Chip manufacturing method
A manufacturing method and chip technology, applied in the field of chip manufacturing, can solve problems such as reduced productivity, poor processing, and crystal orientation changes, and achieve the effects of suppressing abnormal elongation, reducing the number of inversions, and reliable segmentation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 2 Embodiment approach
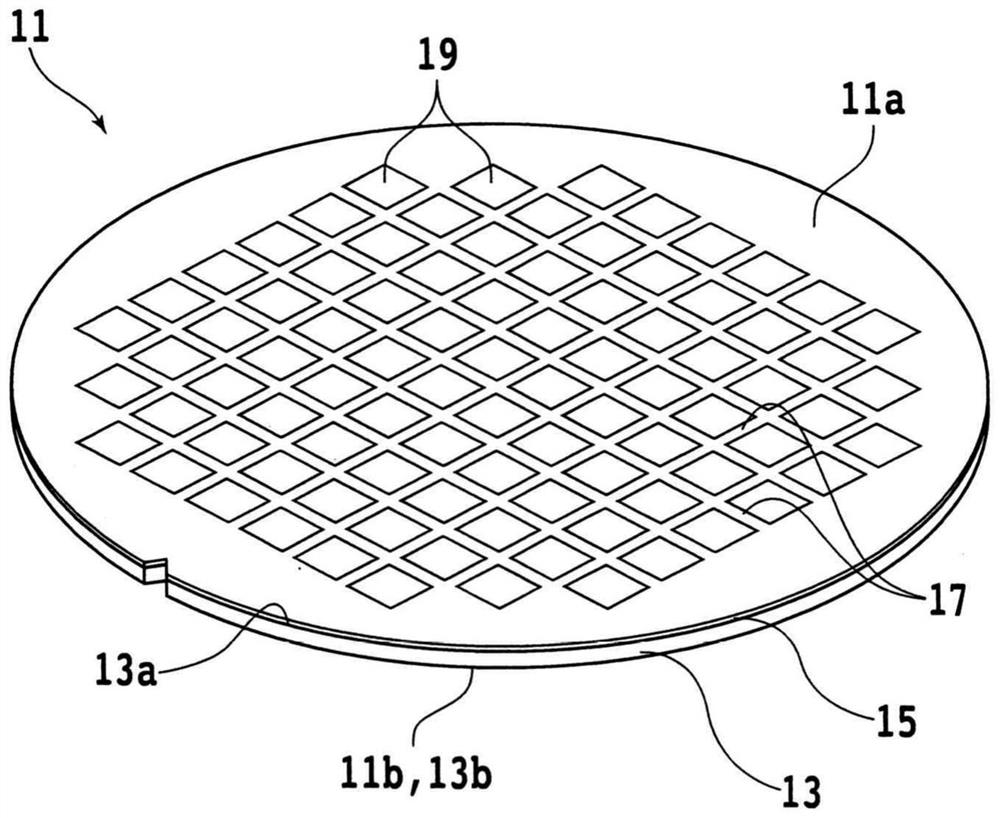
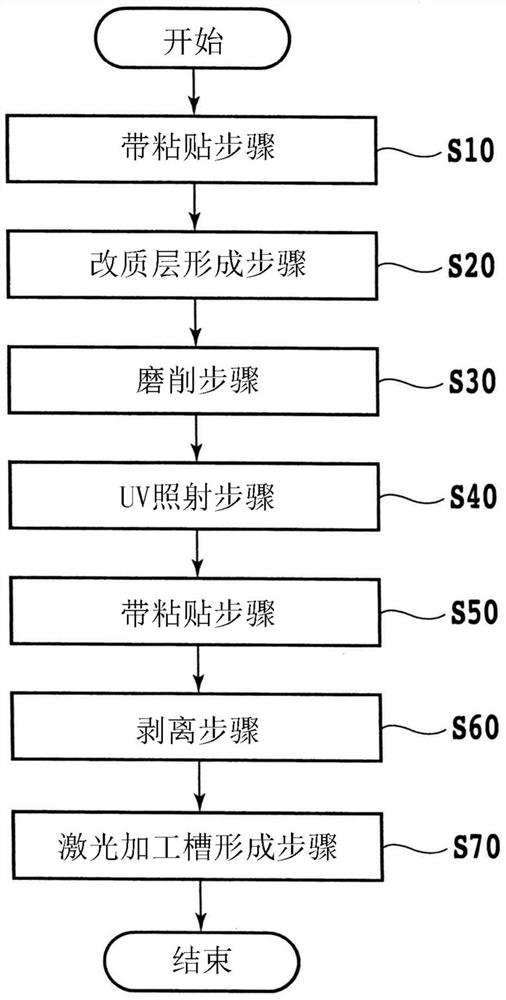
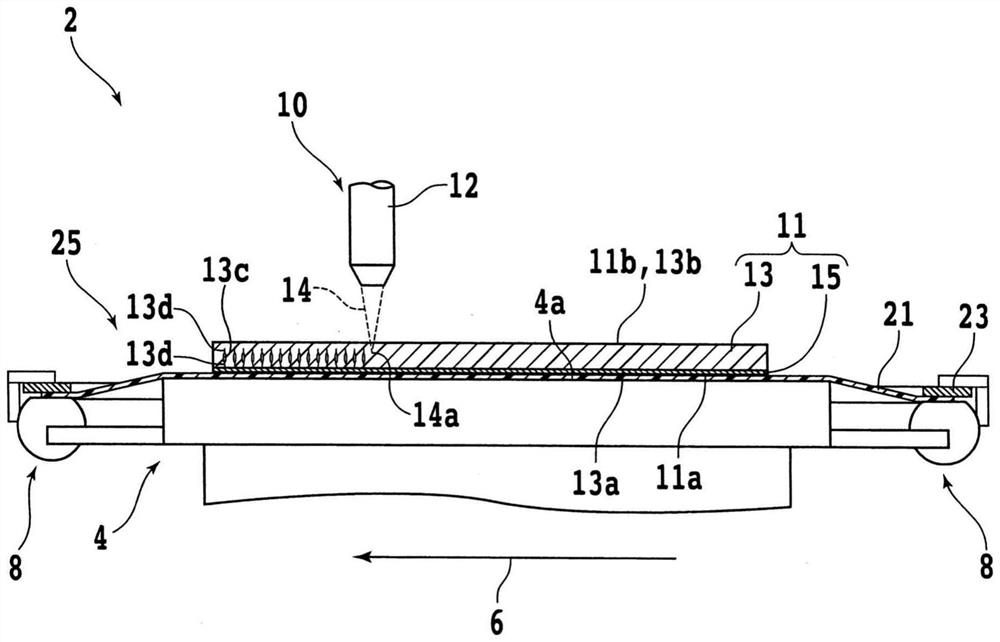
[0128] Next, the second embodiment will be described. Figure 12 It is a flowchart of the manufacturing method of the device chip 35 of 2nd Embodiment. In the laser processing groove forming step S70 of the second embodiment, as Figure 13 As shown, a laser-machined groove 15a having a predetermined depth that does not completely break the laminated body 15 is formed. 4 .
[0129] Figure 13 is one laser-machined groove 15a that does not reach the front surface 13a of the substrate 13 4 An enlarged cross-sectional view of the wafer 11 . For example, the laser processing groove 15a can be formed by reducing the average output, the repetition frequency, increasing the processing feed rate, or changing the height position of the light-converging point 50a. 4 .
[0130] By forming laser processing grooves 15a that do not reach the front surface 13a 4 , the damage on the front surface 13a side of the substrate 13 in the laser processing groove forming step S70 can be reduced...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com