Intelligent minimally invasive implanted nucleus pulposus stent capable of inducing regeneration and preparation and driving method
A technology of nucleus pulposus implantation, which is applied in the field of intelligent minimally invasive implantation of nucleus pulposus scaffolds and its preparation and driving, can solve the problems of inducible regeneration of degenerative nucleus pulposus tissue, and achieve the effect of relieving nerve compression
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
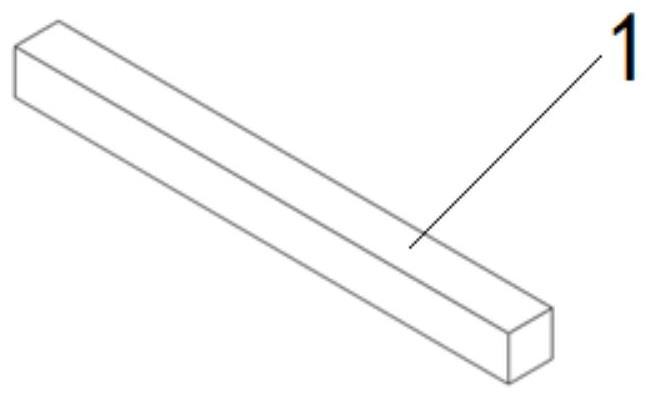
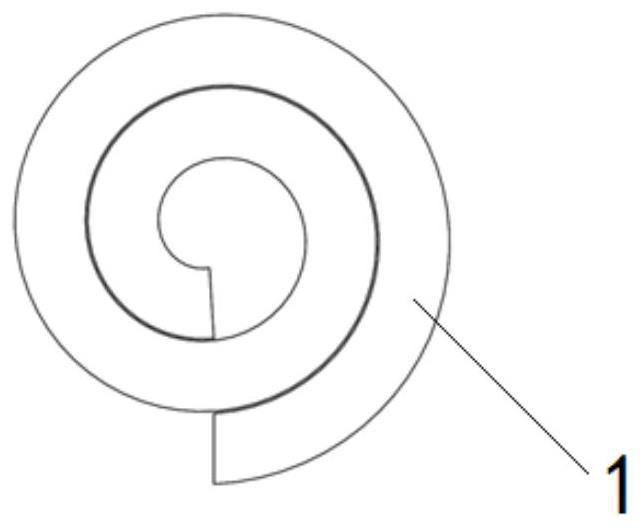
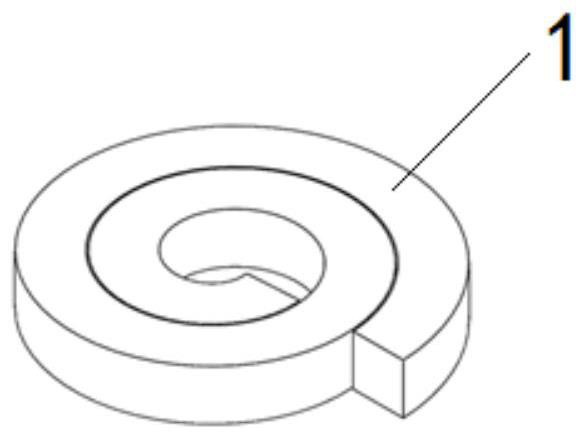
[0040] The present embodiment provides an intelligent minimally invasive implanted nucleus pulposus scaffold capable of inducible regeneration. figure 1 As shown, the temporary shape of the artificial nucleus pulposus scaffold 1 is a long strip with a small cross-sectional area, and the cross-section of the long structure is 12.5 mm. 2 A developing wire made of platinum-iridium alloy is arranged at the head of the elongated structure. The artificial nucleus pulposus stent 1 is curled and spiraled under human body temperature conditions, forming a permanent shape with a larger cross-sectional area. like figure 2 shown. The elongated section is not limited to a square, as an alternative embodiment, the elongated section can also be set to other shapes, such as image 3 The polygon shown is formed by multiple segments of concave arcs, Figure 4 A circle shown provided with two opposing concave arcuate notches, or as Figure 5 A circle or the like provided with a single co...
Embodiment 2
[0046] This embodiment provides an intelligent and minimally invasive implanted nucleus pulposus stent 1 that can induce regeneration. The artificial nucleus pulposus stent 1 is in a temporary shape under the condition of lower temperature than the human body, and is a long strip with a small cross-sectional area. A developing wire made of platinum-iridium alloy is arranged at the head of the elongated structure. The artificial nucleus pulposus stent 1 has a main body section of 19mm under the condition of lower temperature than the human body. 2 round strips, such as Image 6 shown. Under human body temperature conditions, it folds twice in the horizontal direction to form three parallel sections. The two folds occur in opposite directions, resulting in the stent folded in a double U shape, with the two U-shaped openings oriented in opposite directions, resulting in a permanent configuration such as Figure 7 shown. In this embodiment, the artificial nucleus pulposus supp...
Embodiment 3
[0052] The structure and preparation method of the artificial nucleus pulposus scaffold 1 in this embodiment are the same as those in Embodiment 2. The difference is that the artificial nucleus pulposus scaffold 1 in this embodiment is loaded with biologically active factors on the surface before implantation, and the artificial nucleus pulposus scaffold 1 is implanted into the human body for inducing regeneration therapy of tissue engineering degenerated nucleus pulposus , the specific process is:
[0053] (1) Place the stent in a water bath of about 40°C, apply a tensile force in the direction shown in the figure to expand it, keep stretching and take the stent out of the water bath to room temperature, and remove the tensile force after standing for a few minutes. At this time, the stent has completed the morphological editing before implantation, and the shape is close to the rod shape;
[0054] (2) The developing wire / ring / sheet made of platinum-iridium alloy is placed o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com