Ester combination local anesthetic
A technology of local anesthesia and anesthesia, applied in the direction of anesthesia, drug combination, prosthesis, etc., can solve discomfort, pain and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0095] Example 1: Formulation
[0096] Element
[0097] Element
[0098] Element
[0099] Element
[0100] Element
[0101] Element
[0102] Element
Embodiment 2
[0103] Example 2: Comparison of Local Anesthetics Administered Alone or in Combination
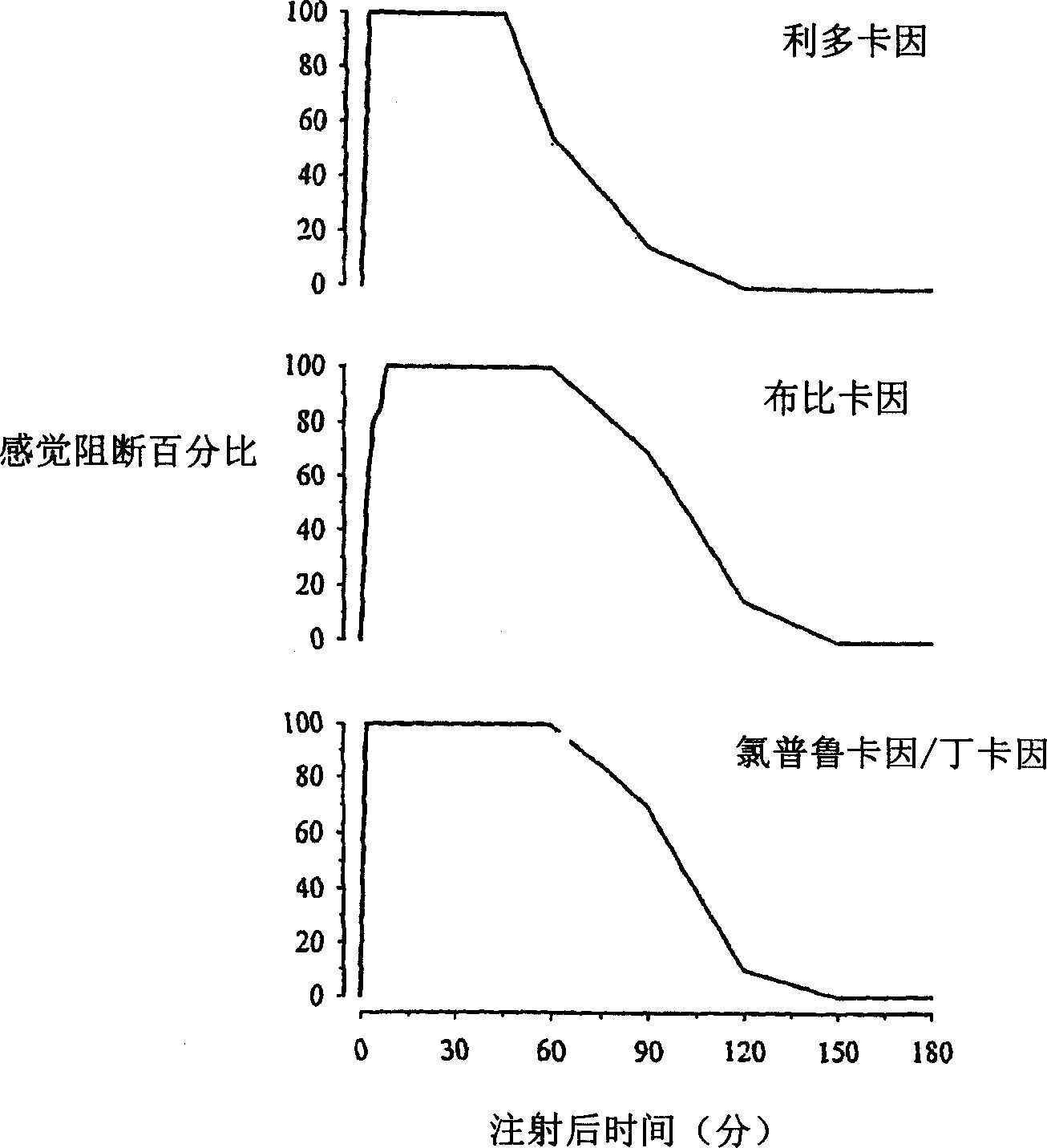
[0104] In a study in rats, the initiation and discontinuation of sciatic nerve blocks by lidocaine, bupivacaine, tetracaine and 2-chloroprocaine were examined. Three different modalities were tested: (1) pain (eg, squeezing and retracting); (2) proprioception (eg, ability to square the paw on a table); and (3) motor intensity (eg, the paw could be placed on a scale apply downward pressure). In each case, the same volume of local anesthetic was tested. The property of interest is withdrawal from pinch pain. Each local anesthetic was tested on 5 rats of approximately the same size and age. The result is as figure 1 shown.
