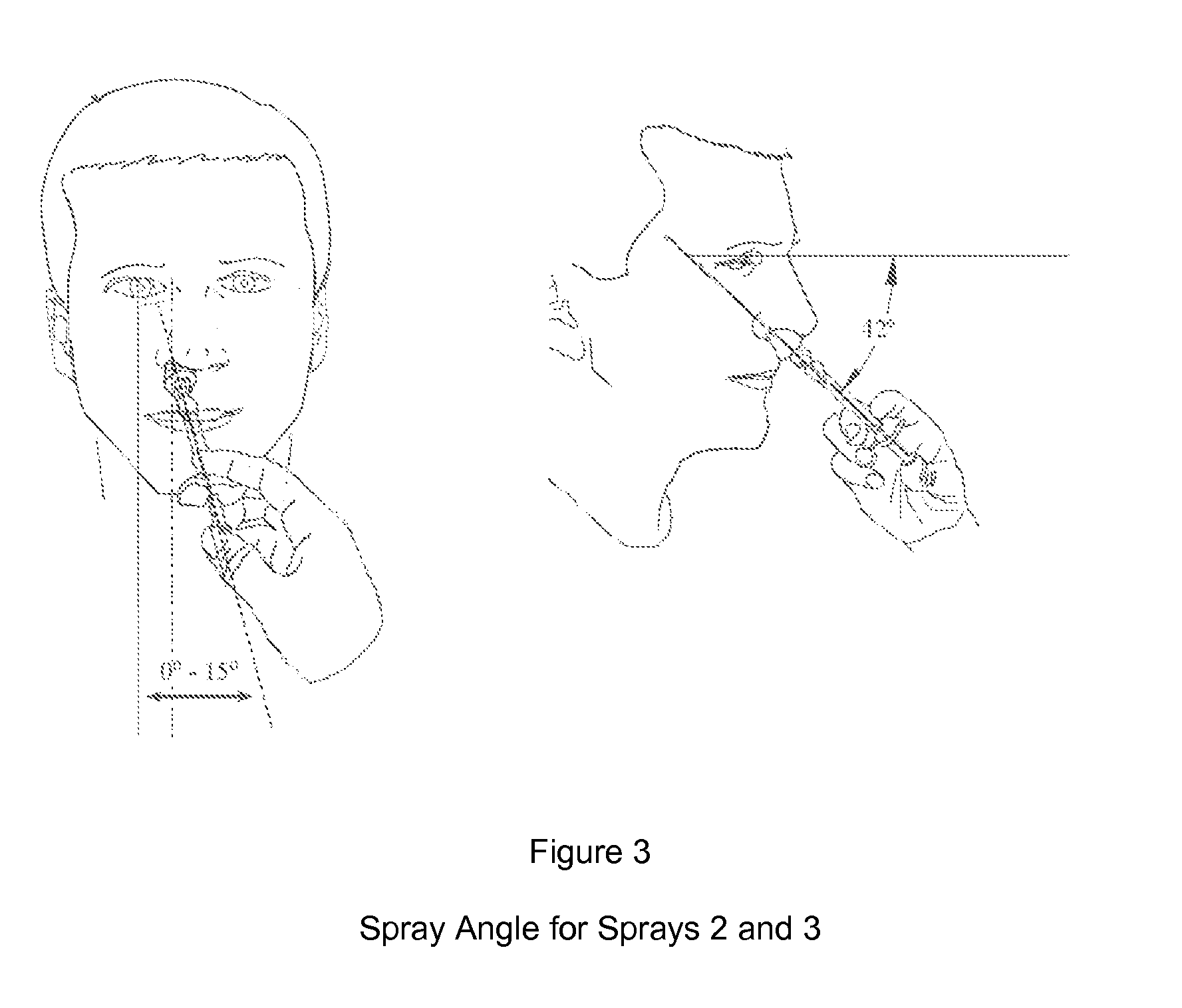
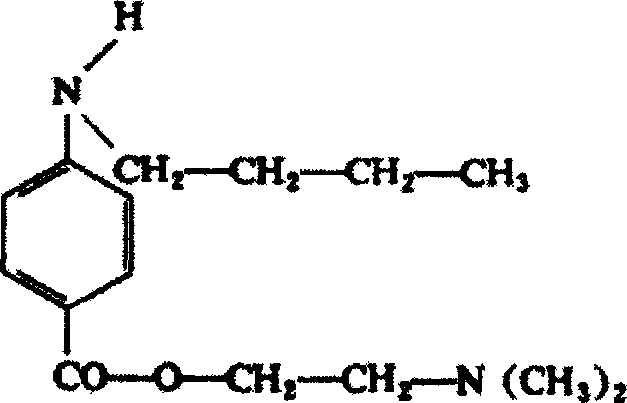
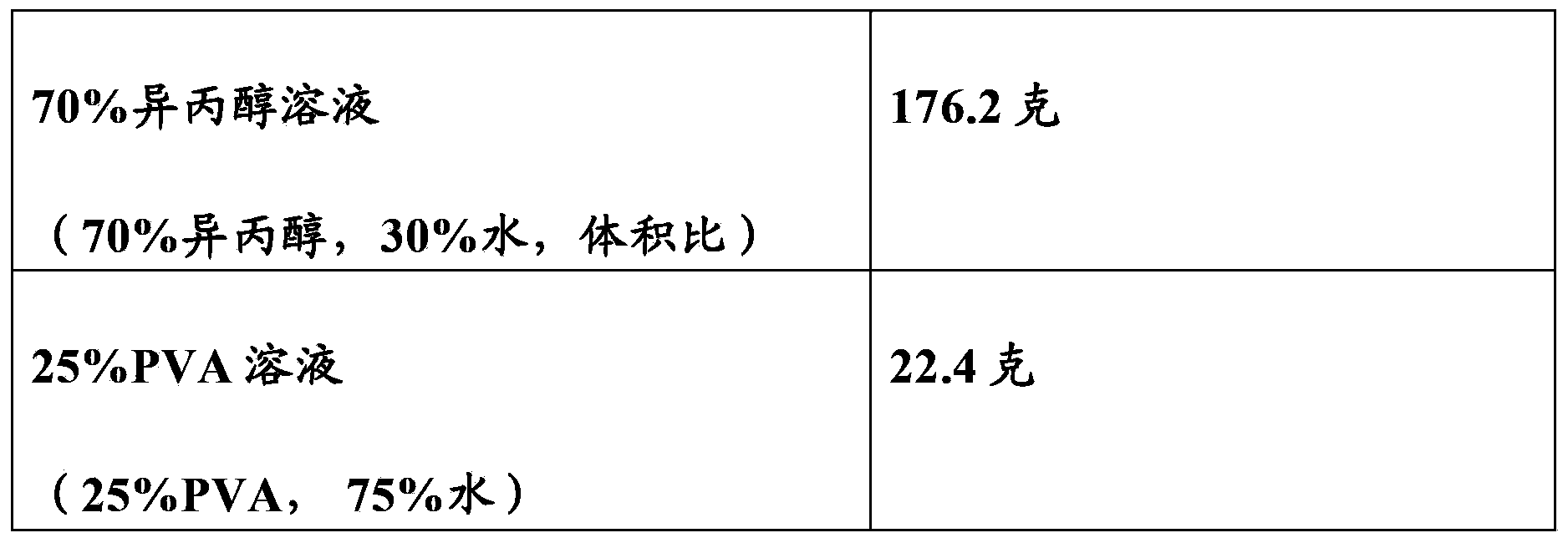
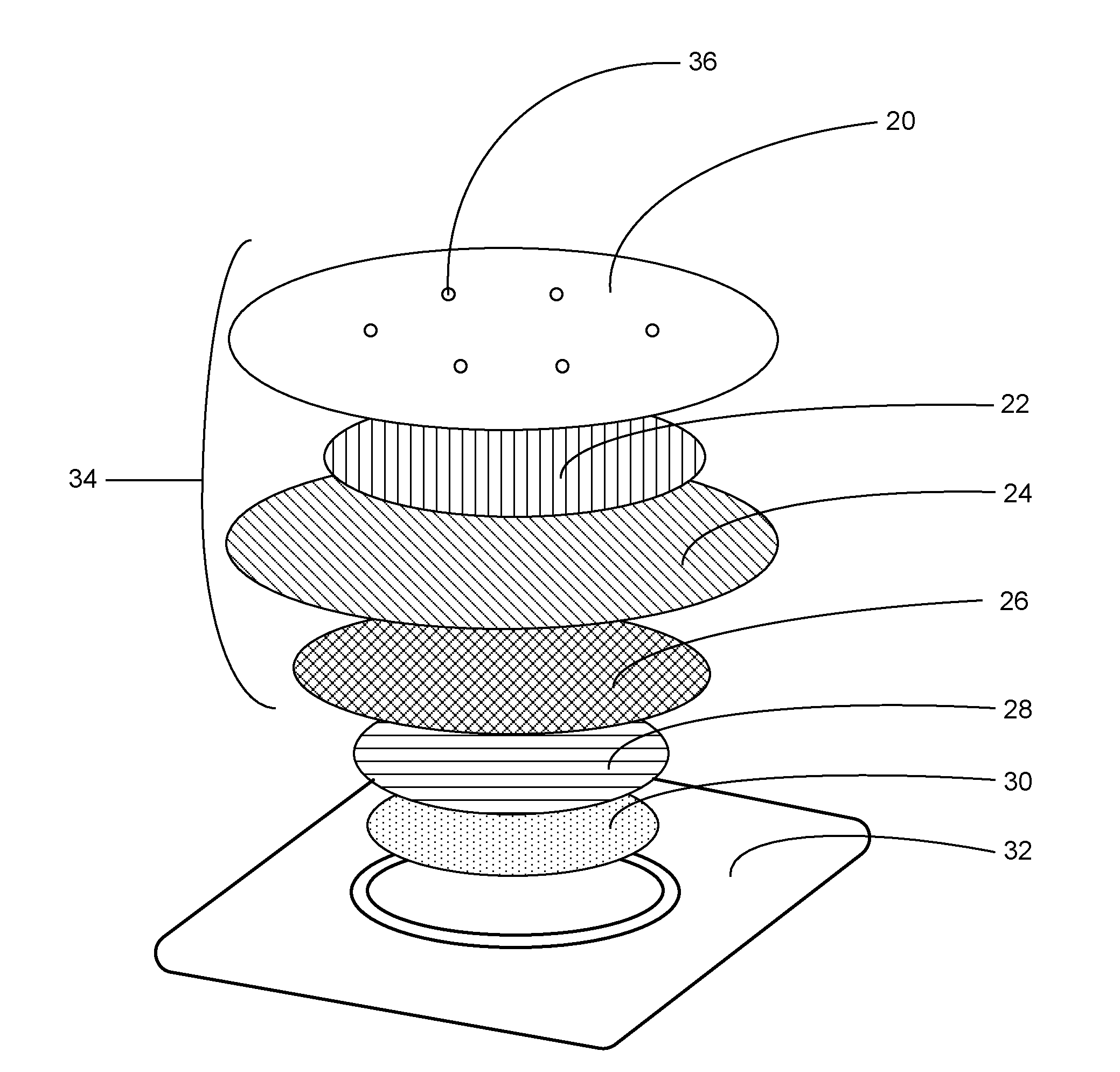
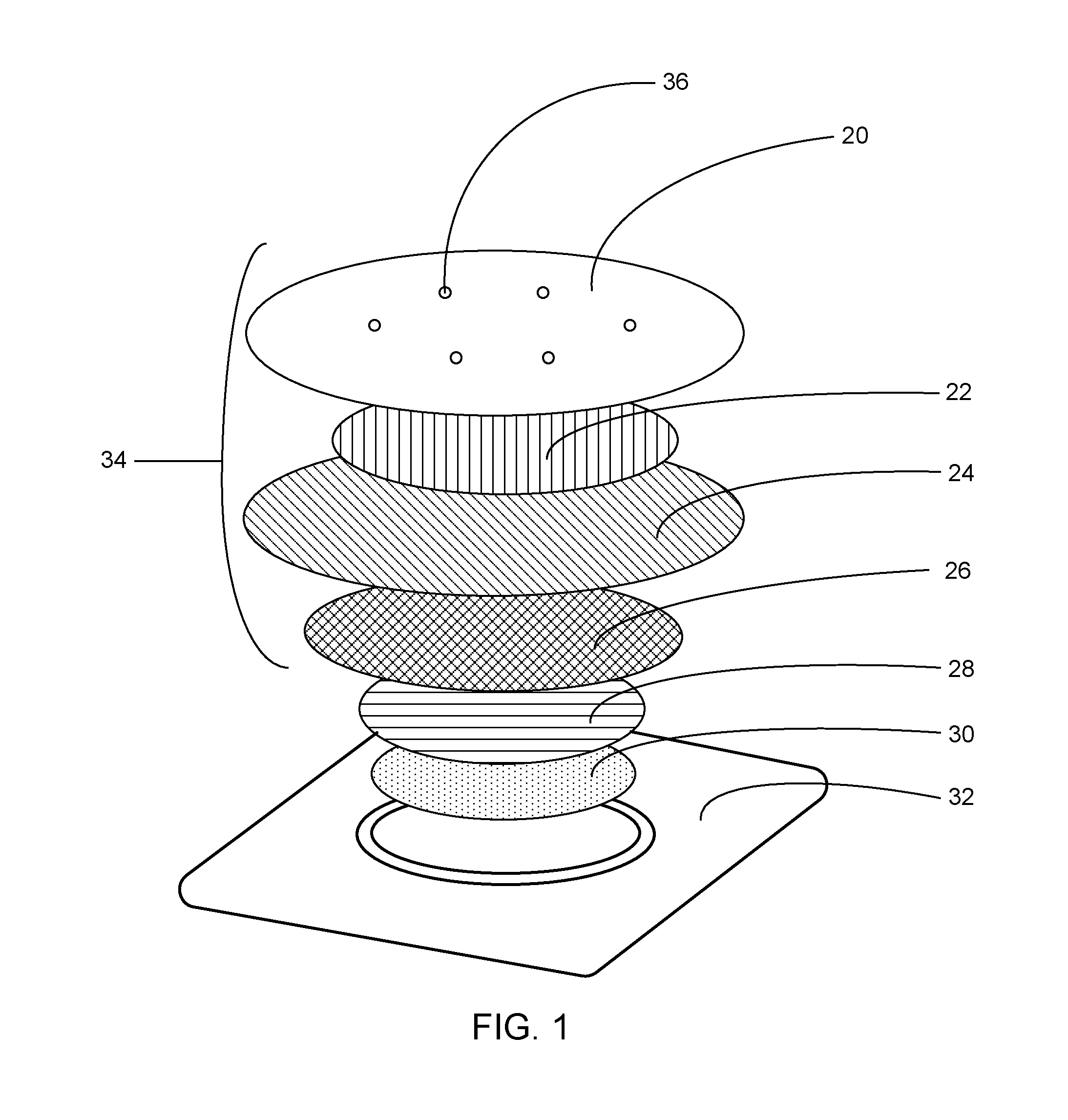
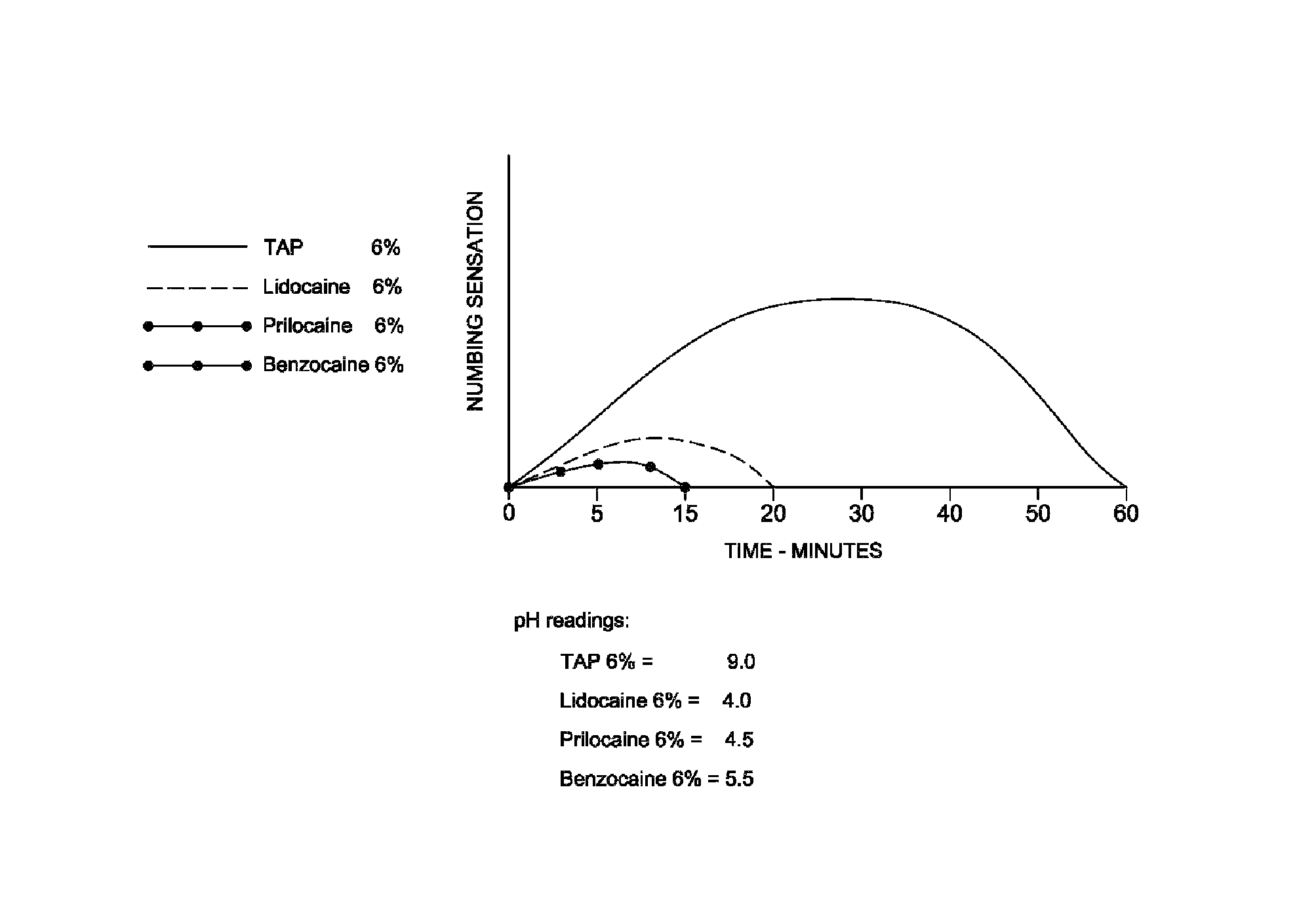
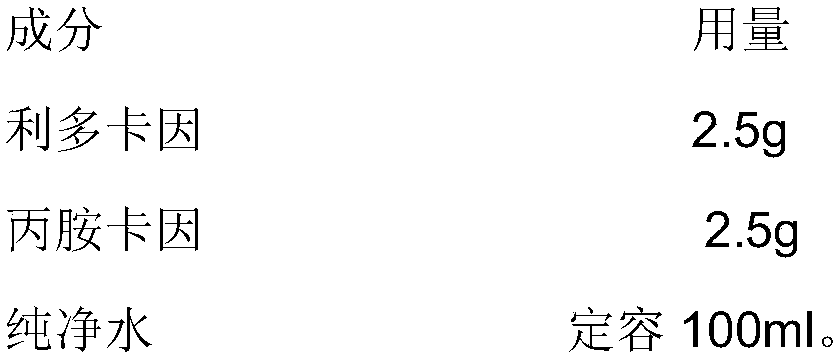
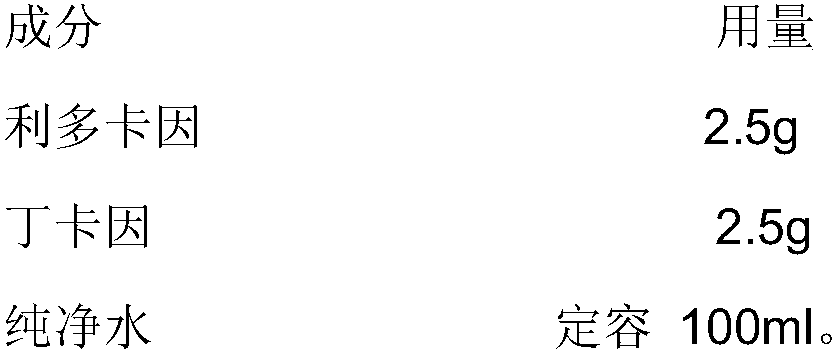
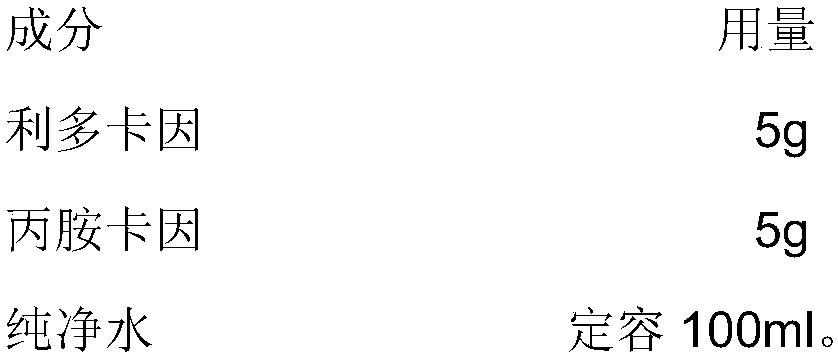
Patents
Literature
56 results about "Tetracaine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tetracaine, also known as amethocaine, is a local anesthetic used to numb the eyes, nose, or throat. It may also be used before starting an intravenous to decrease pain from the procedure. Typically it is applied as a liquid to the area. Onset of effects when used in the eyes is within 30 seconds and last for less than 15 minutes.
