Contact hole etching method of CMOS device and CMOS device manufacturing method
A contact hole etching and contact hole technology, which is applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of device cost increase, save manufacturing steps, avoid insufficient etching, and avoid over-etching The effect of the phenomenon
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
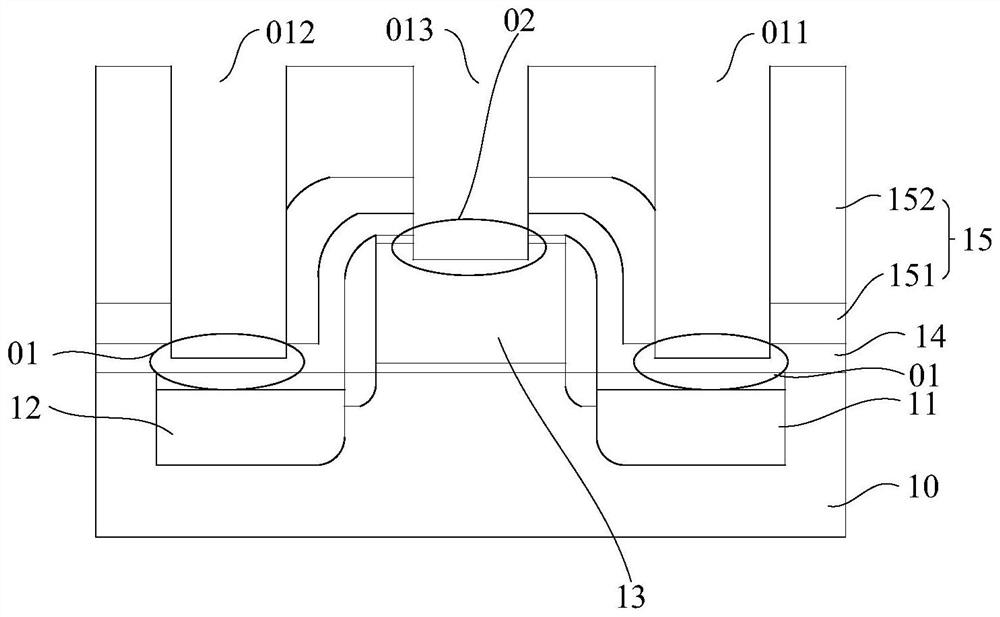
[0065] In semiconductor devices, contacts are typically formed on the gate and active regions (ie, source or drain). like figure 1 As shown, taking a CMOS device as an example, a device layer is formed in the substrate 10, and the device layer includes a source electrode 11 and a drain electrode 12 located inside the substrate and a gate electrode 13 located above the substrate. The drain has a deeper depth than the gate. An interlayer dielectric layer 15 (usually a multilayer structure, such as figure 1 When the first dielectric layer 151 and the second dielectric layer 152) and the etch stop layer 14 are etched to form the source contact hole 011, the drain contact hole 012 and the gate contact hole 013, it is usually synchronous etching, At this time if figure 1 As shown, over-etching 02 occurs at the bottom of the gate contact hole 013 with a shallow depth, and under-etching 01 occurs at the bottom of the source contact hole 011 and the drain contact hole 012 with a dee...
