Method for manufacturing recombinant polyclonal proteins
A protein and recombinant enzyme technology, applied in peptide/protein components, animal/human proteins, immunoglobulins, etc., can solve the problems of lack of original diversity, affecting long-term production of antibodies, mitotic instability of immunoglobulin loci, etc. The effect of avoiding ethical and clinical dilemmas
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0214] Site-specific integration versus random integration
[0215] For the following transfection experiments, CHO-Flp-In cells (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) were used. The efficiency of the system was tested using human secreted alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) as a reporter gene. Prepare two plasmid constructs:
[0216] 1. Insert SEAP into pcDNA3.1 hygro+ (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) (for random integration)
[0217] 2. Insertion of SEAP into pcDNA5 / FRT (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) (for site-specific integration)
[0218] The two plasmid constructs were very similar in terms of regulatory elements (ie promoter, polyadenylation, etc.), which allowed the comparison of random versus site-specific integration using the plasmids.
[0219] CHO Flp-In cells were transfected with plasmid construct 1 alone or with plasmid construct 2 in combination with the recombinase-encoding plasmid pOG44 as described by Invitrogen. Transfectants were selected using hygromycin and the production of SEAP ...
Embodiment 2
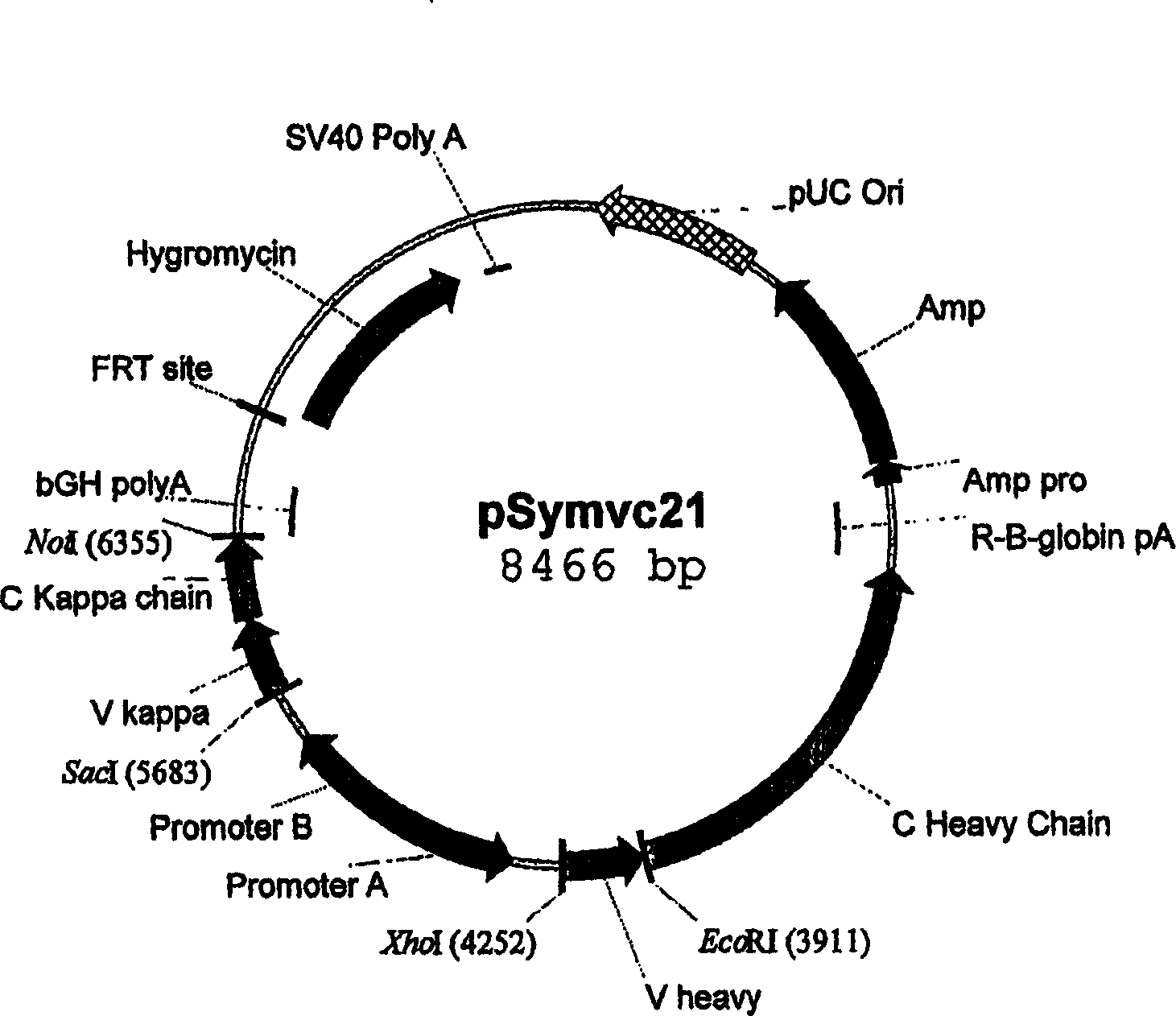
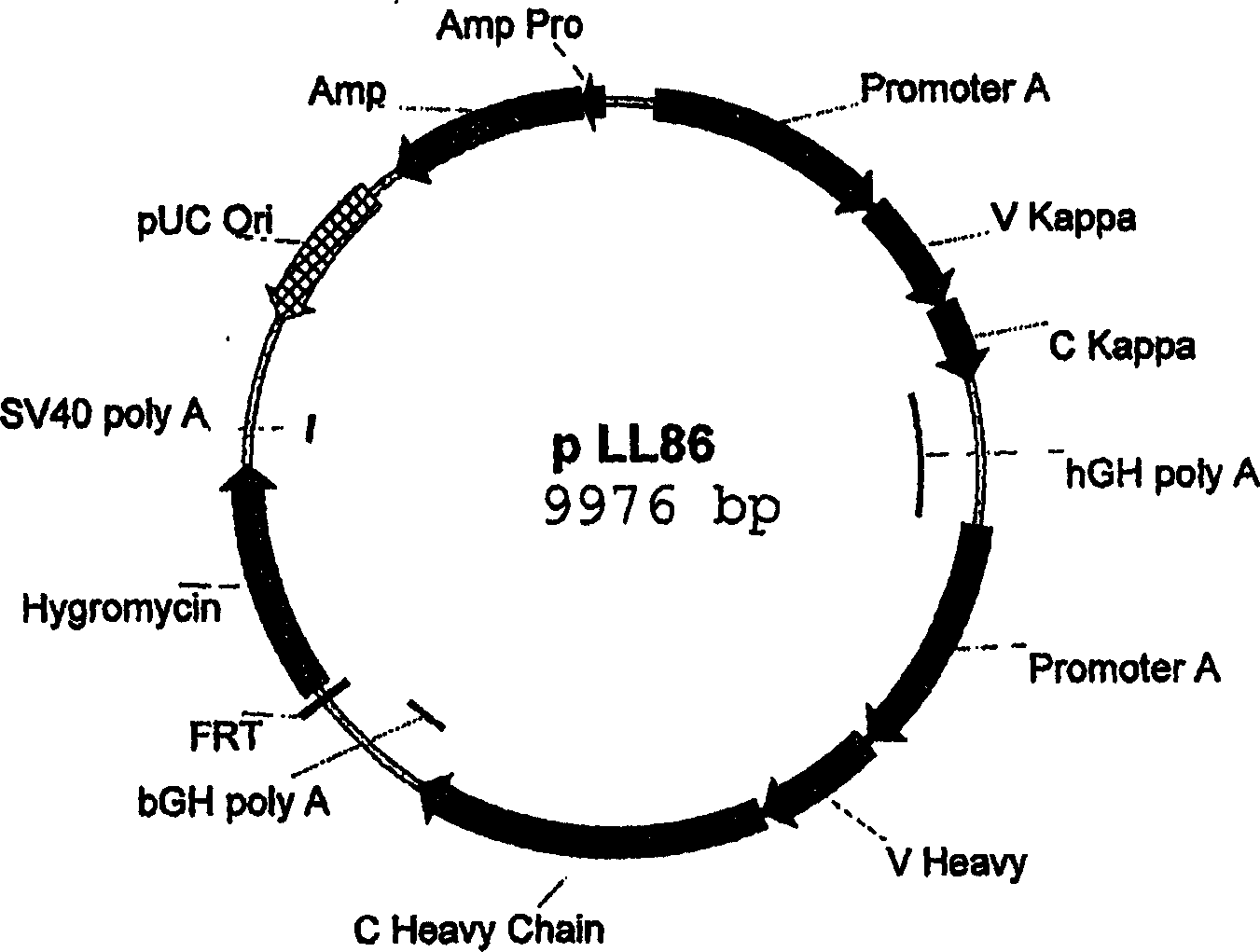
[0222] Design and preparation of expression vectors for site-specific integration in host cells
[0223] Expression vectors suitable for site-specific integration into hotspot chromosomal regions of host cells can be assembled from the following DNA elements:
[0224] a) the FRT recombination site linked to the hygromycin resistance gene,
[0225] b) pUC replication initiation site,
[0226] c) Ampicillin resistance gene (bla),
[0227] d) the bla promoter allowing expression of the ampicillin (bla) resistance gene,
[0228] e) Genes encoding proteins of interest (GOIs),
[0229] f) a promoter allowing expression of said GOI, and
[0230] g) Optionally, additional transcriptional or translational regulatory elements, such as enhancers or UCOE's, to increase expression at the integration site or IRES.
[0231] In order to better understand the construction of the expression vector, a more detailed description of each element is given:
[0232] a) The FRT recombination sit...
Embodiment 3
[0248] Estimation of polyclonality preservation in developed production systems
[0249] In order to be able to assess the stability and reproducibility of the production system, cell lines expressing polyclonal compositions of different antibodies in known combinations were prepared. The polyclonal antibody composition is called a minisix composition. The nucleic acid sequence library encoding the mini six composition is called mini six library.
[0250] (a) Cloning origin
[0251] The following sequences encoding Fab fragments (genes of interest) reactive with antigens 1-6 were used in this example:
[0252] 1. Ovalbumin (OVA). The Fab coding fragment is selected from a mouse anti-OVA phage display library.
[0253] 2. Alkaline phosphatase (AP). The Fab coding fragment is selected from a mouse anti-AP phage display library.
[0254] 3. beta 2 - Microglobulin (β 2 m). The Fab coding fragment is cloned from hybridoma BBM.1 (gifted by Dr.L.Ф.Pedersen, Denmark), which t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com