Catheter Locking Solution Having Antimicrobial and Anticoagulation Properties
ActiveUS20100318040A1Inhibiting antimicrobial activityPrevent coagulationAntibacterial agentsBiocideAnesthetic AgentAmino esters
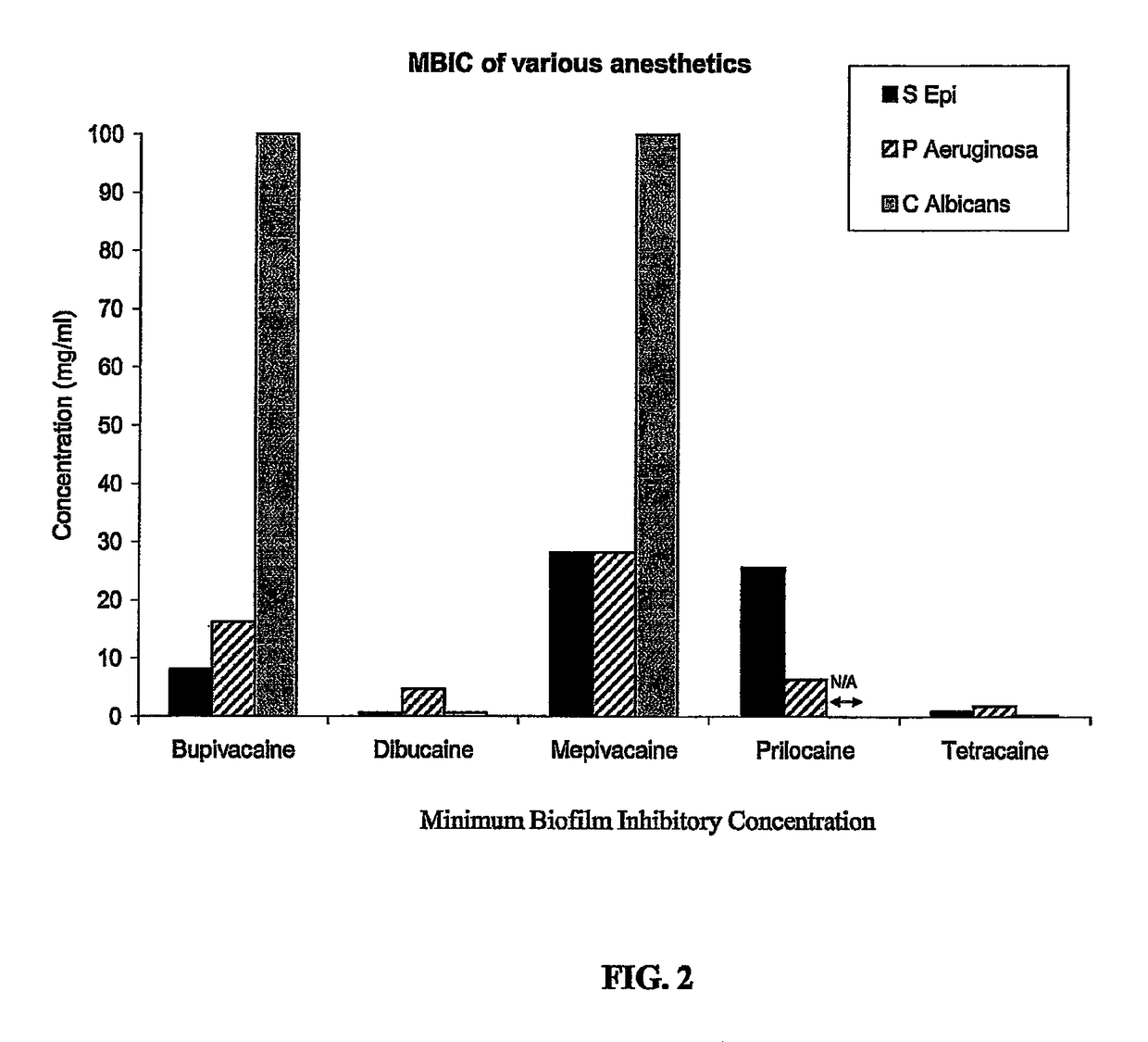
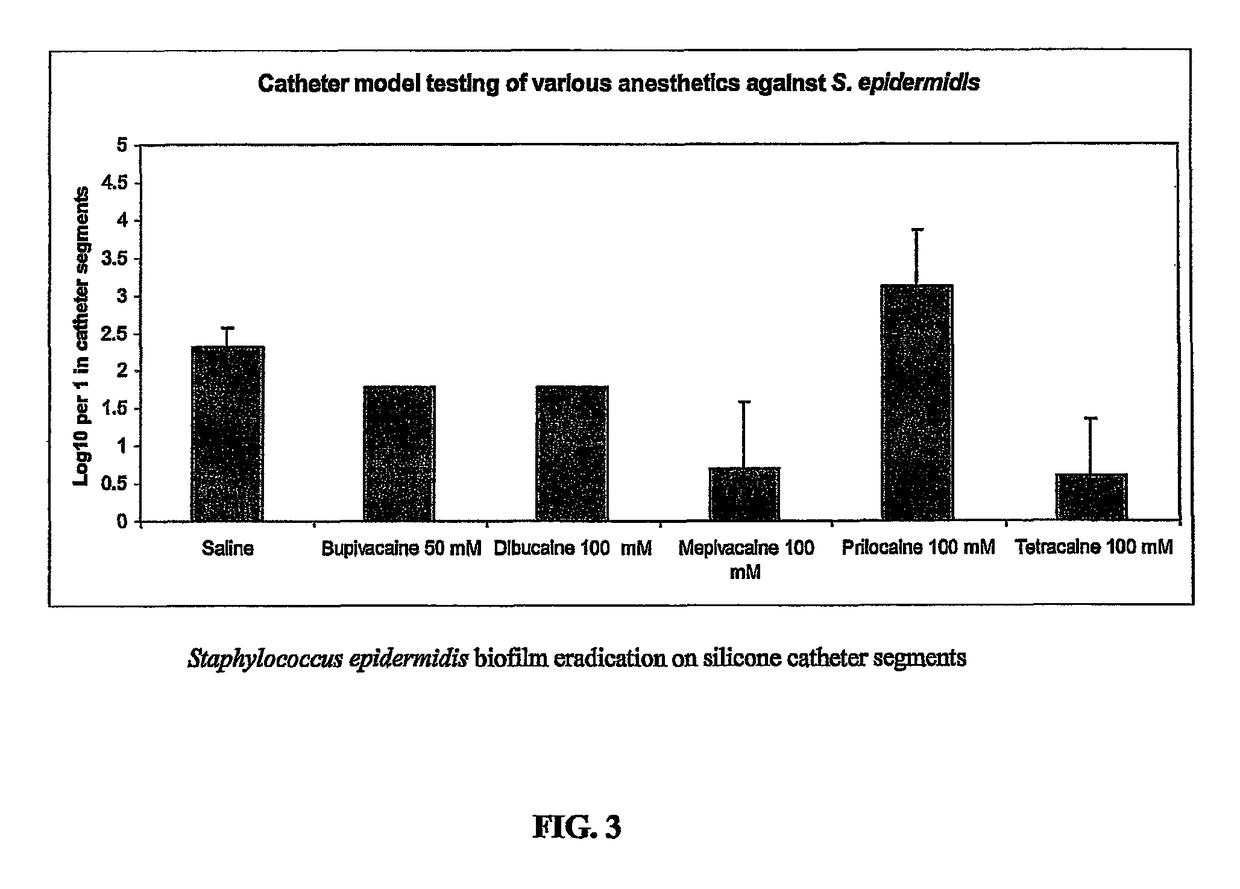
The present invention includes a catheter locking solution having both antimicrobial and anticoagulant properties including a local anesthetic and a viscosifying agent. The local anesthetic of the present invention may be an amino amide; an amino ester; an aminoacylanilide; an aminoalkyl benzoate; an amino carbonate; an N-phenylamidine compound; an N-aminoalkyl amid; an aminoketone, or combinations and mixtures thereof. In a particular embodiment of the present invention, the local anesthetic is tetracaine or dibucaine.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Anesthetic composition for topical administration comprising lidocaine, prilocaine and tetracaine
ActiveUS20070269465A9Rapid onsetImprove skinBiocidePharmaceutical delivery mechanismHigh concentrationHyaluronidase
Owner:FITA FERNANDO BOUFFARD
Non-flammable topical anesthetic liquid aerosols
A topical liquid aerosol formulation for accurate metered dose delivery has been developed which includes a concentrate comprising a local anesthetic in a non-alcohol solvent and a hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) propellant. In the preferred embodiment, the concentration of the non-alcohol solvent in the concentrate is between about 75% and 85% by weight of the formulation. In the most preferred embodiment, the non-alcohol solvent is a water-soluble polyol such as ethylene glycol, propylene glycol, glycerol, diethylene glycol, dipropylene glycol, oligoalkylene glycols, liquid polyalkylene glycols, or combinations thereof. In one embodiment, the concentration of the local anesthetic in the concentrate is between about 15% and 25% by weight. In the preferred embodiment, the hydrofluorocarbon propellant is 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane 1,1,1,2,3,3,3-heptafluoropropane or combinations thereof, in a concentration between about 35% and 65% by weight of the final formulation, more preferably between about 45% and 55% by weight of the final formulation. A particularly preferred formulation includes benzocaine, tetracaine, and butylaminobenzoate, wherein the concentration of benzocaine in the concentrate is 14% by weight, the concentration of tetracaine in the concentrate is 2% by weight, and the concentration of butylaminobenzoate in the concentrate is 2% by weight. It has been found that the formulation is more stable in the substantial absence of oxygen. The formulation is preferably administered using a metered dose device for release of a controlled amount of the local anesthetic.
