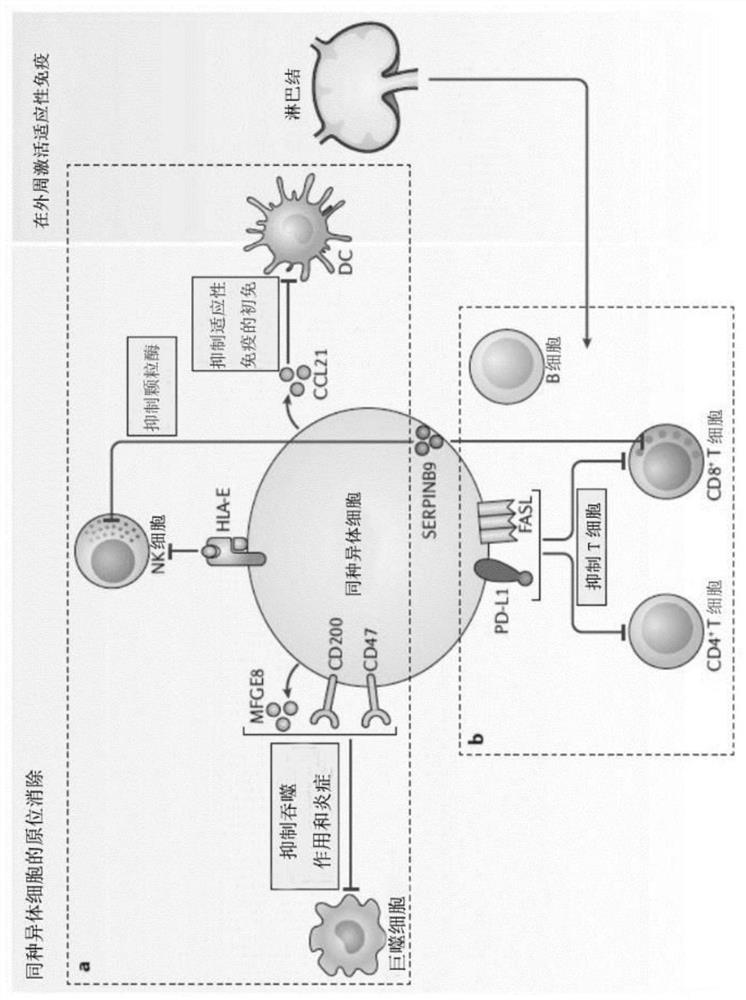
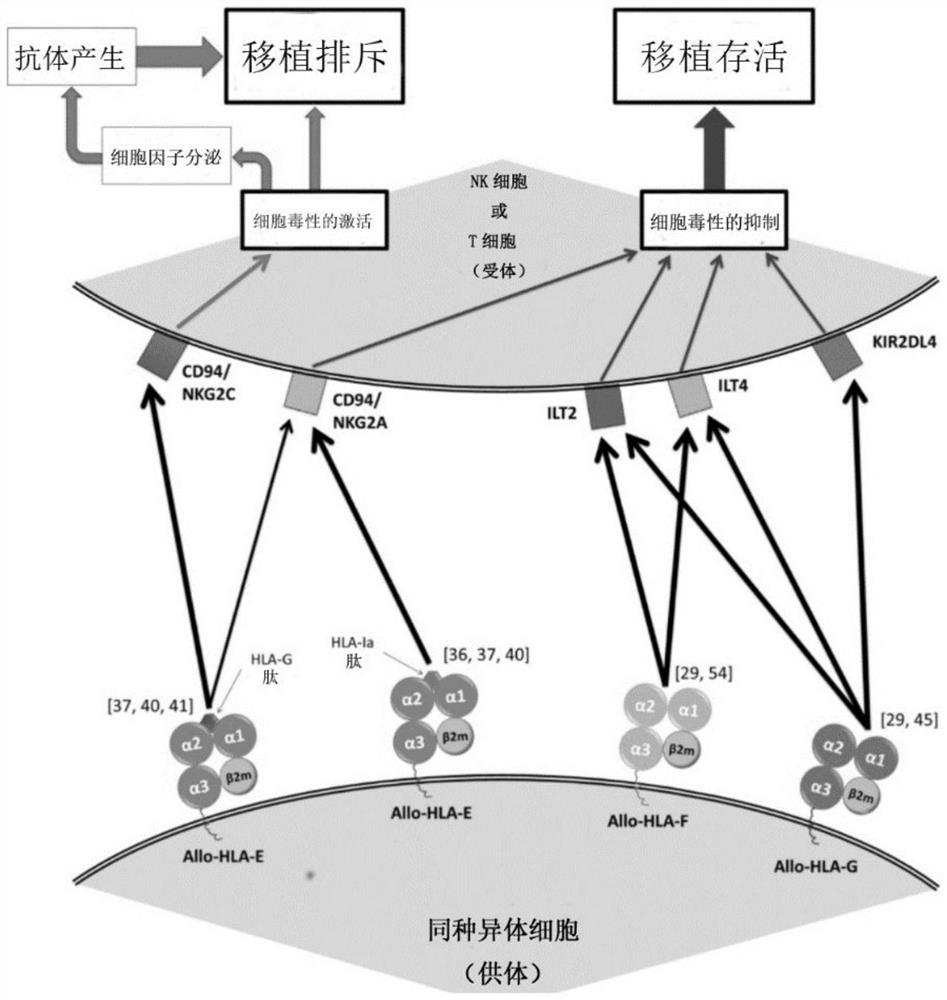
HLA-F modified cells and methods
A technology of HLA-F and HLA-G, which is applied in the direction of genetically modified cells, chemical instruments and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of time-consuming and high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0127] This example illustrates the expression levels of HLA-F in iPS (iPSC 9211) and HEK-293 cells with or without transfection of exogenous nucleic acid.
