Semiconductor device
A semiconductor, conduction technology, applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, output power conversion devices, transistors, etc., can solve problems such as deviation, short circuit of power devices 12 and 13, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0088] A-1. Device structure
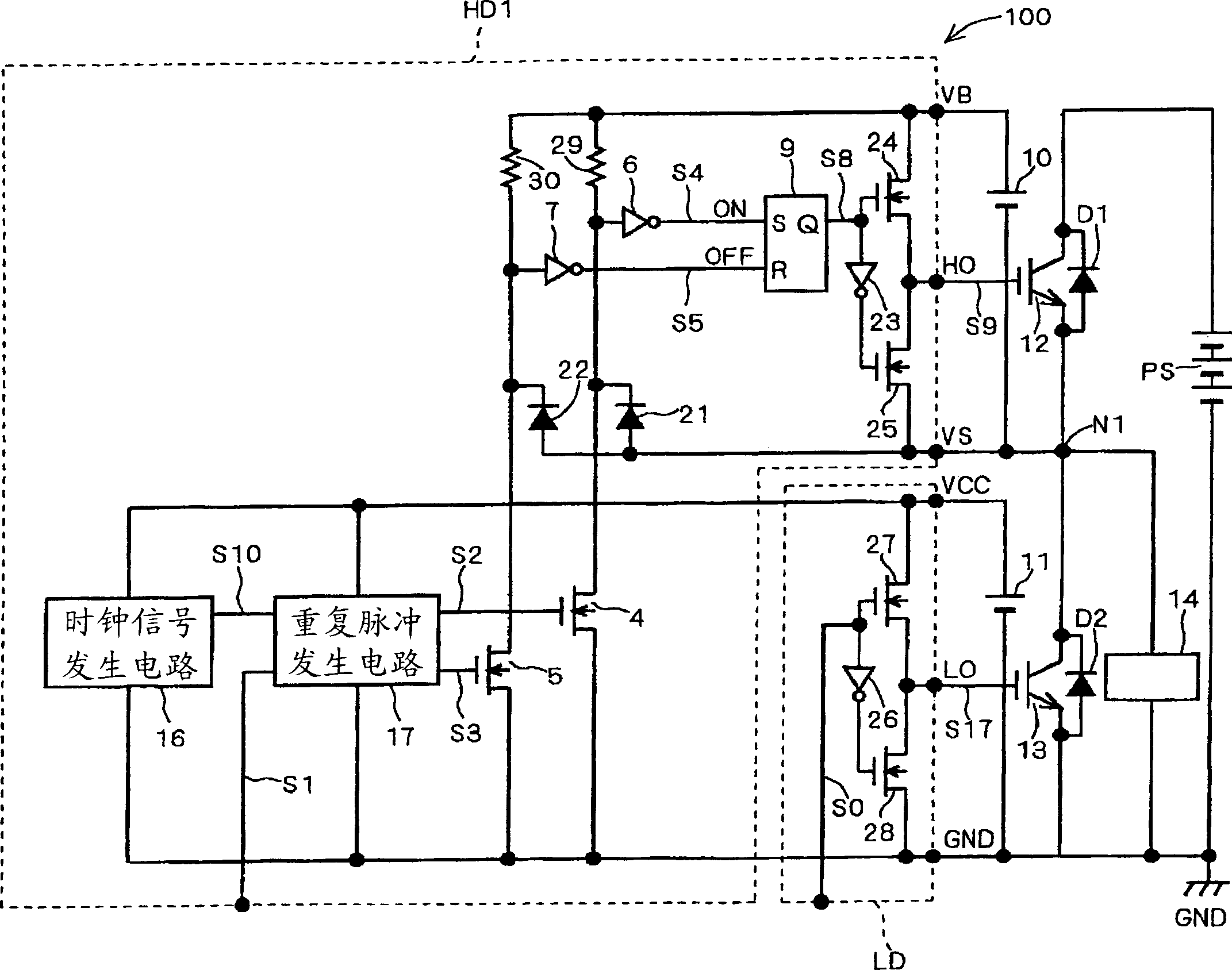
[0089] As Embodiment 1 of the semiconductor device of the present invention, figure 1 The structure of the level shift circuit 100 in the state mode is shown.
