Electronic ballast and method for selecting its working frequency
An electronic ballast and operating frequency technology, applied in the field of applied electronics, can solve the problems of high cost and large volume, and achieve the effects of low cost, small volume and low crest factor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
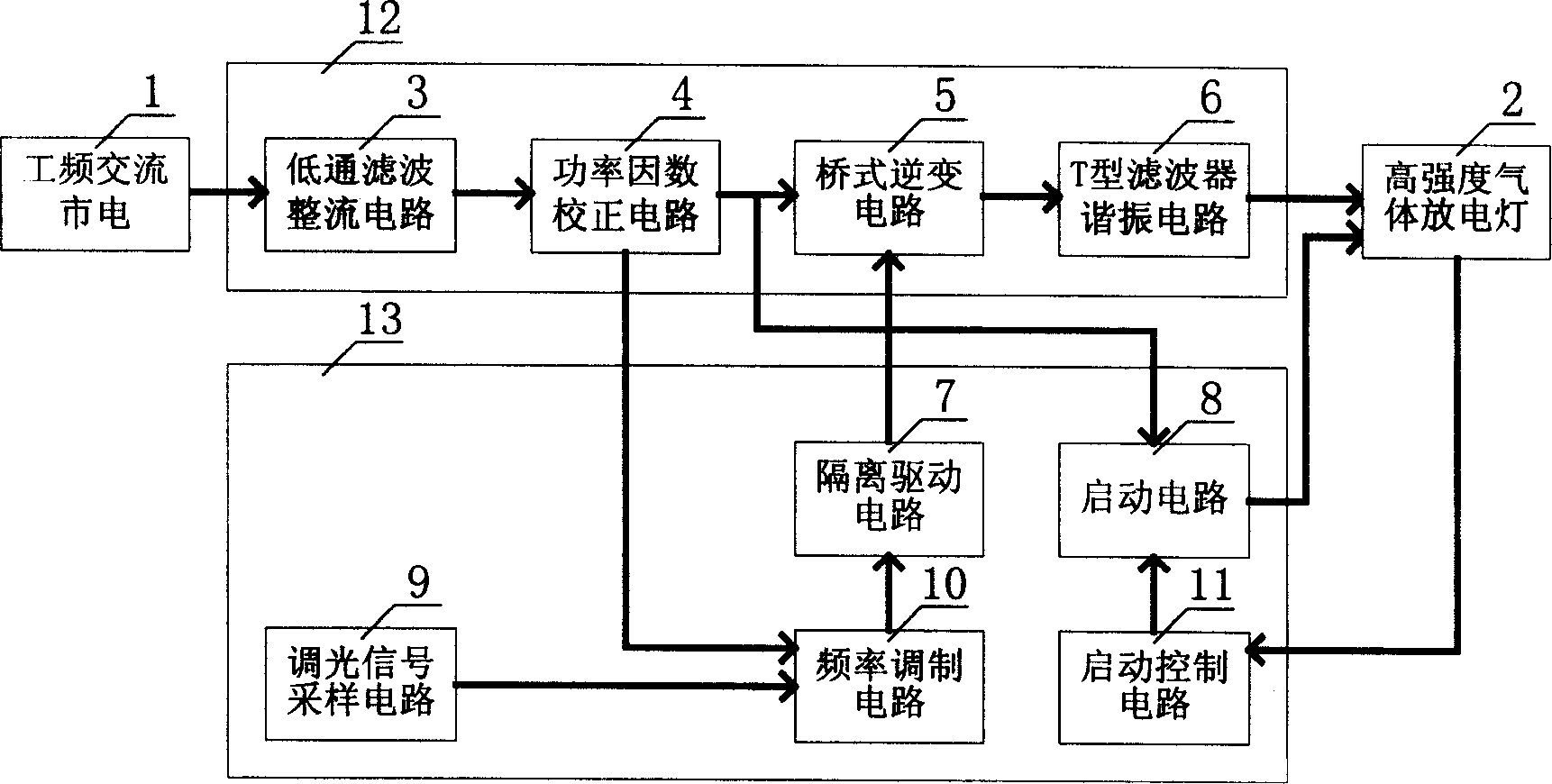
[0023] Specific embodiment 1: The electronic ballast for dimming high-intensity gas discharge lamps includes a gas discharge lamp main circuit 12 connected to the high-intensity gas discharge lamp 2 and a control circuit 13 connected to the gas discharge lamp main circuit. The main circuit of the gas discharge lamp is composed of a low-pass filter rectifier circuit 3, a power factor correction circuit 4, a bridge inverter circuit 5, and a T-type filter resonance circuit 6. The control circuit is a dimming signal sampling circuit 9 , Frequency modulation circuit 10, isolation drive circuit 7, start control circuit 11, start circuit 8; the low-pass filter rectifier circuit 3, power factor correction circuit 4, bridge inverter circuit 5, T-type filter resonance The circuit 6 is connected in sequence between the power frequency AC mains 1 and the high-intensity gas discharge lamp 2; the dimming signal sampling circuit 9 is connected to the frequency modulation circuit 10, the power fa...
