Bridge multi-point synchronous movement real-time monitoring method and system and readable storage medium
A real-time monitoring system and synchronous movement technology are applied in the design of systems and readable storage media, and in the field of real-time monitoring methods for multi-point synchronous movement of bridges, which can solve the problems of low precision and insufficient real-time performance, and achieve the effect of high transmission rate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
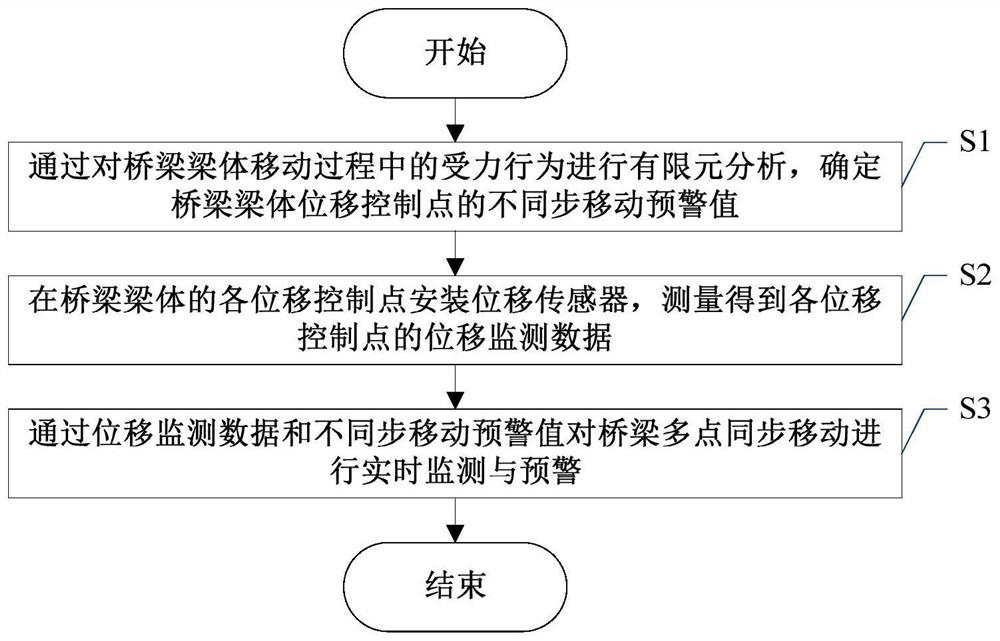
[0044] The embodiment of the present invention provides a real-time monitoring method for bridge multi-point synchronous movement, such asfigure 1 shown, including the following steps S1-S3:
[0045] S1. Through the finite element analysis of the force behavior of the bridge beam body during the movement process, the asynchronous movement early warning value of the bridge beam body displacement control point is determined.
[0046] In the embodiment of the present invention, the finite element analysis of the force behavior of the bridge beam during the movement process can be realized by finite element analysis software, such as Midas, Bridge Doctor, ANSYS, ABAQUS, etc. The selection of specific finite element software requires Determined according to the actual bridge beam movement.
[0047] S2. A displacement sensor is installed at each displacement control point of the bridge beam body, and the displacement monitoring data of each displacement control point is obtained by ...
Embodiment 2
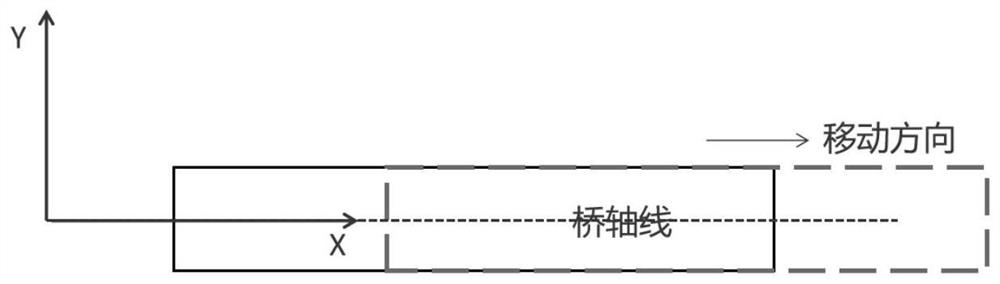
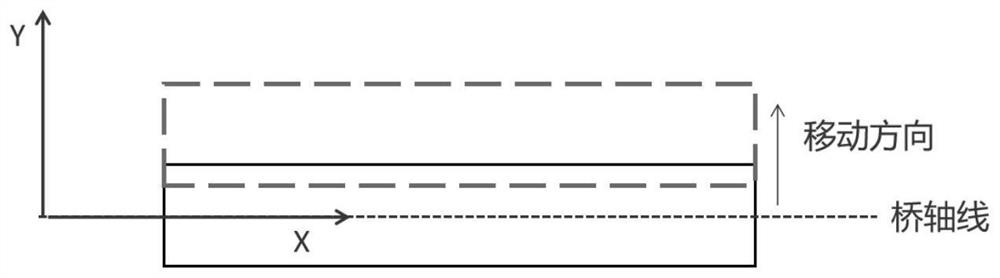
[0051] For the multi-point synchronous movement of the bridge in Embodiment 1, it includes the lateral movement of the bridge beam body in a direction perpendicular to its axis (referred to as lateral movement, such as figure 2 shown), the bridge beam body moves longitudinally along its axis direction (referred to as longitudinal movement, such as image 3 shown) and the bridge beam body moves vertically along the direction perpendicular to the ground (referred to as vertical movement, such as Figure 4 shown).
[0052] The real-time monitoring method for multi-point synchronous movement of bridges provided by the present invention can be applied to the real-time monitoring of lateral, vertical and vertical movements of bridges, and can be used for synchronous movement in any one of the three directions of xyz during bridge construction. The method provided by the invention performs real-time monitoring.
Embodiment 3
[0054] For the displacement control point in Embodiment 1, the embodiment of the present invention selects the temporary support point during the synchronous movement of the bridge beam as the displacement control point.
[0055] Since the bridge beam is moving synchronously, each temporary support point is the force point where the traction external force acts on the bridge beam, and these force points are exactly the points that need to monitor the displacement synchronization in real time. The asynchronous displacement of the two temporary support points may cause the distortion of the bridge beam. Therefore, once a large asynchronous displacement of any two adjacent temporary support points is found, an early warning can be given in time. Taking these temporary support points as displacement control points, on the one hand, is consistent with the actual points that need to monitor displacement, and on the other hand, it is not necessary to select additional displacement con...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com