 62 , the second composite layer of Bragg mirror 63 , the third composite layer of Bragg mirror 64 , and the pad layer 81 ; the epitaxial layer includes an N-type semiconductor layer 721 , an active light-emitting layer 722 , and a P-type semiconductor layer 723 .
[0062] The Bragg reflection layer single-material layer 61, the first composite layer 62, the second composite layer 63, and the third composite layer 64 are all interposed between the acti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| reflectance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| refractive index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| refractive index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com