Method for cooperatively treating nitrobenzene wastewater by coal water slurry technology
A technology for nitrobenzene wastewater and synergistic treatment, which is applied in the fields of water/sewage multi-stage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, etc. The increase in maintenance times and the increase in the corrosion of coal slurry can reduce the risk of unplanned shutdowns, reduce inspection and maintenance costs, and solve corrosion problems.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] The present embodiment provides a method for co-processing nitrobenzene wastewater with coal-water slurry technology, which comprises the following steps:
[0058] After the nitrobenzene wastewater is deoxygenated, the pH is adjusted, and then the deoxygenated nitrobenzene wastewater is passed into a reactor containing iron fillers for reaction, and then the pH of the reacted nitrobenzene wastewater is adjusted, and finally mixed with coal. , Additives complete pulping in the mill.
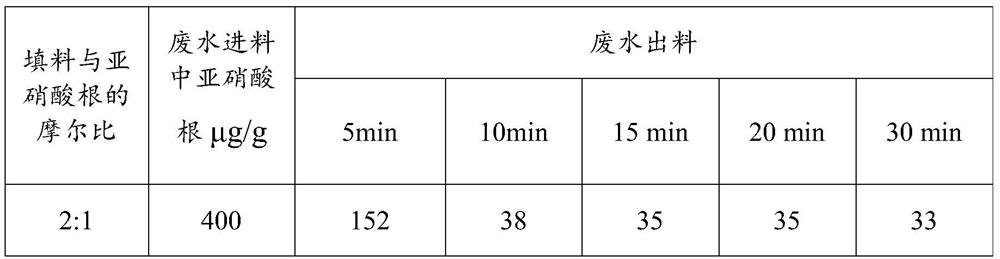
[0059] The pH of the nitrobenzene wastewater was adjusted to 3 after the deoxidation treatment, the iron-containing filler was sintered iron-carbon filler, the molar ratio of sintered iron-carbon and nitrite was 2:1, and the pH of the reacted nitrobenzene wastewater was adjusted is 7.
[0060] Table 1 is the molar ratio of different sintered iron carbon and nitrite in the nitrobenzene wastewater by the coal-water slurry technology in Example 1, and the change data of the nitrous acid conte...
Embodiment 2
[0065] The present embodiment provides a method for co-processing nitrobenzene wastewater with coal-water slurry technology, which comprises the following steps:
[0066] After the nitrobenzene wastewater is deoxygenated, the pH is adjusted, and then the deoxygenated nitrobenzene wastewater is passed into a reactor containing iron fillers for reaction, and then the pH of the reacted nitrobenzene wastewater is adjusted, and finally mixed with coal. , Additives complete pulping in the mill.
[0067] Wherein, after the deoxidation treatment, the pH of the nitrobenzene wastewater is adjusted to 3, the iron-containing filler is sponge iron filler, the molar ratio of sponge iron and nitrite is 3:1, and the pH of the reacted nitrobenzene wastewater is adjusted to 7 .
[0068] Table 2 is the variation data of nitrous acid content in the co-processing of nitrobenzene wastewater by coal-water slurry technology in Example 2.
[0069] Table 2 Test results
[0070]
[0071] As can be...
Embodiment 3
[0073] The present embodiment provides a method for co-processing nitrobenzene wastewater with coal-water slurry technology, which comprises the following steps:
[0074] After the nitrobenzene wastewater is deoxygenated, the pH is adjusted, and then the deoxygenated nitrobenzene wastewater is passed into a reactor containing iron fillers for reaction, and then the pH of the reacted nitrobenzene wastewater is adjusted, and finally mixed with coal. , Additives complete pulping in the mill.
[0075] Wherein, after the deoxidation treatment, the pH of the nitrobenzene wastewater was adjusted to 3, the iron-containing filler was iron filings, the molar ratio of iron filings and nitrite was 4:1, and the pH of the reacted nitrobenzene wastewater was adjusted to 7.
[0076] Table 3 is the variation data of the nitrous acid content in the co-processing of nitrobenzene wastewater by the coal-water slurry technology in Example 3.
[0077] Table 3 Test results
[0078]
[0079]
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com