[0090] exist figure 1 Among them, the power devices 12 and 13 such as IGBT (insulated gate bipolar transistor) are connected between the positive pole and the negative pole (ground potential GND) of the power supply PS in a push-pull type to form a half-bridge power device. In addition, freewheeling diodes D1 and D2 are connected in parallel with power devices 12 and 13 in reverse direction, respectively. Furthermore, a load (inductive load such as a motor) 14 is connected to a connection point N1 between the power device 12 and the power device 13 .
[0091] exist figure 1 Among them, the power device 12 uses the potential of the connection point N1 with the power device 13 as a reference potential, and switches between the reference potential and the power supply potential suppli...
Embodiment 2
[0123] B-1. Device structure
[0124] As Embodiment 2 of the semiconductor device of the present invention, Figure 4 The structure of the level shift circuit 200 is shown. exist Figure 4 in, for with figure 1 The same structures of the level shift circuit 100 shown are denoted by the same symbols, and repeated explanations are omitted.
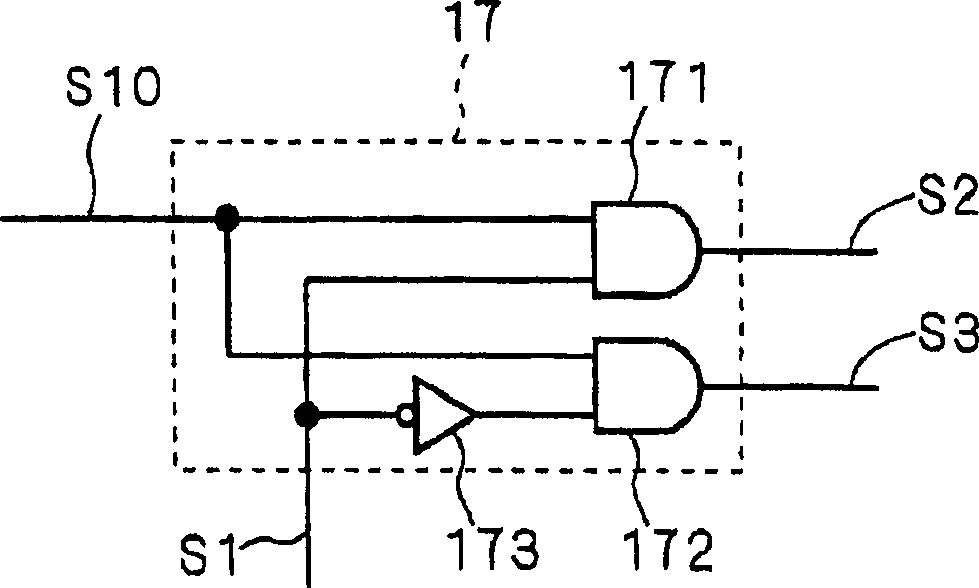
[0125] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the level shift circuit 200 is divided into a high potential side power device drive circuit HD2 and a low potential side power device drive circuit LD. In the high potential side power device drive circuit HD2, there is no figure 1 The clock signal generation circuit 16 provided in the shown level shift circuit 100 supplies a clock signal supplied from the outside as a signal S10 to the repetitive pulse generation circuit 17 .