Embodiment 2
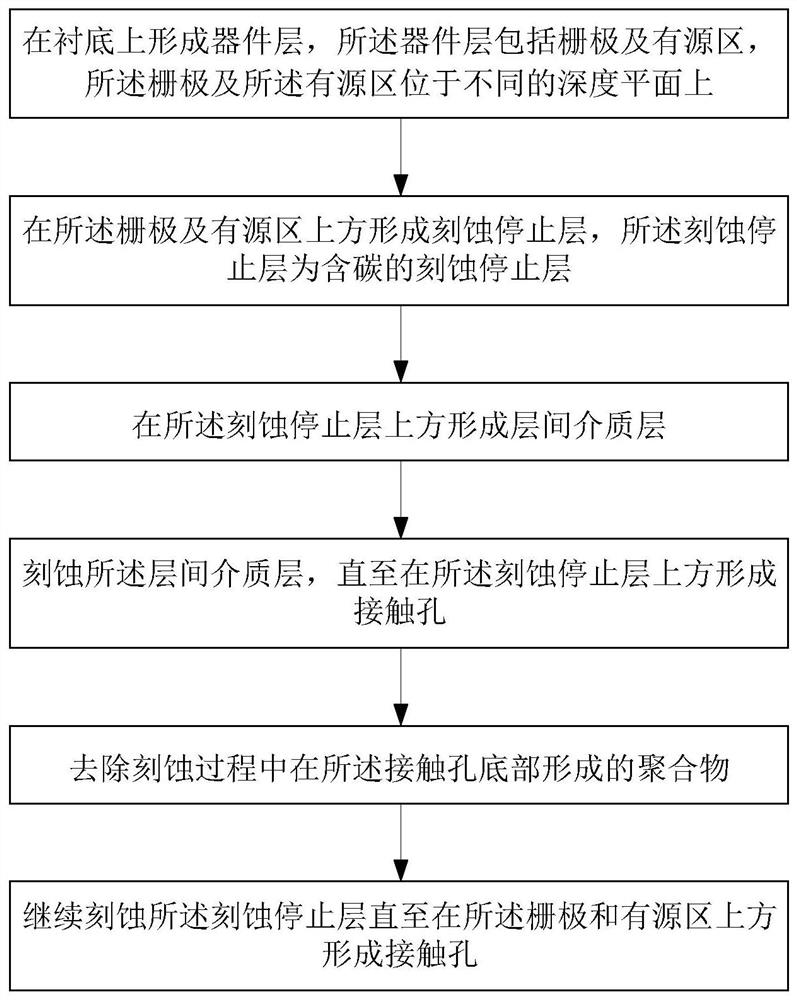
[0081] This embodiment also provides a method for etching a contact hole of a CMOS device. An etch stop layer containing carbon is formed above the device layer to eliminate under-etching or over-etching. The similarities between this embodiment and the contact hole etching method of the CMOS device provided in the first embodiment will not be repeated, and the differences are:
[0082] In step S102, an etch stop layer is formed over the gate electrode and the active region. When the etch stop layer is an etch stop layer containing carbon, in this embodiment, a carbon-rich layer is formed on the surface of the etch stop layer. 205 , specifically, an ion implantation method is used to implant carbon particles in the surface layer of the etch stop layer, the implantation concentration is between 1E15 cm-2 and 1E16 cm-2, and the implantation energy is less than 5Kev. The thickness of the formed carbon-rich layer 205 is also less than or equal to 1 nm.
[0083] After the carbon-r...
Embodiment 3
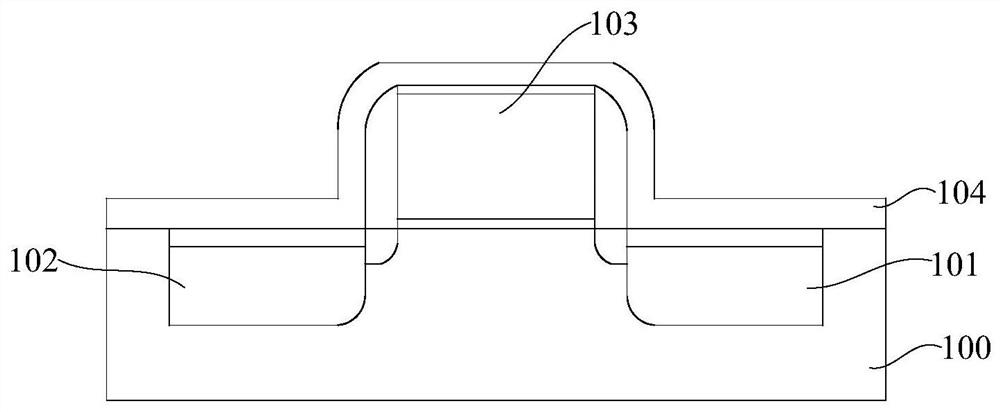
[0086] This embodiment provides a method for manufacturing a CMOS device. The method first forms a device layer on a substrate through a front-end process. Taking a CMOS device as an example, the device layer includes a gate electrode 103 , a source electrode 101 and a drain electrode 102 .
[0087] Then, using the contact hole etching method described in the first embodiment, a gate contact hole 1030 , a source contact hole 1010 and a drain contact hole 1020 are formed above the device layer. For the formation of the above-mentioned contact holes, reference may be made to the method described in the first embodiment, which will not be described in detail here. After that, as Figure 14 As shown, each contact hole is filled with conductive material to form a gate contact 130 , a source contact 110 and a drain contact 120 . In an optional embodiment, the above-mentioned conductive material to be filled is tungsten, and other conductive materials such as copper and silver may a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com