Owner:PRECISION DERMATOLOGY
Catheter locking solution having antimicrobial and anticoagulation properties
ActiveUS9248093B2Increase the viscosity of the solutionAvoid aspirationAntibacterial agentsBiocideAnesthetic AgentAmino esters
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Gelled Periodontal Anesthetic Preparation
InactiveUS20070232695A1Improves ease of diffusionBiocidePharmaceutical delivery mechanismHigh concentrationButamben
A composition for anesthetizing oral or buccal tissues, especially periodontal pockets, is provided. The composition has a high concentration of topical anesthetic carried in a non-aqueous liquid vehicle containing a gelling agent. The anesthetics are optionally stabilized in the solution by ion-exchange complexation. The composition can anesthetize the gingivae for an extended period, such as 30 minutes or longer. Preferred anesthetics include tetracaine, benzocaine, butamben, and mixtures of these.
Owner:COLLEGIUM PHARMA INC
Microneedle devices and methods
A medical device, comprising: an array of microneedles, and a coating disposed on the microneedles, wherein the coating comprises: a local anesthetic selected from the group consisting of lidocaine, prilocaine, and a combination thereof; and a local anesthetic dose-extending component selected from the group consisting of tetracaine, ropivacaine, bupivacaine, procaine and a combination thereof; wherein the local anesthetic is present in an amount of at least 1 wt-% based upon total weight of solids in the coating, and wherein the local anesthetic and dose-extending component are in a non-eutectic weight ratio; a medical device, comprising an array of dissolvable microneedles, the microneedles comprising: a dissolvable matrix material; at least 1 wt-% of a local anesthetic selected from the group consisting of lidocaine, prilocaine, and a combination thereof; and a local anesthetic dose-extending component selected from the group consisting of tetracaine, ropivacaine, bupivacaine, procaine and a combination thereof; wherein the local anesthetic and dose-extending component are in a