Screening machine
A screening machine and screen basket technology, which is applied in the fields of filter screen, textile and paper making, solid separation, etc., can solve problems such as non-design, and achieve the effects of improving efficiency, reducing speed, high output and separation performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
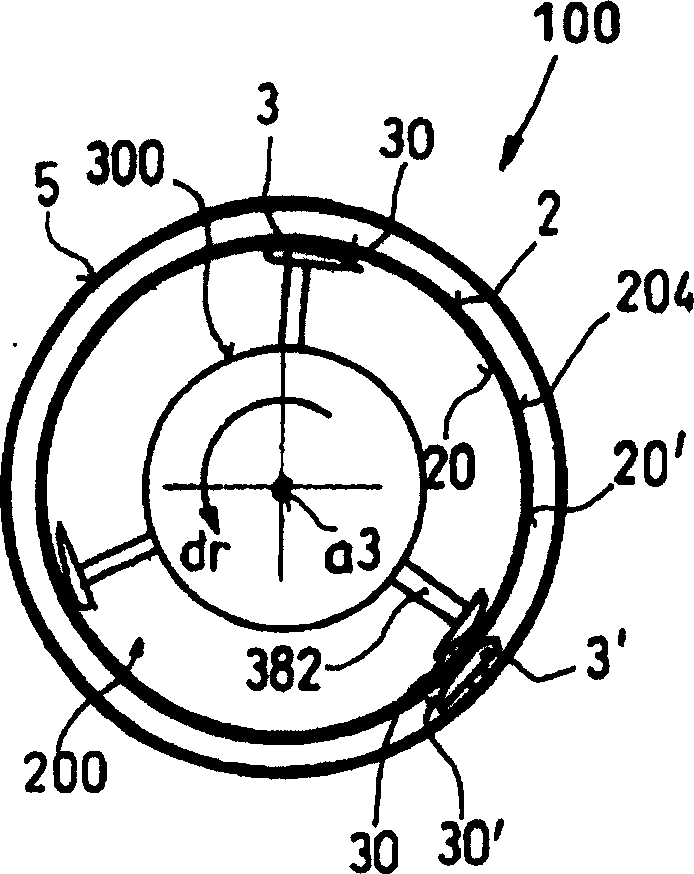
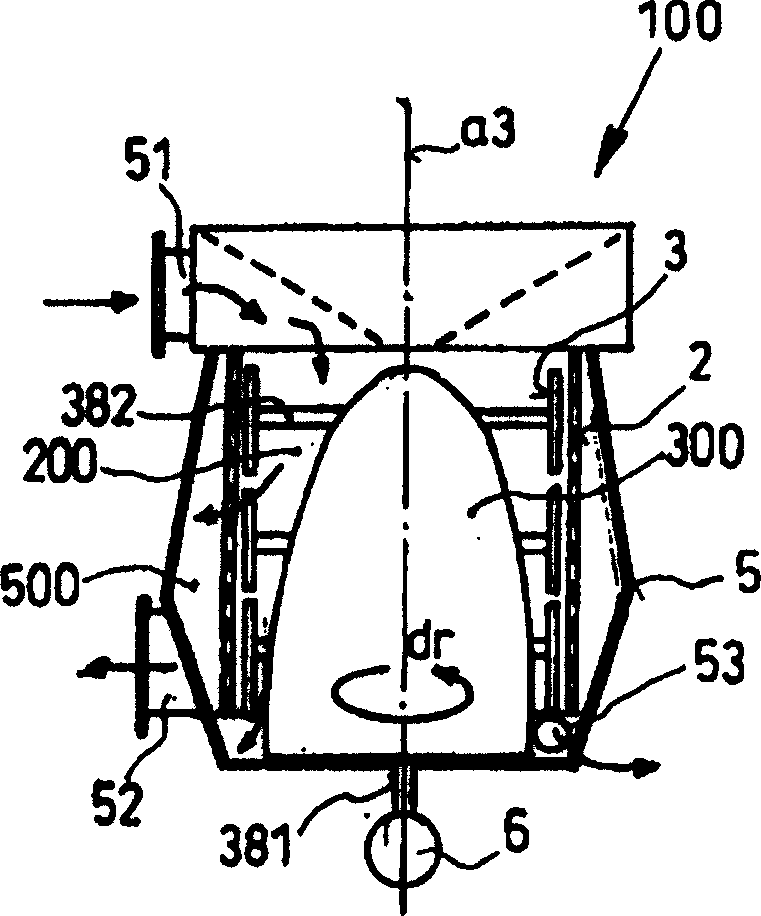
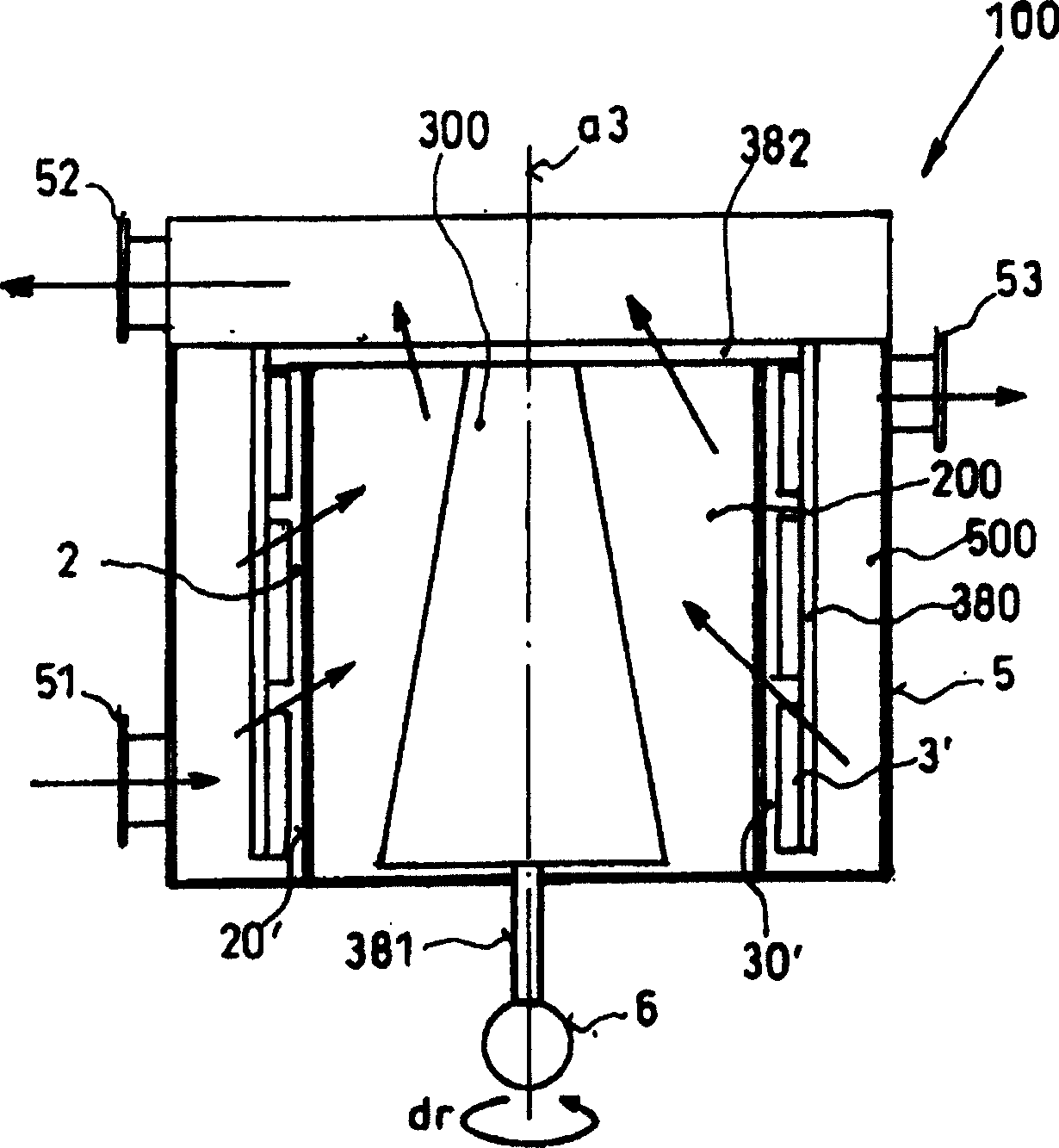
[0033] Such as figure 1 with 2As shown, respectively represent the schematic diagram of the horizontal cross section and the vertical cross section of the screening machine 100, the screening machine includes a housing 5 with an inlet 51 and an outlet 52, the inlet 51 is used for the entry of the screening material suspension, and the outlet 52 is used for For receiving pulp from which impurities have been removed. An outlet 53 or similar structure is provided at the bottom of the housing 5 for discharging impurities separated from the screening material. In the inner chamber 500 of the generally barrel-shaped or cylindrical housing 5, a cylindrical screen basket 2 is coaxially arranged, and the screen basket 2 has a circular or slot-type screening aperture 204 for clean pulp The suspension is passed through. Inside the inner chamber 200 of the screen basket 2 there is arranged a rotor 300 mounted on a central support on a shaft 381 driven by an electric motor 6, the rotor ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com