specific Embodiment 2
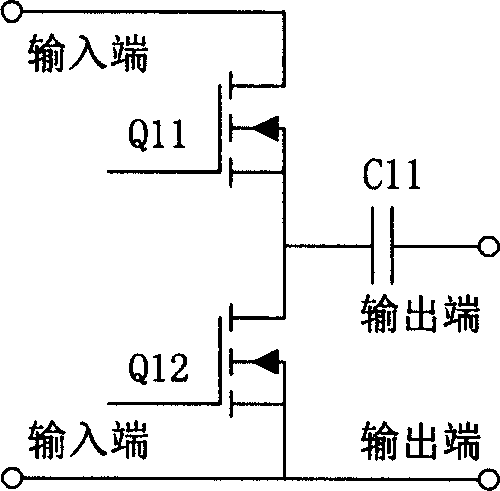
[0029]Specific embodiment 2: The electronic ballast for dimming high-intensity gas discharge lamps described in embodiment 1, wherein the bridge inverter circuit 5 adopts: consisting of switching tubes Q21, Q22, capacitors C21, C22; switching tubes Q21 and the output terminal of the switching tube Q22 are connected in series; the capacitor C21 and the capacitor C22 are connected in series; the output terminals of the switching tubes Q21 and Q22 are connected in series and the capacitors C21 and C22 are connected in series in parallel; the output terminals of the switching tubes Q21 and Q22 are connected in series with the capacitor The two ends of C21 and C22 in series and the two ends in parallel are the input ends; the middle end of the output ends of the switch tubes Q21 and Q22 in series and the middle end of the series capacitors C21 and C22 are the output ends of a half-bridge inverter circuit.
specific Embodiment 3
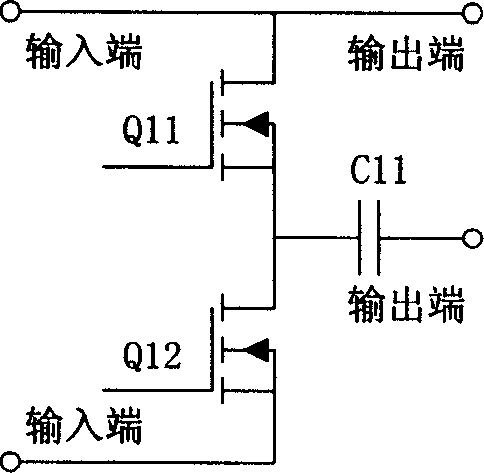
[0030] Specific embodiment 3: In the electronic ballast for dimming high-intensity gas discharge lamps described in embodiment 1, the bridge inverter circuit 5 adopts a full-bridge inverter circuit: switch tubes Q31, Q32, Q33, Q34 constitutes; the output terminals of the above-mentioned switching tubes Q31 and Q32 are connected in series, the output terminals of the switching tubes Q33 and Q34 are connected in series, and the output terminals of the switching tubes Q31 and Q32 are connected in series and the output terminals of the switching tubes Q33 and Q34 are connected in series and connected in parallel. The output terminal of Q32 is connected in series with the output terminals of Q33 and Q34, and the output terminal of Q32 is connected in series. The output terminals of Q31 and Q32 are connected in series, and the output terminals of Q33 and Q34 are connected in series. The output terminal.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com