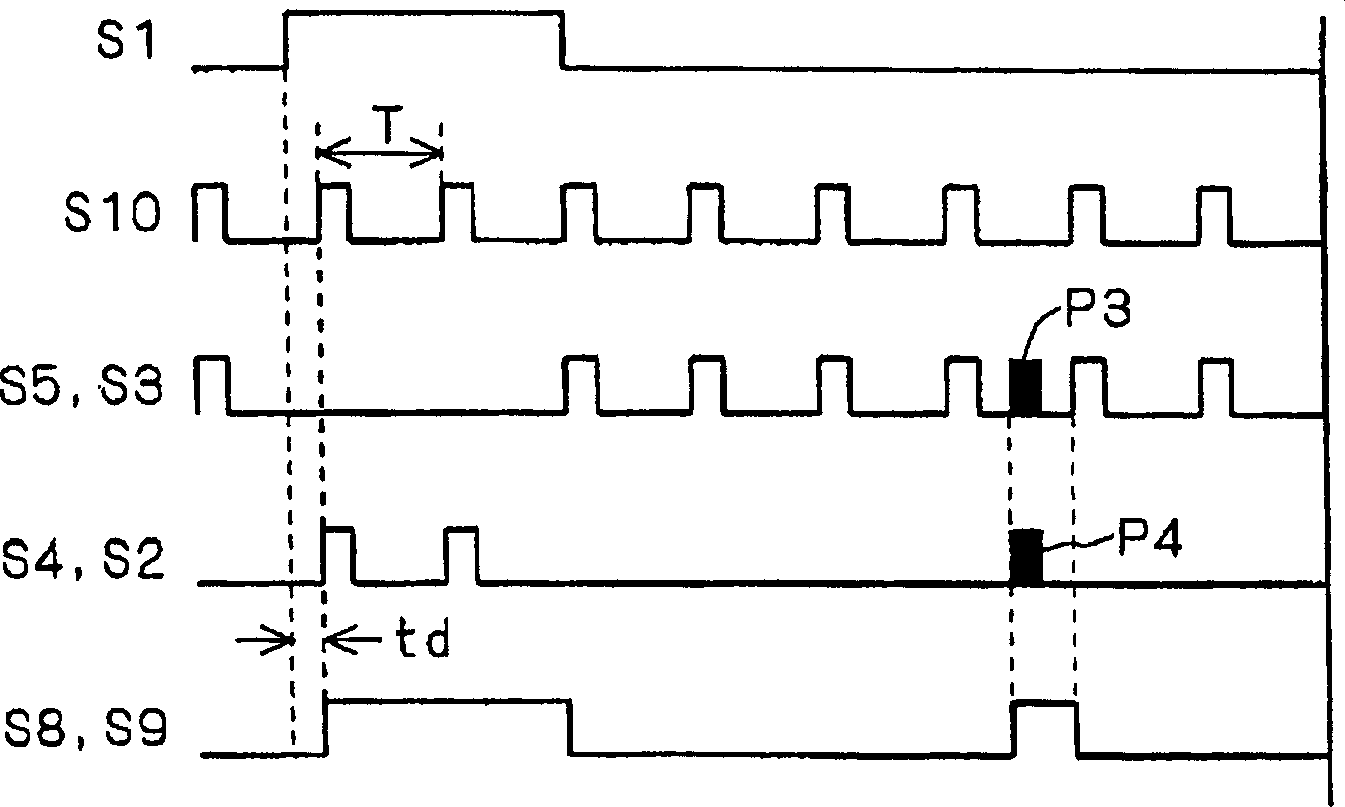
[0126] exist figure 1 In the shown level shift circuit 100, the pulse signal generated by the own clock signal generation circuit 16 is used. However, at this time, the ti...
Embodiment 3
[0137] C-1. Device structure
[0138] As Embodiment 3 of the semiconductor device of the present invention, Figure 6 The configuration of the level shift circuit 300 is shown. exist Figure 6 in, for and figure 1 The same structures of the level shift circuit 100 shown are denoted by the same symbols, and repeated explanations are omitted.
[0139] Such as Figure 6 As shown, the level shift circuit 300 is divided into a high potential side power device drive circuit HD3 and a low potential side power device drive circuit LD. In the high potential side power device drive circuit HD3, there is a level shifted OR circuit 19 that obtains a clock signal with the same frequency as the oscillation frequency of clock signal generating circuit 16 in the high potential area by logical sum of on-signal S4 of one bit and off-signal S5 that has been level-shifted.
[0140] That is, the outputs of the inverter circuits 6 and 7 are connected to the set input and reset input of the SR...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com