[0128] To measure the mRNA levels of HLA-E, HLA-F and HLA-G in cells, total RNA was extracted from cells using the Quick-RNA Microprep kit (Zymo Research). cDNA was prepared from total RNA extracts using the iScript cDNA synthesis kit (Bio-Rad). HLA-E, F and G levels were determined by real-time PCR using go-Tag green polymerase (Promega) and the following primers.
[0129] Table 1: Primers used to detect HLA-E, F and G
[0130] primer sequence SEQ ID NO HuHLA-E-F TTCGCCTACGACGGCAAGGA 32 HuHLA-E-R CCCTTCTCCAGGTATTTGTG 33 HuHLA-F-F GGCAGAGGAATATGCAGAGGAGTT 34 HuHLA-F-R CTTCTGTGTCCTGGGTCTGTTC 35 HuHLA-G-F TTGGGAAGAGGAGACACGGAACA 36 HuHLA-G-R AGGTCGCAGCCAATCATCCAC 37 XC423-HLA-G-F-1 GAGCGAGGCCAGTGAGTAA 38 XC424-HLA-G-R-1 TCTCCCAGGTAGAGGGTCTG 39 ...
Embodiment 2
[0135] This example illustrates HLA-F expression in modified and unmodified HEK293 cells.
[0136] The inventors have previously made TARGATT TM HEK293 cells are ready for gene insertion (see Figure 7 ). Use TARGATT TM HEK293 cells, the inventors generated modified HEK293 cells comprising a single copy insertion of HLA-F or HLA-G at the H11 locus of the safe harbor genome. The same qRT-PCR was performed to measure mRNA expression. The data in Table 3 demonstrate that HEK293 cells have higher basal levels of HLA expression compared to iPS cells, with more HLA-F and G expressed in HEK293 compared to HLA-E. One copy of exogenous HLA-F and HLA-G increased HLA-F and HLA-G expression 10-fold and 7-fold, respectively.
[0137] Table 3: Expression of HLA-E, F and G in modified or unmodified HEK293 cells. For comparison purposes, iPSCs were included in the same experiment.
[0138]
[0139]
Embodiment 3
[0141] This example illustrates the expression of HLA-F variants in HEK293 cells.
[0142] Naturally occurring HLA-F contains from N-terminal to C-terminal: HLA-Fα1 domain, α2 domain, α3 domain, transmembrane domain and cytoplasmic domain. The HLA-Fα1 domain and the α2 domain form the peptide binding groove. The HLA-Fα3 domain binds to β-2 globulin (β2M), which is required for the stability of the HLA-F complex.
[0143] In addition to the "canonical" isoform 1 (SEQ ID NO: 1 or 2), which has 346 amino acids (the short form of HLA-F in Table 4, referred to as "HLA-F-S"), HLA-F exists in various subtypes, mainly subtype 3, which is the longest subtype with an additional 96 amino acid sequence in its cytoplasmic region (for the HLA-F long form, referred to as "HLA-F-L", SEQ ID NO: 3 or 4).
[0144] The inventors have produced an HLA-F-β2M fusion protein ( Figure 5 C and Figure 5 D), which contains a signal peptide, α1, 2 and 3 domains, 15 amino acids (GGGGS) from N-termina...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com