LDPC decoder for decoding a low-density parity check (LDPC) codewords
A low-density parity and parity bit technology, applied in the application of multi-bit parity error detection coding, error correction/detection using block codes, data representation error detection/correction, etc., can solve the problem of LDPC decoders Deteriorated performance, high storage size, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
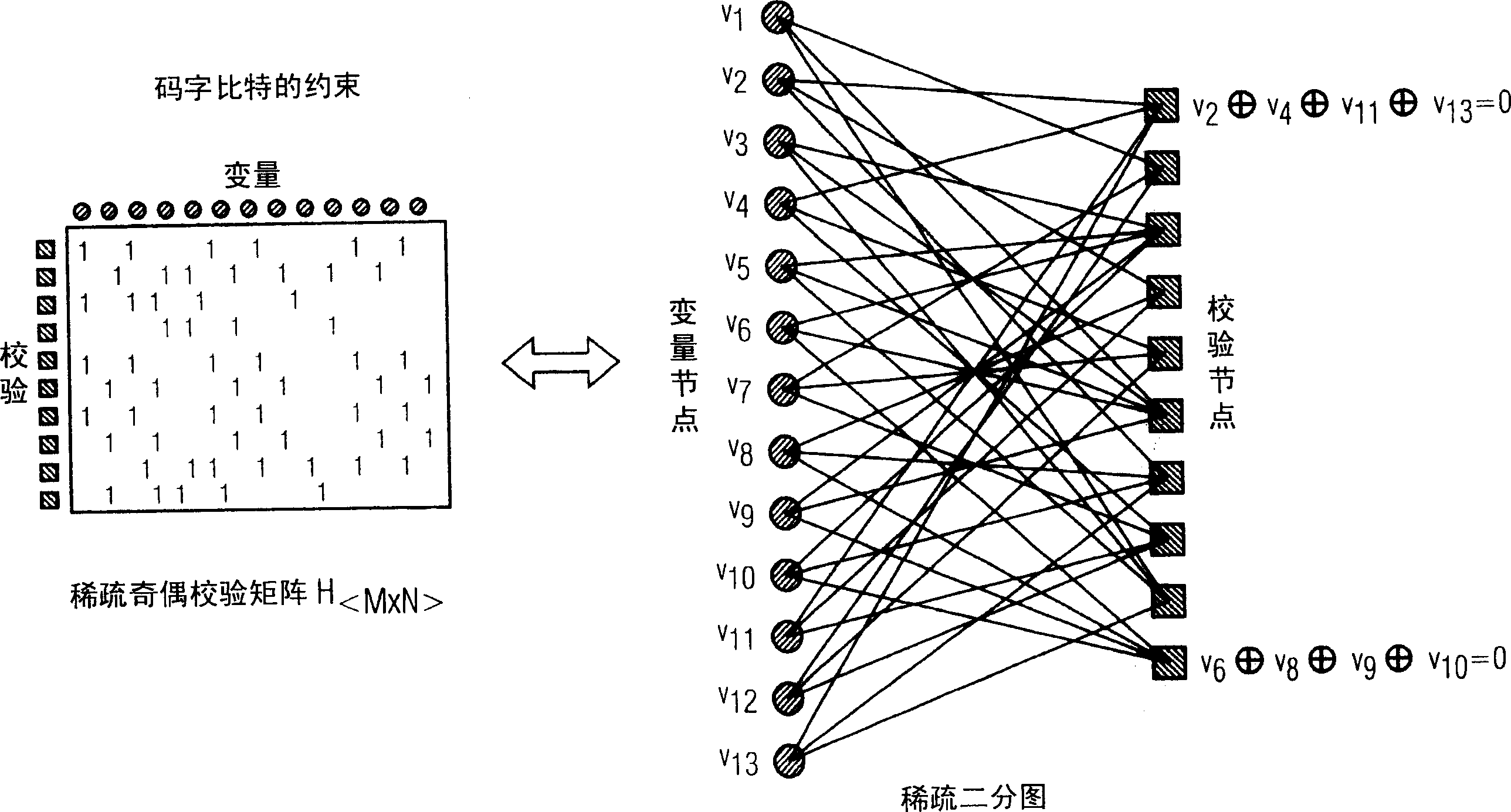
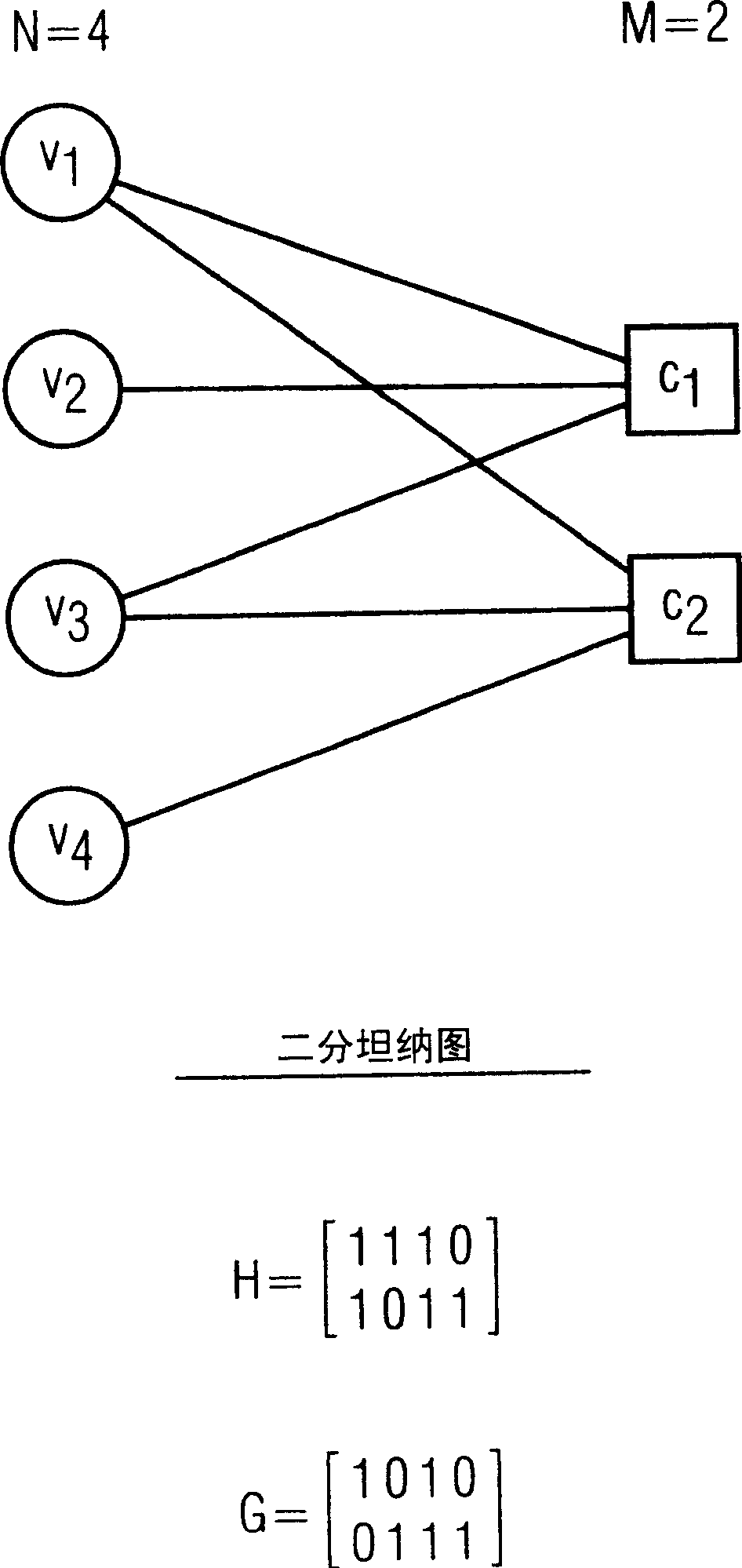
[0128] From Figure 9 As can be seen in , the method for decoding a low density parity check codeword according to the present invention is performed on the basis of received channel observations, ie estimated values or estimates indicating that the received codeword bits have predetermined values. These estimates are computed from the received codeword Y and predetermined parameters of the communication channel. The predetermined parameters of the communication channel are known. In an alternative embodiment of the invention, if the parameters of the communication channel are unknown, the minimum sum message passing calculation rule may be used, for which no parameters of the communication channel are required.
