Organic luminescent device with enhanced light extraction efficiency
A light extraction and device technology, applied in organic semiconductor devices, semiconductor devices of light-emitting elements, electric solid devices, etc., can solve problems such as incompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
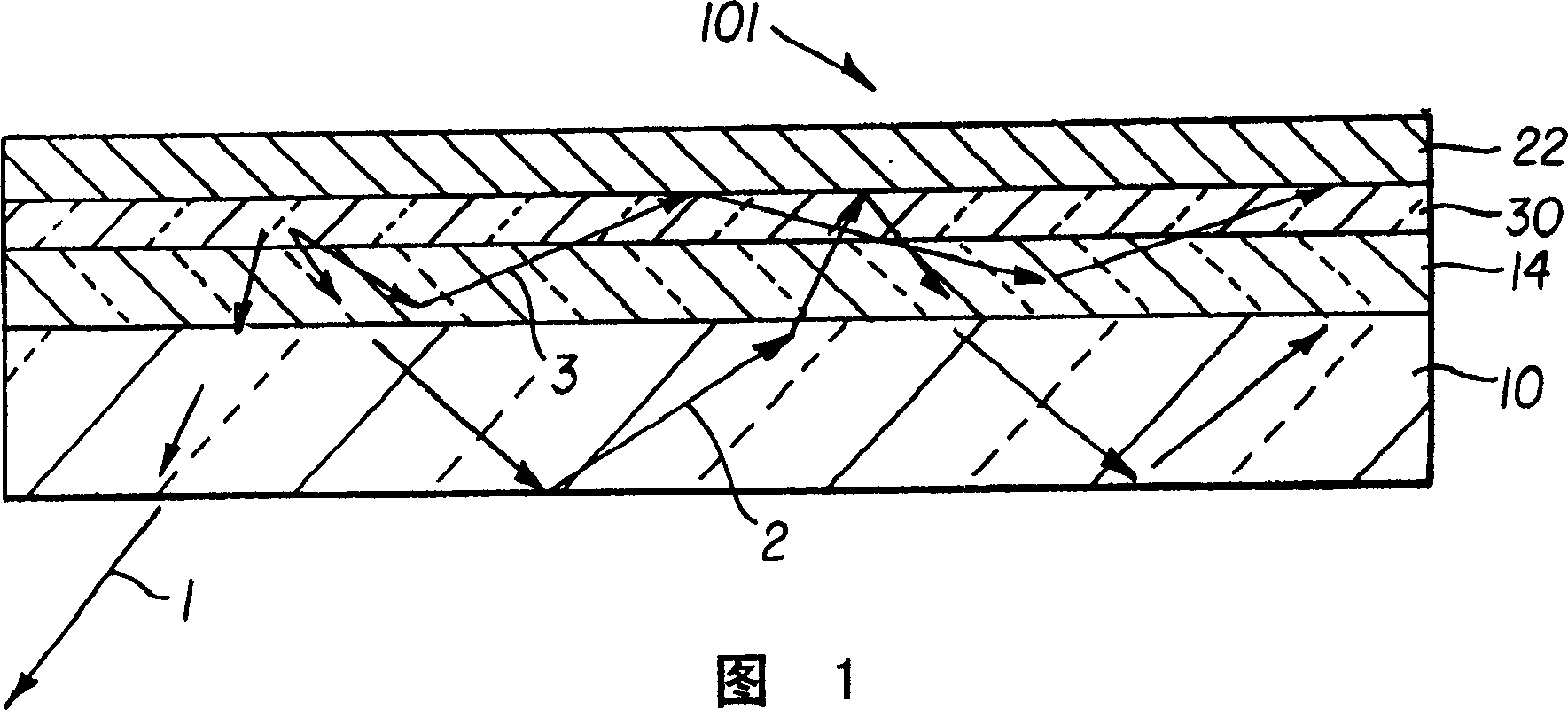
[0032] FIG. 1 is a schematic cross-sectional view of a typical common OLED device 101 . The device 101 includes a substrate 10 , an anode layer 14 , an organic EL element 30 and a cathode layer 22 . The organic EL element 30 may contain one or more sublayers, including a hole injection layer, a hole transport layer, a light emitting layer, an electron transport layer, and an electron injection layer. Most generally, substrate 10 and anode layer 14 are transparent, cathode layer 22 is reflective, and light generated from the device is emitted through anode layer 14 and substrate 10 . This is often referred to as a bottom emitting OLED device. OLED devices can also be top emitting. In a top emitting OLED device, the anode layer is made reflective and the cathode layer is made transparent, and the generated light is emitted through the cathode layer. The discussion below based on bottom-emitting devices also applies to top-emitting devices. Additionally, the order of the layer...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| electron work function | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electron work function | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com