non-eutectic weight ratio, and wherein wt-% is based upon total weight of solids in all portions of the dissolvable microneedles which contain the local anesthetic; a method of extending a topically delivered local anesthetic dose in mammalian tissue using the devices; and methods of making the devices are provided.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Method for preparing tetracaine
ActiveCN102731333ALow priceCheap price, effectively reduce production costOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationBenzoic acidHydrogen
The invention relates to a method for preparing tetracaine, which comprises the following steps: dissolving para aminobenzoic acid and n-butanal in absolute methanol, preserving temperature and mixing; then concentrating to remove methanol to obtain 4-(n-butene amino) benzoic acid; adding the 4-(n-butene amino) benzoic acid, water and sodium hydroxide into a high pressure reaction kettle; then adding palladium carbon (10%), and introducing hydrogen to reduce so as to obtain 4-(n-butyl amino) benzoic acid; adding the 4-(n-butyl amino) benzoic acid into another reaction flask, adding toluene and then adding N,N-dimethylethanolamine; refluxing and dividing water; and then purifying and drying to obtain tetracaine. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of low cost of raw materials, high yield and high purity and the like.
Owner:山东诚汇双达药业有限公司
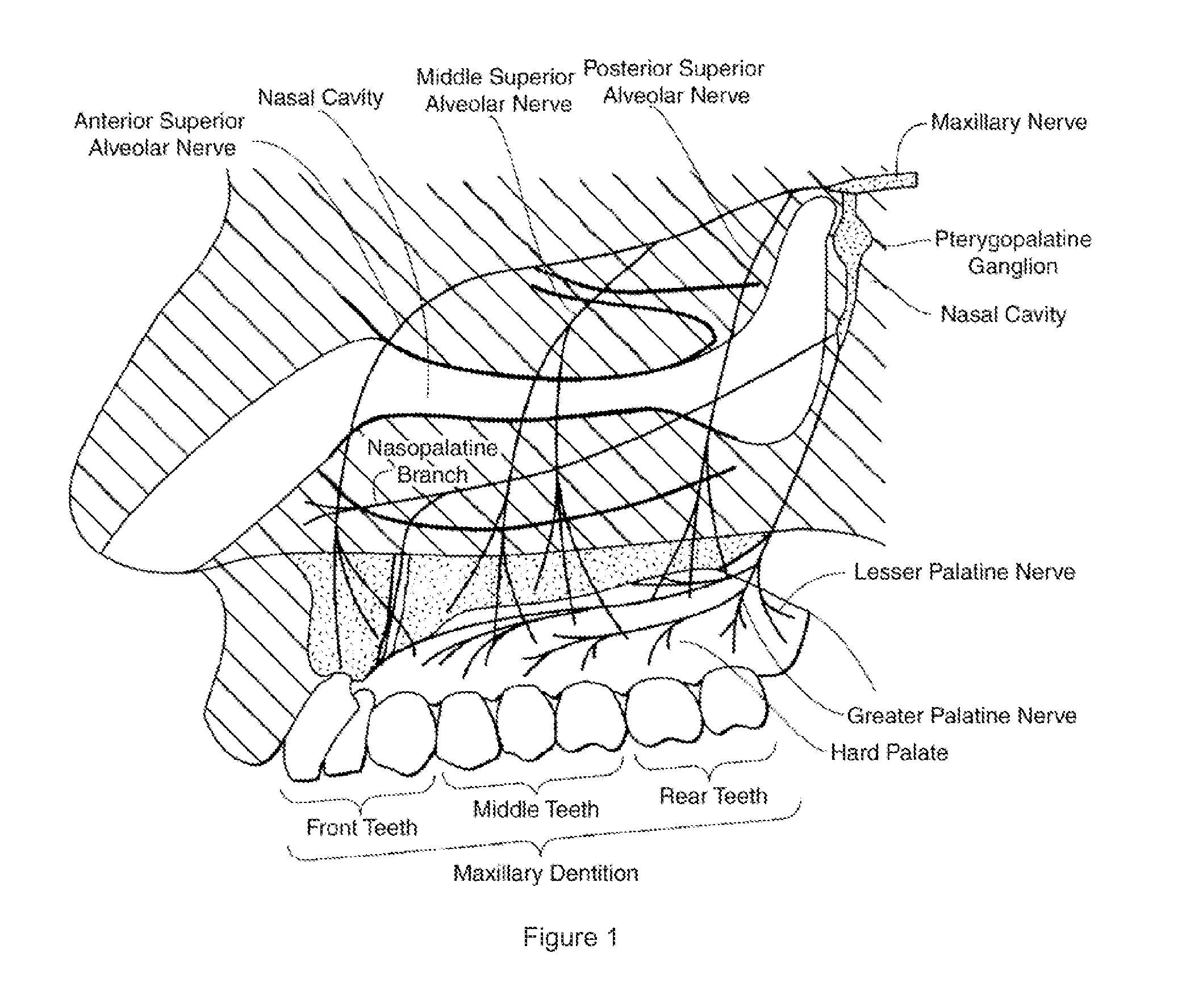
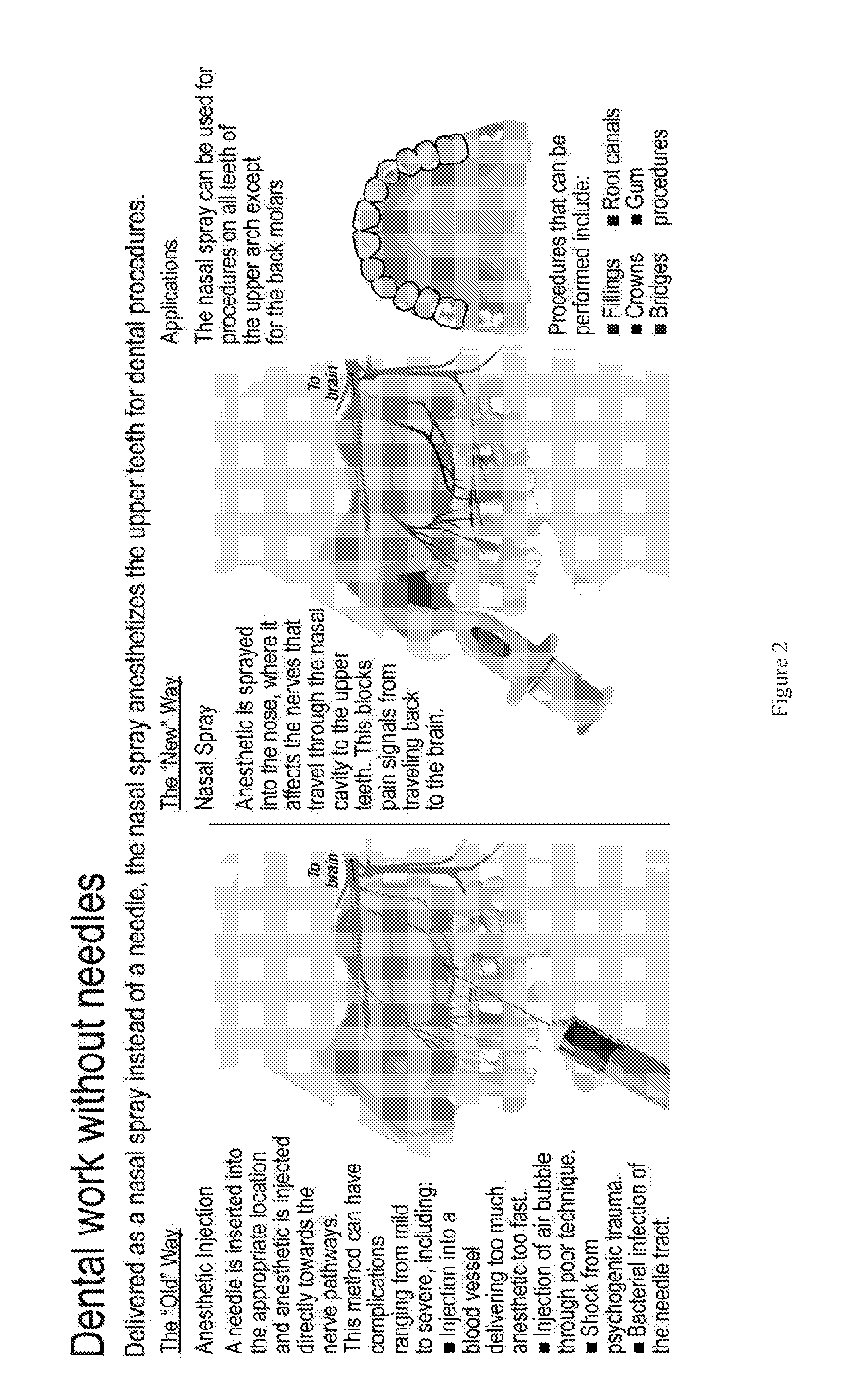
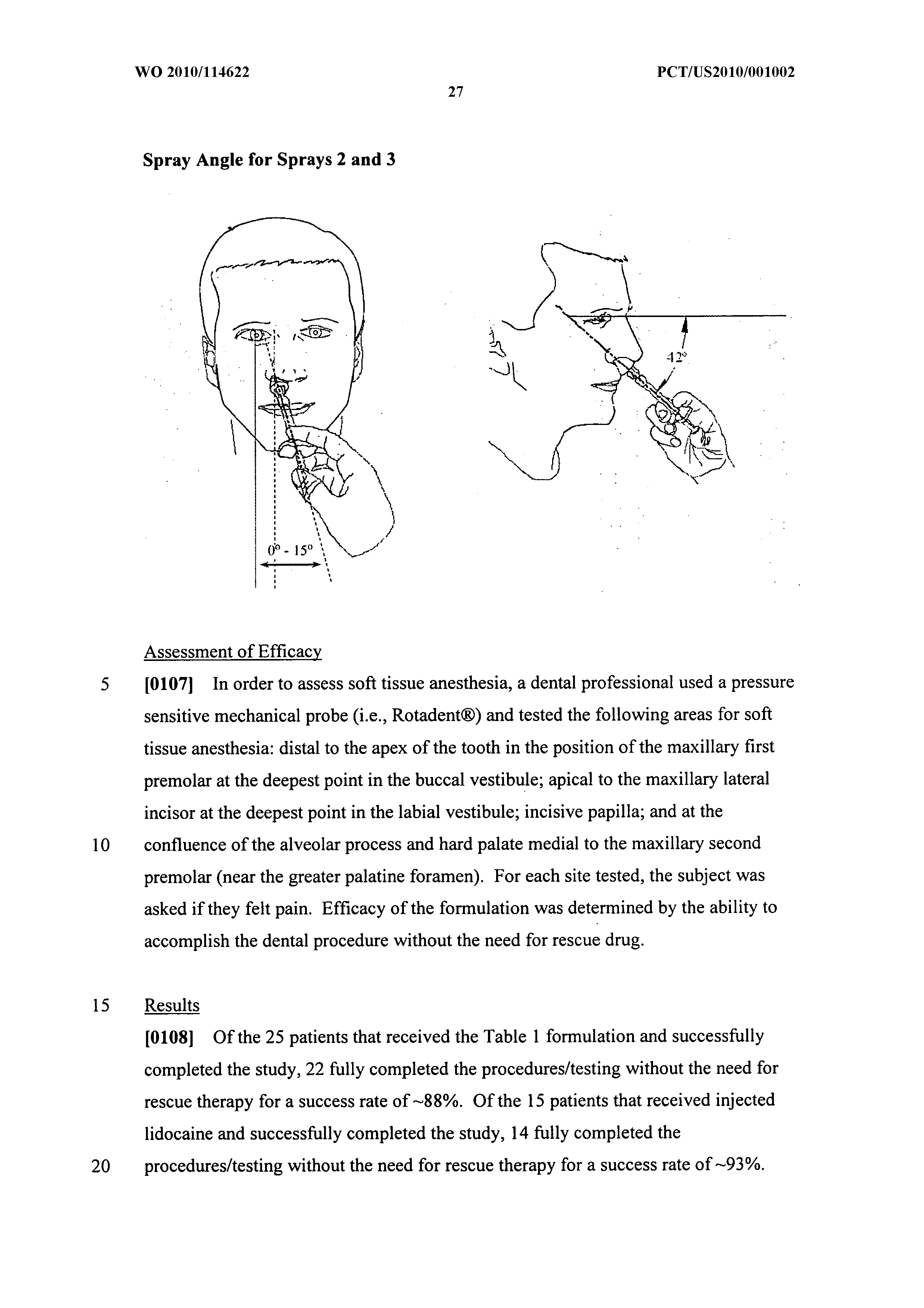
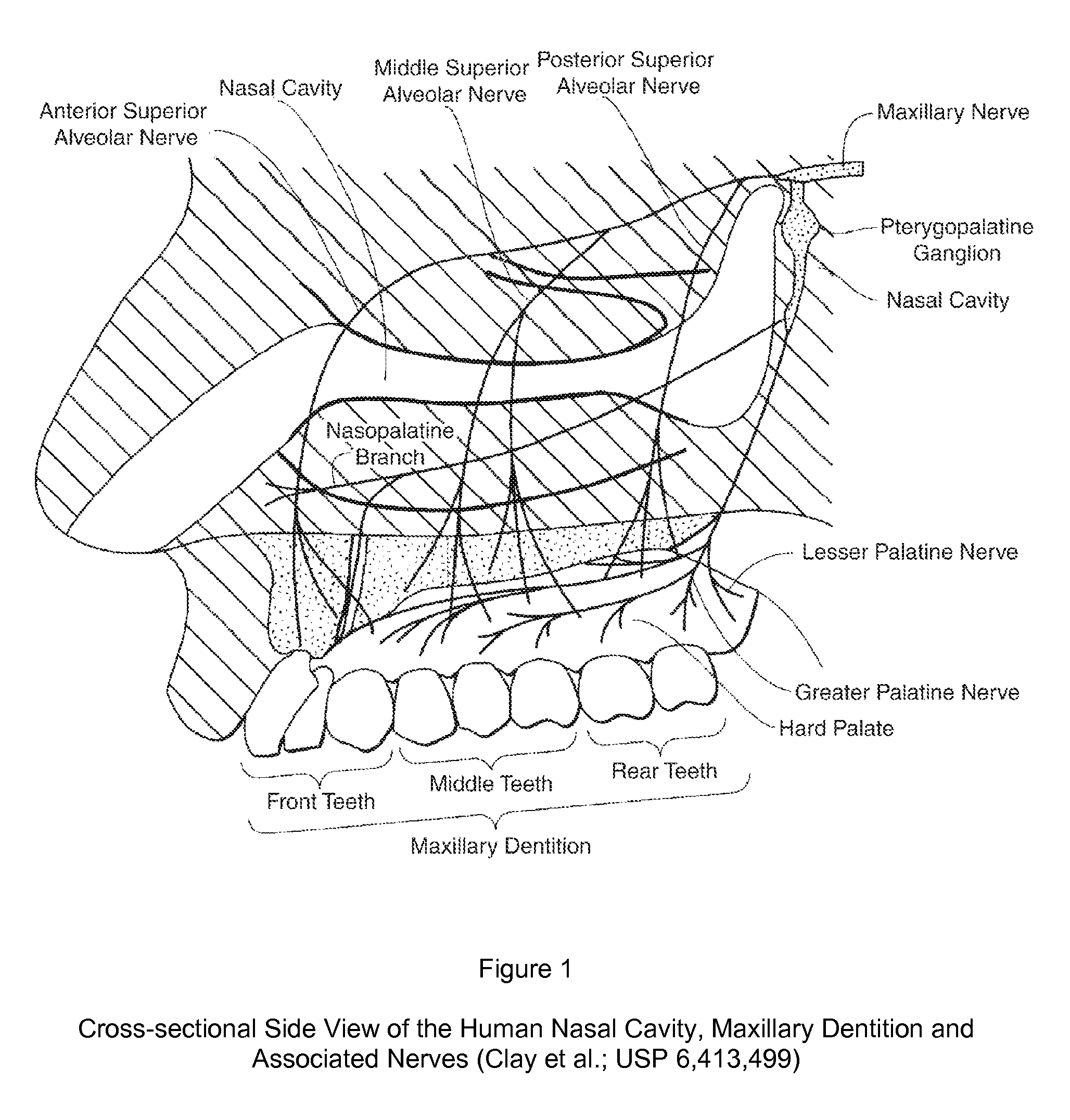
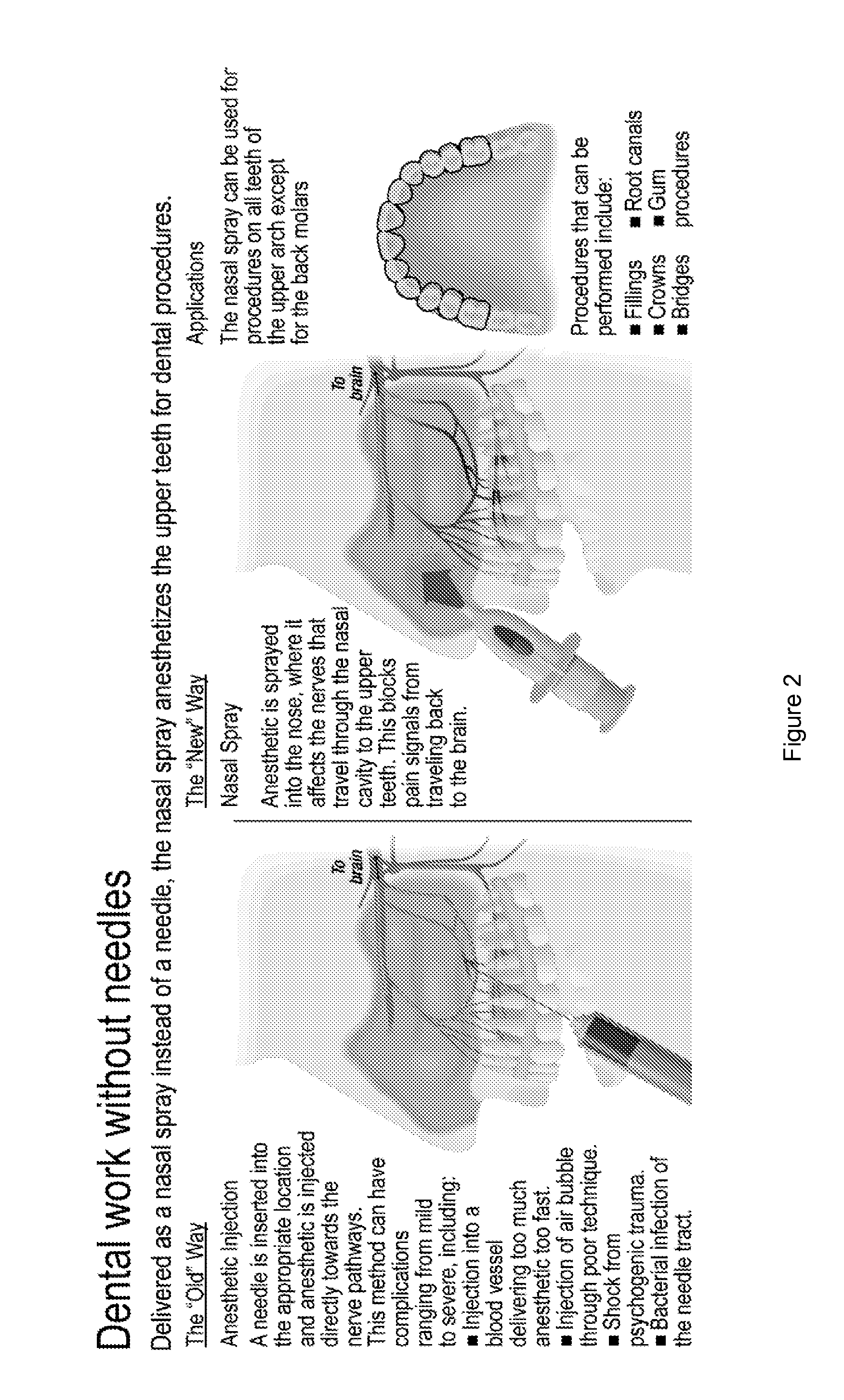
Dental anesthetic comprising tetracaine and a vasoconstrictor for intranasal administration
The present invention relates to tetracaine based anesthetic formulations and methods of use thereof. The invention further relates to topical formulations of tetracaine and methods of topically anesthetizing body tissues. The present invention also relates to tetracaine based dental anesthetic formulations and methods for anesthetizing the maxillary dental arch using these formulations.