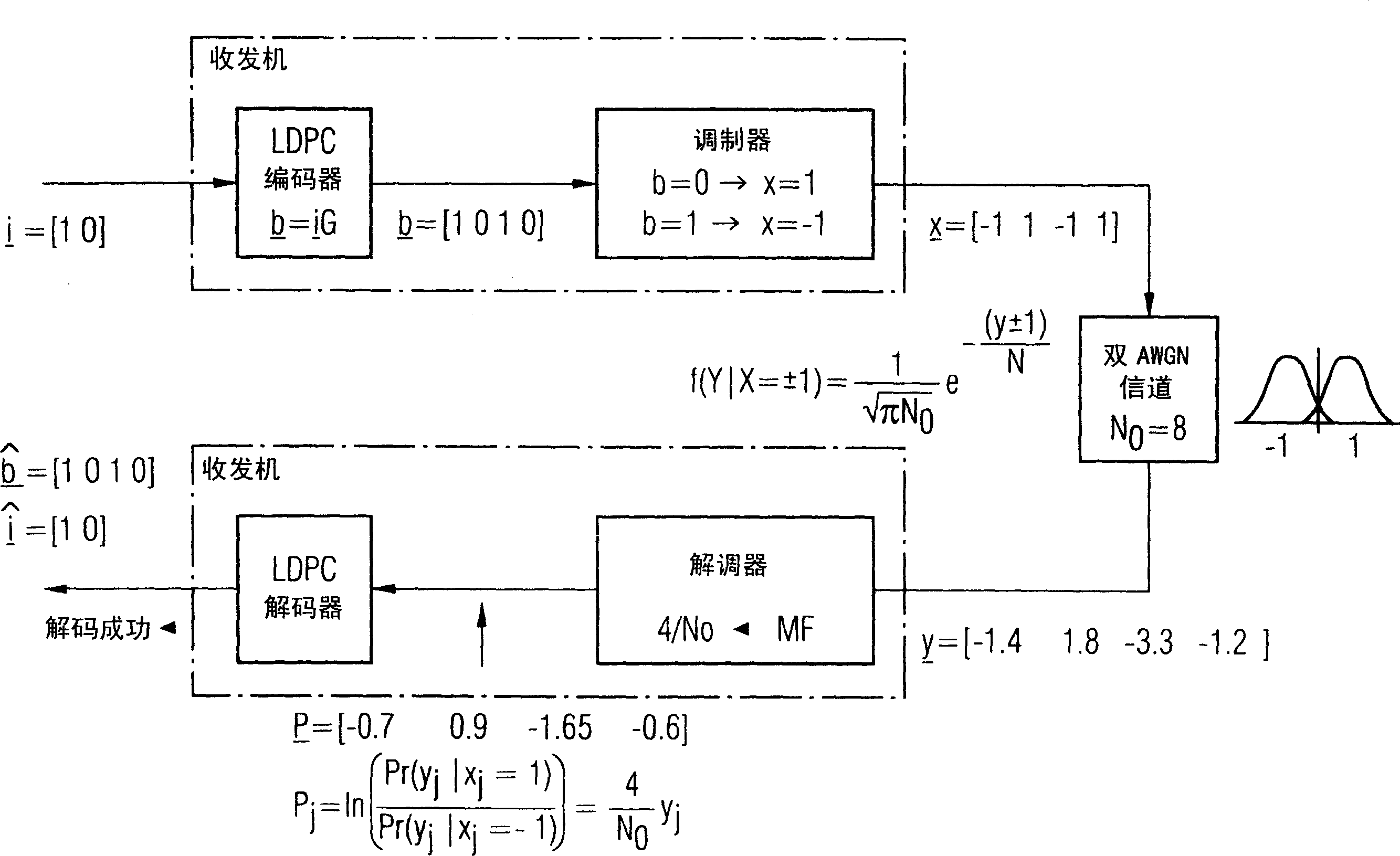
[0129] Figure 11 A general message passing decoding process covering all embodiments is shown in . In the preferred embodiment, these estimates are log-likelihood ratios (LLRs) of the received bits.
[0130] Fig. 15b shows a block diagram of a preferred embodi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com