[0105] figure 1 The upper panel shows the time course of sciatic nerve blockade of 2.0%, the strongest concentration of commercially available lidocaine. At this concentration, lidocaine started to block almost immediately (ie 100% at the first time point tested, w...
Embodiment 3
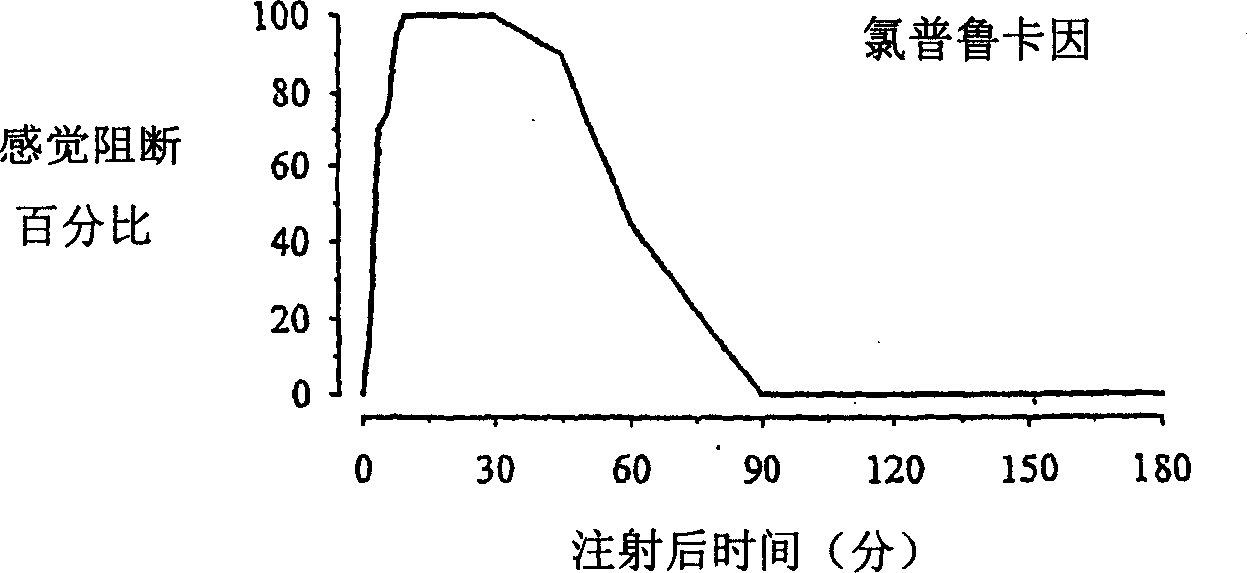
[0108] Example 3: Demonstration of synergistic effect of combination administration of local anesthetics
[0109] figure 2 Shows the onset and duration of sciatic nerve blockade in rats following administration of 2% 2-chloroprocaine. Without administration of tetracaine, the duration of hypoblockia was significantly shorter, with complete sensory blockade lasting only about 30 minutes. In addition, the block onset of 2-chloroprocaine administration was slower than that of tetracaine administration, indicating that tetracaine played a synergistic effect in enhancing the onset of anesthesia with 2-chloroprocaine.