Owner:ST RENATUS
Topical anesthetic for dental procedures
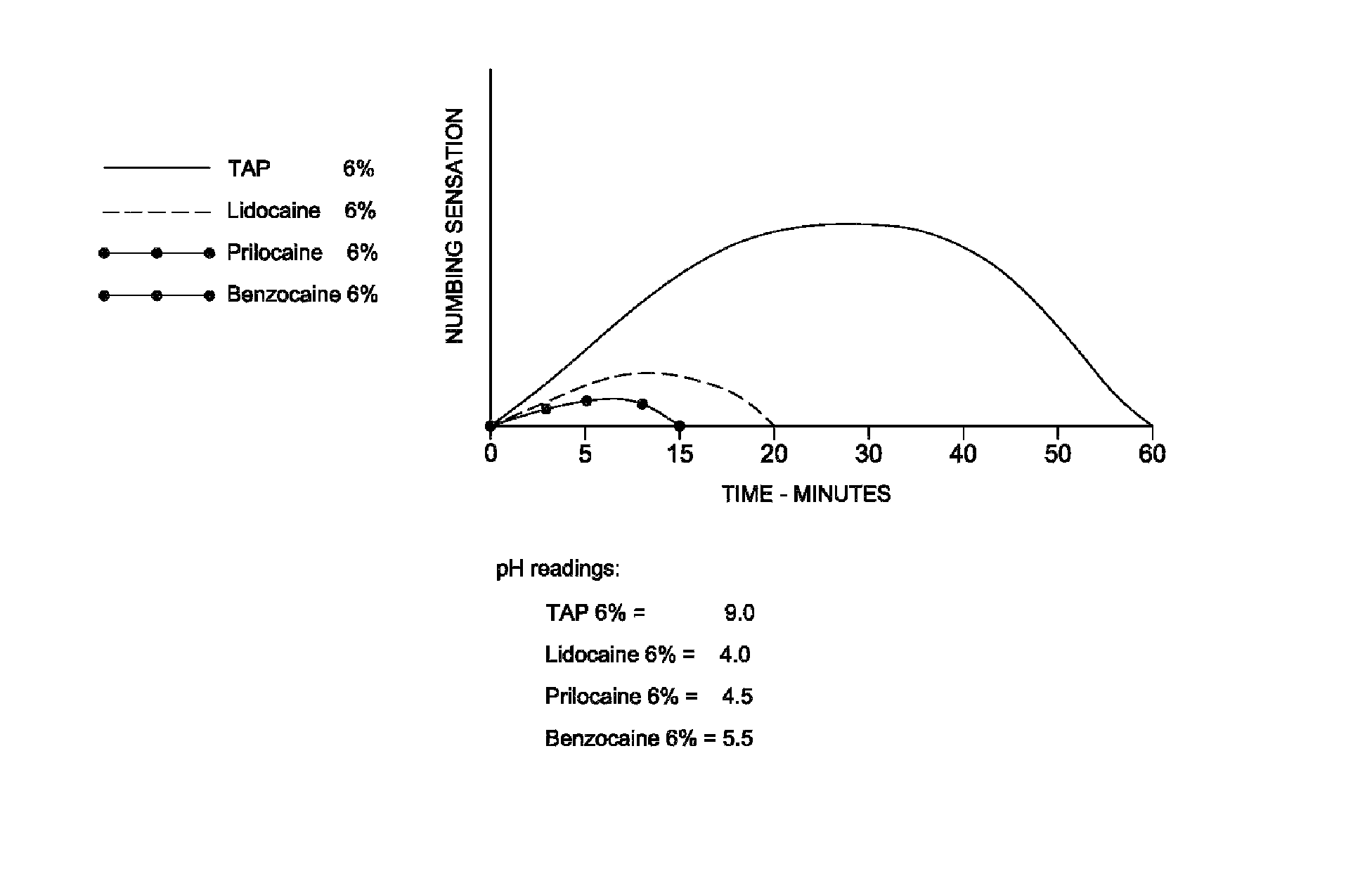
ActiveUS20070071802A1Improves subsequent injection comfortEasy injectionCosmetic preparationsBiocideEthylene HomopolymersTetracaine
A topical anesthetic for dental procedures is provided containing about 3 wt % to 10 wt % tetracaine in a vehicle suitable for administration to the oral mucosa. The vehicle for transporting the tetracaine includes a water soluble mucoadhesive or a combination of mucoadhesives such as a high molecular weight poly(ethylene oxide) homopolymer and a cellulose polymer. The vehicle may additionally include a penetration enhancer such as propylene glycol. The tetracaine is ground into a powder and is suspended in a plasticized hydrocarbon gel which completes the vehicle.
Owner:PHARMADENT
Medicine composition with functions of narcotizing in operation and alleviating pain after operation
InactiveCN101732524AHas an anesthetic effectRelieve painNervous disorderHydroxy compound active ingredientsSurgical operationMenthol
The invention discloses a medicine composition with the functions of narcotizing in an operation and alleviating pain after the operation. The medicine composition comprises tetracaine, bupivacaine, mastic, rhizoma cyperi, girald daphne bark, white peony root and menthol. The medicine composition is added with conventional auxiliary materials in pharmacy according to a conventional process to prepare a clinically acceptable medicament form. The medicine composition is a medicine for injecting and narcotizing in the operation and alleviating pain in a long acting way after the operation and is already applied to clinic successfully throughout the years. The medicine composition can enable the surgical field to be clear, can also avoid pain, sagging distention, frequent defecation and uroschesis caused by the operation, can loosen the anal canal fully and is convenient for the surgical operation.
Owner:刘振起
Sustained-release analgesic drug
The invention relates to a sustained-release analgesic drug, which is microsphere of a topical anesthesia agent. The topical anesthesia agent comprises lidocaine, tetracaine, bupivacaine, oxybuprocaine and procaine. The sustained-release microsphere provided by the invention can be prepared into a sterile microsphere injection, a powder, a spray, a tablet, a capsule, a lozenge, a soft capsule, a pill, a syrup, an external ointment, an emulsion, a bandage, a binder and a gauze. The sustained-release microsphere can be prepared by a multiple double emulsion method, a non-aqueous method, a low temperature spray extraction method or a phase coacervation method. The sustained-release analgesic drug provided by the invention can be used for pain killing of skin wounds with small area, such as cuts, abrasions and burns, and operation wounds.
Owner:伍丽娟
Dental anesthetic comprising tetracaine and a vasoconstrictor for intranasal administration
The present invention relates to tetracaine based anesthetic formulations and methods of use thereof. The invention further relates to topical formulations of tetracaine and methods of topically anesthetizing body tissues. The present invention also relates to tetracaine based dental anesthetic formulations and methods for anesthetizing the maxillary dental arch using these formulations.
Owner:ST RENATUS
Electrooptical eye drops for preventing and treating electric ophthalmia
InactiveCN1528342AEasy to makeEasy to useSenses disorderAlkali/alkaline-earth metal chloride active ingredientsCure rateCurative effect
The present invention relates to an eye drops for preventing and curing electric ophthalmitis with high cure rate and obvious therapeutic effect. Its composition contains dicaine hydrochloride 0.5g, sodium chloride 0.82g, 0.1% adrenaline injection solution 5 ml and distilled water adding to 100ml.
Owner:赵凯
Sheet and liquid combination systems for dermal drug delivery
A dermal drug delivery system is provided which comprises at least two components, for example, a sheet of a solid and flexible material, and a vehicle liquid comprising a solvent and optionally other ingredients. A drug, which can be unstable in said solvent but needs the solvent for being delivered into the skin, can be impregnated in the sheet. Other ingredients, such as agents for fastening the drug on the sheet can also be impregnated in the sheet. These two components may be stored separately and joined either shortly before or at the time of application. To use the system, the vehicle liquid may be applied either on the target skin area or on the sheet, and the sheet may then be applied on the target skin area so that the vehicle liquid is positioned between the sheet and the skin and brought into contact with the ingredients impregnated in the sheet. After the sheet and the vehicle liquid are combined in this way, the ingredients in the sheet and in the vehicle liquid are joined to form a combined formulation that is capable of delivering a drug through the skin at a desired rate. The sheet may have low enough permeability to the solvent or its vapor to control the time it takes for the solvent to evaporate across the sheet. When an appropriate local anesthetic agent, such as a tetracaine, is the drug, some embodiments of the system can have wide applications in anesthesia and pain control.
