Lattice for testing multiple biological molecule and use method thereof
A technology of biomolecules and dot arrays, applied in biological testing, measurement devices, analytical materials, etc., can solve the problems that cannot meet the needs of large-scale determination of the expression and intracellular location of different proteins
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0074] Example 1: Making antibody arrays.
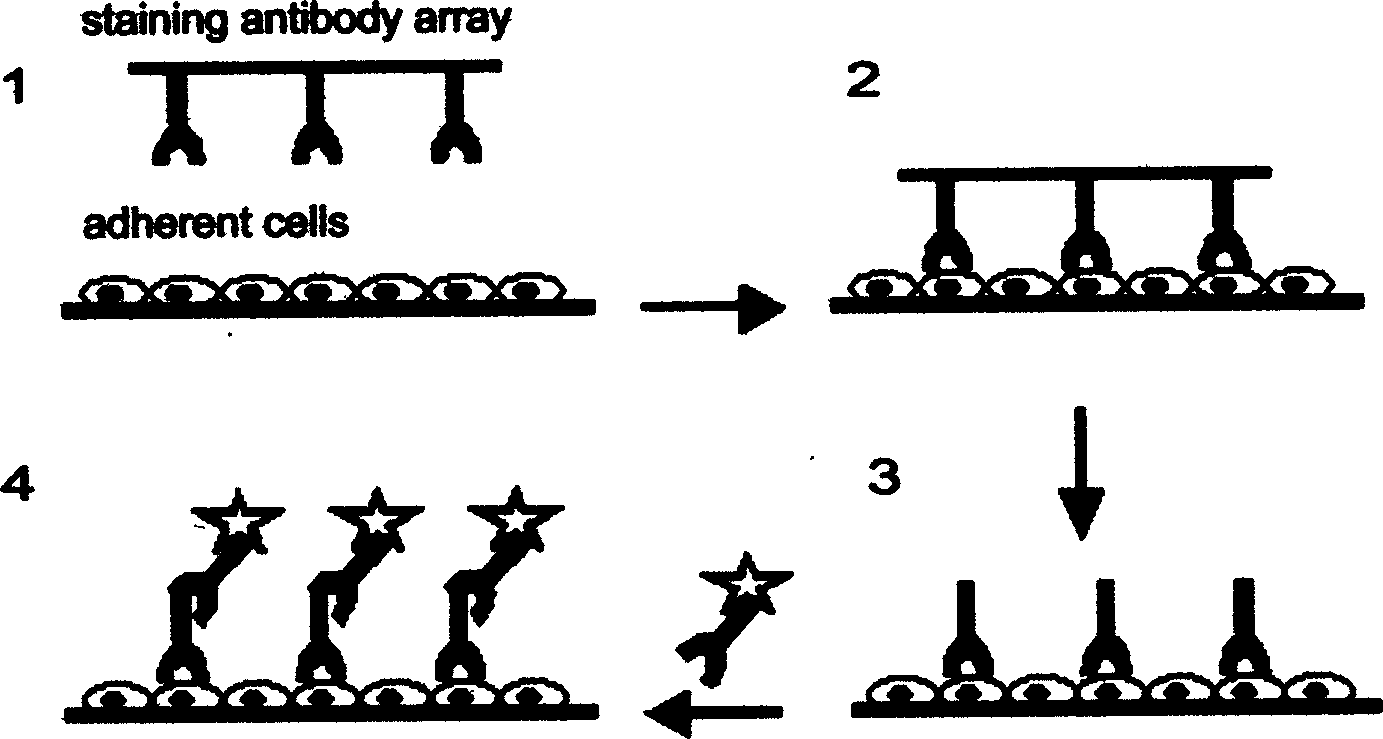
[0075] Antibody (approximately 0.5 μg / μl) was first spotted onto the nylon membrane using a mechanical spotter. The spotter drops approximately 80 nanoliters of antibody solution (approximately 40 nanograms) onto each spot using a 0.6 mm tip. The distance between points is about 0.6 mm. Antibodies are non-covalently bound to the nylon membrane. The antibody dot array prepared by this method can be used immediately or kept at 4°C within 48 hours.
example 2
[0076] Example 2: Using antibody arrays in immunochemical staining.
[0077] This example is immunochemical staining using antibody arrays prepared by the method described in Example 1. This array contains 200 antibodies.
[0078] MDCK cells were cultured on coverslips for 2 days until confluence. The cells were then fixed and permeabilized in a methanol / acetone (1:1 ratio) mixed solution at -20°C for 10 minutes. After washing with saline, MDCK cells were exposed to the antibody array for about 1 hour. The antibody array support is then separated from the cells and their support. After the cells were washed again with normal saline, the alkaline phosphatase-labeled secondary antibody was added to react for half an hour. After washing, staining was observed by chromogenic reaction using 5-bromo-4 chloro-indolyl-phosphatase (BCIP) and nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) as substrates. The color reaction was terminated by washing with saline. The developed image is scanned by a dig...
example 3
[0079] Example 3: Using antibody arrays in fluorescent immunochemical staining.
[0080] In this example, the spotter drops approximately 10 nanoliters of antibody solution (approximately 5 ng) onto each spot using a 0.3 mm tip. The distance between points is about 0.3mm. then apply Figure 1 Antibody arrays were used to stain A431 cells as indicated in . Similar to Example 2, except that a fluorescently labeled secondary antibody was used, and the staining was observed under a fluorescent microscope (see Figure 3). Cells were bound with fluorescently labeled secondary antibodies for half an hour. After washing, the cells were observed under a fluorescent microscope. Cells are stained by antibody at several different locations, while no diffusion of antibody is seen, as can be seen from the fact that different antigens have different subcellular sites and the areas between immobilized antibodies are not stained . Regular fluorescent spots can be observed under low magnif...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com