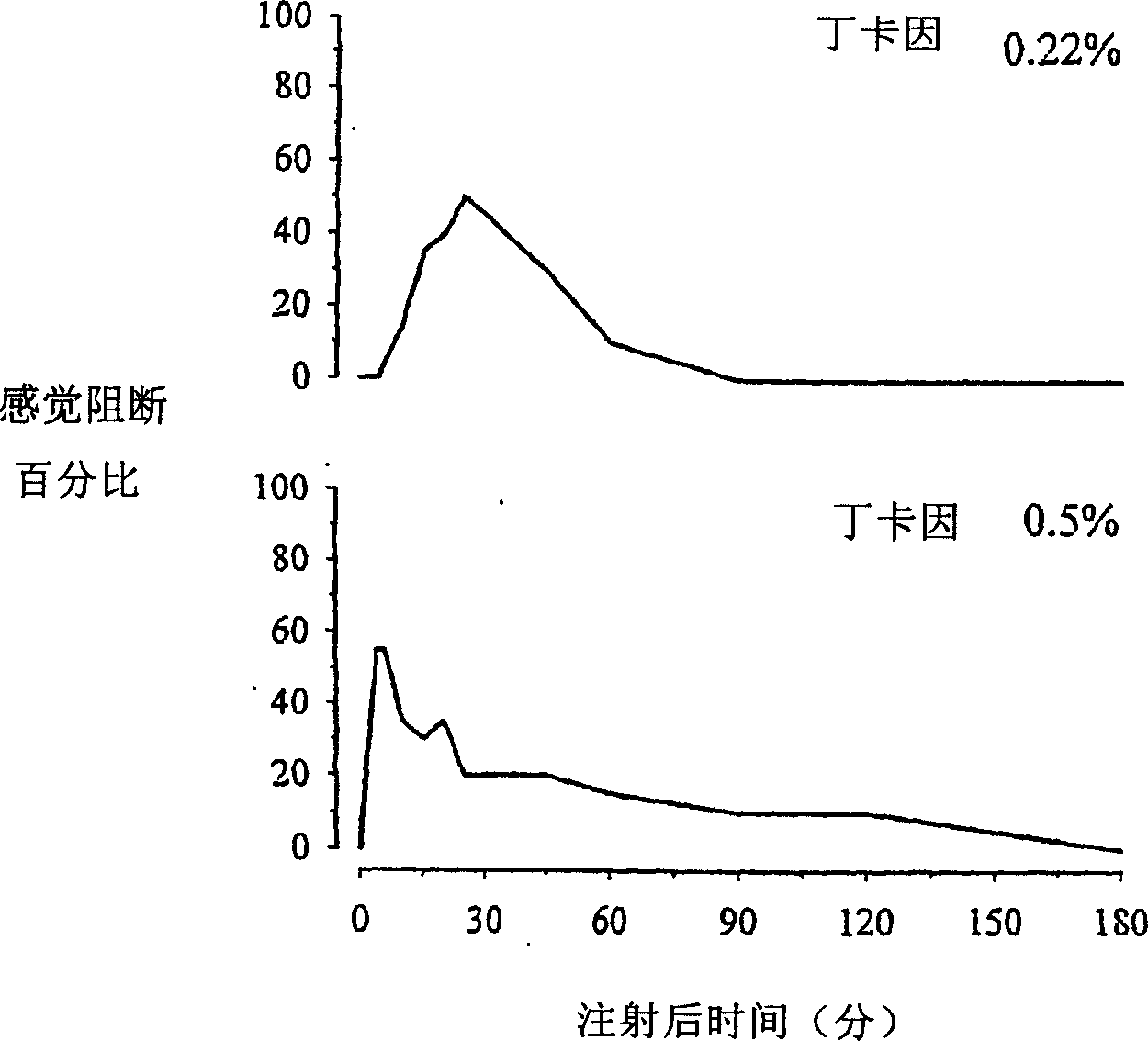
[0110] image 3 Onset and duration of sciatic nerve block following administration of 0.22% tetracaine (upper panel) or 0.5% tetracaine (lower panel) are shown. Surprisingly, neither concentration of tetracaine produced sufficient sensory blockade (eg, less than 60% sensory blockade). Complete sensory blockade was achieved at lower concentrations of tetracaine c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com