Owner:张洁
Heat assisted lidocaine and tetracaine for transdermal analgesia
The present disclosure is drawn to methods for treating various types of pain, including pain associated nerve entrapment, neuroma, headaches, connective tissue, arthritis, injury, and / or overuse. Specifically, the method includes the application of an analgesic system to a skin surface of a subject experiencing the pain and maintaining the analgesic system on the skin surface for an application period of at least 30 minutes. Following the application period the analgesic system can be removed and the subject being treated continues to experience reduction of pain for a period of 2 to 10, or even 4 to 12 hours after removal of the analgesic system. The analgesic system applied to the skin surface can include a heating component and a local anesthetic formulation.
Owner:NUVO RES
Topical anesthetic
ActiveUS8623334B1Improves subsequent injection comfortEasy injectionBiocideCosmetic preparationsEthylene oxideMedicine
A topical anesthetic is provided containing about 3 wt % to 10 wt % tetracaine in a vehicle suitable for administration to the mucosa. The vehicle for transporting the tetracaine includes a water soluble mucoadhesive or a combination of mucoadhesives such as a high molecular weight poly(ethylene oxide) homopolymer and a cellulose polymer. The vehicle also includes propylene glycol. The tetracaine is ground into a powder and is suspended in a plasticized hydrocarbon gel which completes the vehicle.
Owner:PHARMADENT
Pharmaceutical composition, patch, and preparation methods and application of pharmaceutical composition and patch
PendingCN110038130AGuaranteed thicknessGet Continuous Pain ReliefNervous disorderAntipyreticProcaineBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
Owner:张洁
Catheter locking solution having antimicrobial and anticoagulation properties
ActiveUS9744273B2Increase the viscosity of the solutionAvoid aspirationAntibacterial agentsPharmaceutical containersAnesthetic AgentAmino esters
The present invention includes a catheter locking solution having both antimicrobial and anticoagulant properties including a local anesthetic and a viscosifying agent. The local anesthetic of the present invention may be an amino amide; an amino ester; an aminoacylanilide; an aminoalkyl benzoate; an amino carbonate; an N-phenylamidine compound; an N-aminoalkyl amid; an aminoketone, or combinations and mixtures thereof. In a particular embodiment of the present invention, the local anesthetic is tetracaine or dibucaine.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Analgesia dosing device used after tissue adhesion separation operation within uterine-cavity
The invention discloses an analgesia dosing device used after a tissue adhesion separation operation within the uterine-cavity. According to the injection dosing device used for postoperative analgesia, a medicine dipping part of the dosing device contains tetracaine gel, the medicine dipping part is left in the vagina after the operation, medicine can continuously anaesthetize the cervix uterus and pudendal nerves, and thus the effect of postoperative analgesia is achieved. The medicine dipping part can be taken out through a traction rope on the next day, no operative instruments are required, a dosing groove which protrudes inwards is formed in the inner wall of an outer sleeve, and atomization spraying heads are arranged in inward through holes of the dosing groove. In the using process, the needle tubing is inserted into a check valve of a medicine inlet in the outer wall of the outer sleeve for dosing and pressurization, atomized drugs can be evenly sprayed onto the surface of the medicine dipping part through the atomization spraying heads, the medicine can arrive at the inside of a human body after being adsorbed onto the surface of the medicine dipping part and performs slow and long-term release, and therefore the effect of postoperative analgesia is achieved.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Topical anesthetic composition
ActiveUS20170252445A1Pain controlControl itchingOrganic active ingredientsAnaesthesiaBENZYL ALCOHOL/WATERTetracaine
A topical anesthetic composition comprising benzocaine, pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, amide thereof and / or ester thereof; tetracaine and / or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof; ethanol; polyethylene glycol; propylene glycol; water; and benzyl alcohol is provided. Also provided is method for dispensing the above topical anesthetic composition to a desired site such by spraying the topical anesthetic from a pump actuated metered dose spray device. The topical anesthetic composition can also be administered subgingivally with a syringe and applicator tip. A product comprising the above topical anesthetic spray composition contained in a pump actuated metered dose spray device.
Owner:CETYLITE IND INC
Topical anesthetic
A topical anesthetic is provided containing about 3 wt % to 10 wt % tetracaine in a vehicle suitable for administration to the skin or mucosa. The vehicle for transporting the tetracaine includes a water soluble mucoadhesive or a combination of mucoadhesives such as a high molecular weight poly(ethylene oxide) homopolymer and a cellulose polymer. The vehicle also includes propylene glycol. The tetracaine is ground into a powder and is suspended in a plasticized hydrocarbon gel which completes the vehicle.
Owner:PAGARI LIFE SCI CORP
Facial mask for surface surgical anesthesia
InactiveCN108272772AGood anesthesiaRealize non-invasive drug deliveryHydroxy compound active ingredientsAnaestheticsChamomile extractToxic reaction
The invention discloses a facial mask for surface surgical anesthesia. A main body material of the facial mask is facial mask paper or facial mask fabric, wherein the main body material is soaked withChinese herbal medicine extract and local anesthetics; and anesthetic components consist of frankincense extract, myrrh extract, Sichuan pepper extract, chamomile extract, sweet-scented osmanthus extract, licorice root extract, borneol, mint, lidocaine and tetracaine. The facial mask for the surface surgical anesthesia combines the traditional Chinese medicines and the western medicines, the amounts of the lidocaine and the tetracaine as well as toxic reaction produced thereby can be apparently reduced, and the facial mask also has a sterilizing effect, an inflammation eliminating effect anda swelling diminishing effect; and in addition, the facial mask can realize the local skin anesthesia in a short time, and has the characteristics of rapidness in effectiveness, strong and lasting action, high permeation force, less unfavorable reaction and the like.
Owner:江苏朗沁科技有限公司
Microneedle devices and methods
The present invention provides a medical device, which comprises: a microneedle array, and a coating disposed on the microneedles, wherein the coating comprises: a local anesthetic selected from lidocaine, Prilocaine and combinations thereof; and local anesthetic dose sustained-release components selected from tetracaine, ropivacaine, bupivacaine, procaine and combinations thereof; wherein based on the solids in the coating The total weight of the local anesthetic is present in an amount of at least 1% by weight, and wherein the weight ratio of the local anesthetic and the dose-extending component is a non-eutectic weight ratio; a medical device comprising An array of dissolving microneedles comprising: a dissolvable matrix material; at least 1% by weight of a local anesthetic selected from the group consisting of lidocaine, prilocaine, and combinations thereof; and a local anesthetic dose sustained release component , which is selected from tetracaine, ropivacaine, bupivacaine, procaine, and combinations thereof; wherein the weight ratio of the local anesthetic and the dose-sustaining component is a non-eutectic weight ratio, and wherein the weight % based on the total weight of solids in all portions of the dissolvable microneedles containing the local anesthetic; a method of using the device to provide sustained release of a locally delivered dose of local anesthetic in mammalian tissue; and a method of manufacturing method of the device.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Drug for preventing or treating oral diseases
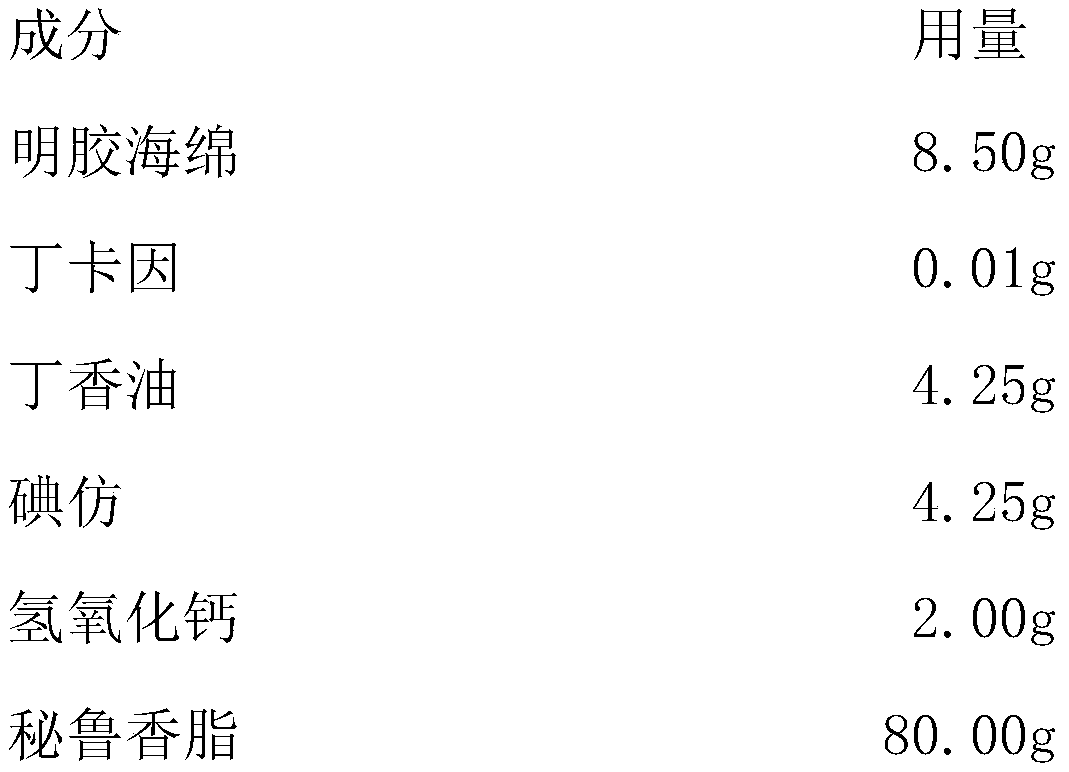
InactiveCN109908205AQuick Pain ReliefMedication convenienceCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsOral diseaseBarrier function
The invention discloses a drug for preventing or treating oral diseases. According to the drug, gelatin sponge, rhizoma cibotii or chitosan serves as a carrier, clove oil, iodoform, calcium hydroxideand Peru balsam serve as active ingredients, and an appropriate amount of local anesthetics are added, wherein the local anesthetics are one of lidocaine, tetracaine and loxoprofen. The drug has various pharmacological effects such as anti-inflammation, pain relief, disinfection, antisepsis, hemostasis, promotion of tissue regeneration, prevention of secondary infections, and promotion of periodontal tissue regeneration. Moreover, the drug is convenient to take and easy to remove and has high permeability; the pain of patient's oral lesions can be quickly relieved, external liquid is effectively prevented from entering cavities, the barrier function of the drug can prevent double infections, the temperatures of the lesions are reduced, and dysfunctions such as local swelling and pain of mucous membranes are quickly eliminated, so that the drug is beneficial to repair of the oral mucous membranes.
Owner:陕西军兴生物医药科技有限公司
Heat assisted lidocaine and tetracaine for transdermal analgesia
The present disclosure is drawn to methods for treating various types of pain, including pain associated nerve entrapment, neuroma, headaches, connective tissue, arthritis, injury, and / or overuse. Specifically, the method includes the application of an analgesic system to a skin surface of a subject experiencing the pain and maintaining the analgesic system on the skin surface for an application period of at least 30 minutes. Following the application period the analgesic system can be removed and the subject being treated continues to experience reduction of pain for a period of 2 to 10, or even 4 to 12 hours after removal of the analgesic system. The analgesic system applied to the skin surface can include a heating component and a local anesthetic formulation.
Owner:NUVO RES
Tetracaine ethosome
InactiveCN105902495AThermodynamically stableSmall particle sizeOrganic active ingredientsAnaestheticsBiotechnologyAlcohol
The invention discloses a tetracaine ethosome prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 0.3-5% of tetracaine, 1.0-5.0% of egg yolk lecithin, 30-80% of short chain alcohol and 14-68% of water. The tetracaine ethosome is a novel percutaneous agent carrier, has a novel mostly spherical or nearly spherical multicellular vesicle structure, has the characteristics of more stable thermodynamics, smaller particle diameter, high encapsulation rate up to 82.36%, faster and stronger percutaneous performance, good skin tolerance, lower dosage and the like, reduces the occurrence rate of adverse response, and improves the safety.
Owner:雷泽
A kind of method for preparing tetracaine
ActiveCN105646261BHigh yieldThe synthesis steps are simpleOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationSodium hydroxideHydrochloride
Owner:JINAN CHENGHUI SHUANGDA CHEM
Topical skin care composition
A topical skin care composition for rejuvenation of the skin containing tetracaine, purified water, stearic acid, lauramide diethanolamine, beeswax, propylene glycol, sodium tetraborate, sodium lauryl sulfate, benzyl alcohol, glycerin, diazolidinyl urea, triethanolamine, methyl salicylate, and eucalyptus oil. The topical skin care composition of the invention is useful in the healing of the skin and in particular, after the skin has been exfoliated.
Owner:BRUCE W MILLER REVOCABLE TRUST
External medicine for treating cancer pain and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103933481ARaw materials are easy to getEasy to prepareAmphibian material medical ingredientsAnthropod material medical ingredientsMyrrhPinellia
The invention discloses an external medicine for treating cancer pain and a preparation method thereof. The external medicine for treating cancer pain is composed of the following raw material medicines: 20-50 g of flos rosae rugosae, 20-50 g of clove, 10-30 g of asarum, 20-50 g of raw pinellia ternate, 20-50 g of cinnamon, 5-20 g of scorpion, 10-20 g of borneol, 20-50 g of rhizoma arisaematis, 10-30 g of frankincense, 10-30 g of myrrh, 10-30 g of rheum officinale, 10-30 g of zedoary, 10-30 g of radix angelicae, 10-30 g of ferula asafoetida, 10-30 g of resurrection lily rhizome, 5-10 g of venenum bufonis, 0.1-0.5 g of muskone, 10-30 g of raw lumbricus, 2-5 g of tetracaine ointment and 5-10 g of diclofenac ointment. The flos rosae rugosae analgesic balm is simple in preparation method, effective in external treatment on cancer pain, capable of improving analgesic effect, definite in curative effect, and capable of reducing the usage amounts of bucinnazine and morphine, reducing the adverse reactions of Western medicines such as morphine, and improving the survival quality of patients.
Owner:梁亮
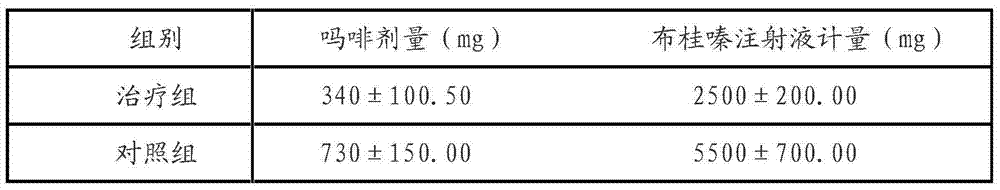
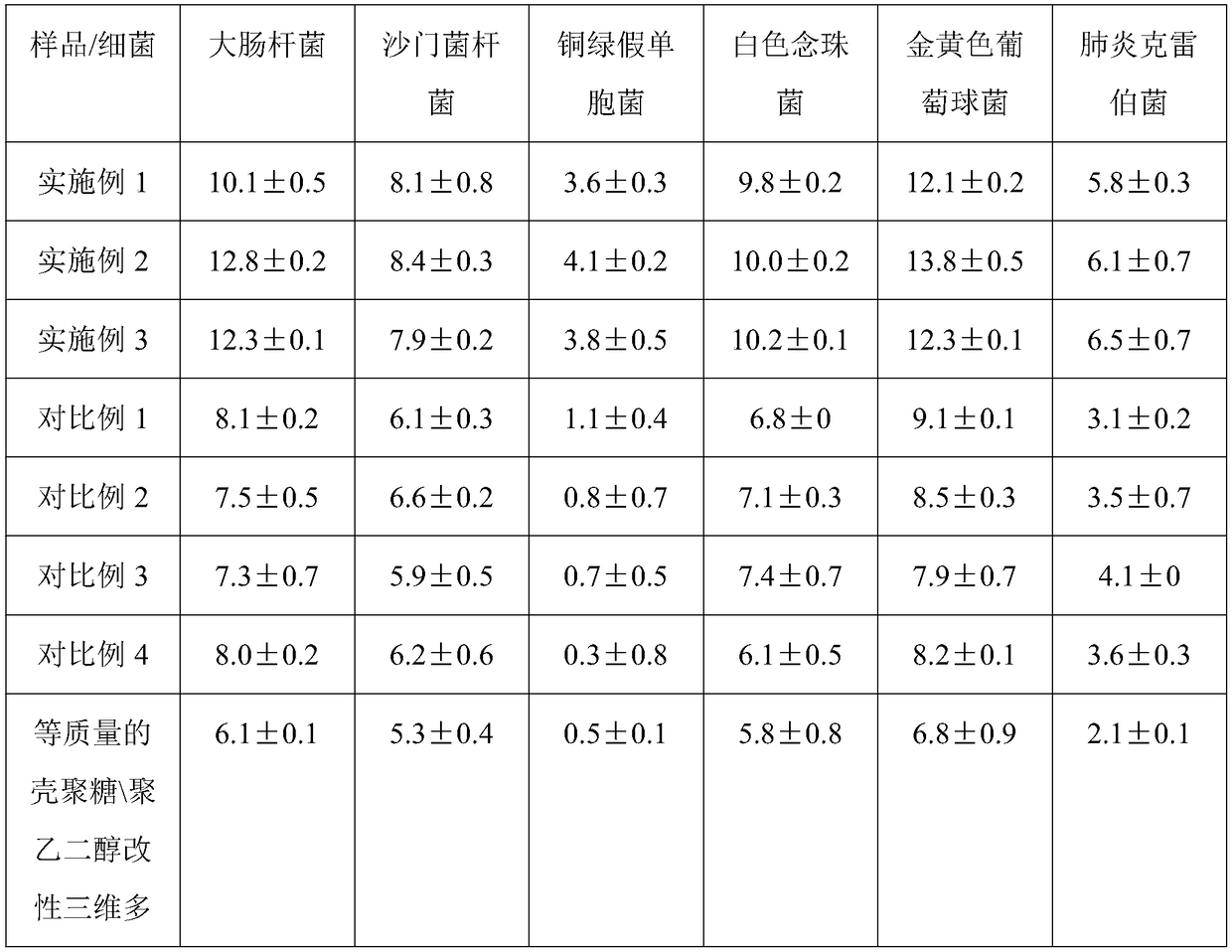
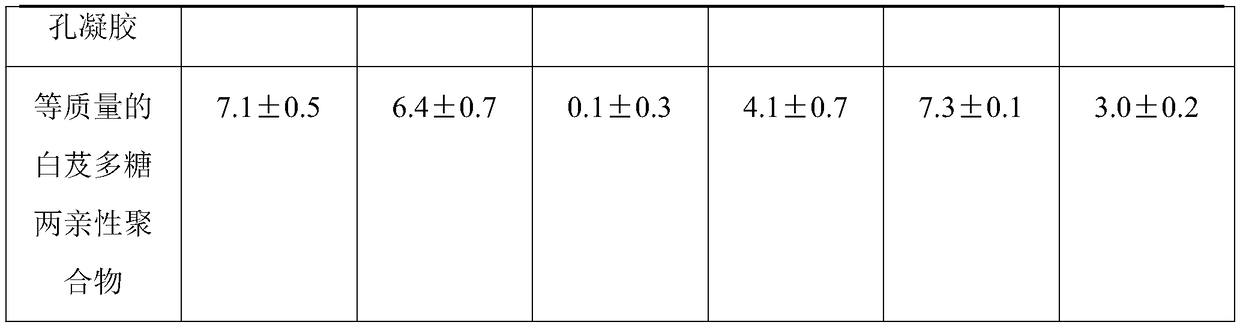
Multifunctional composite sponge with effects of easing pain, stopping bleeding, disinfecting and sterilizing and preparation method of multifunctional composite sponge
InactiveCN109091700AGood for sterilization and hemostasisGood antibacterial and anti-inflammatorySurgical adhesivesCapsule deliveryAnesthetic AgentBletilla striata
The invention discloses a multifunctional composite sponge with effects of easing pain, stopping bleeding, disinfecting and sterilizing. The multifunctional composite sponge is mainly composed of a sponge matrix material and a local anesthetic, wherein the sponge matrix material is chitosan / polyethylene glycol modified three-dimensional porous gel; the local anesthetic is tetracaine hydrochlorideentrapped by a bletilla striata polysaccharide amphiphilic polymer shell. The multifunctional composite sponge is prepared by the following steps: taking the sponge matrix material as a drug-loading substrate, taking the local anesthetic as a loaded drug, and loading according to a weight part ratio of (4-9):(91-96). The sponge has multiple composite functions of stably easing pain and stopping bleeding in a long-acting manner as well as sterilizing and disinfecting, is excellent in biocompatibility, safe and convenient to use and high in comfort, and is a multifunctional composite sponge withhigh medical value and practical value.
Owner:SICHUAN LIZHI JIUCHUANG INTPROP OPERATION CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com