Microneedle devices and methods
A technology of microneedles and microneedle arrays, which is applied in the direction of microneedles, needles, and pharmaceutical formulations, and can solve the problems of expensive system manufacturing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0171] Preparations containing lidocaine and tetracaine
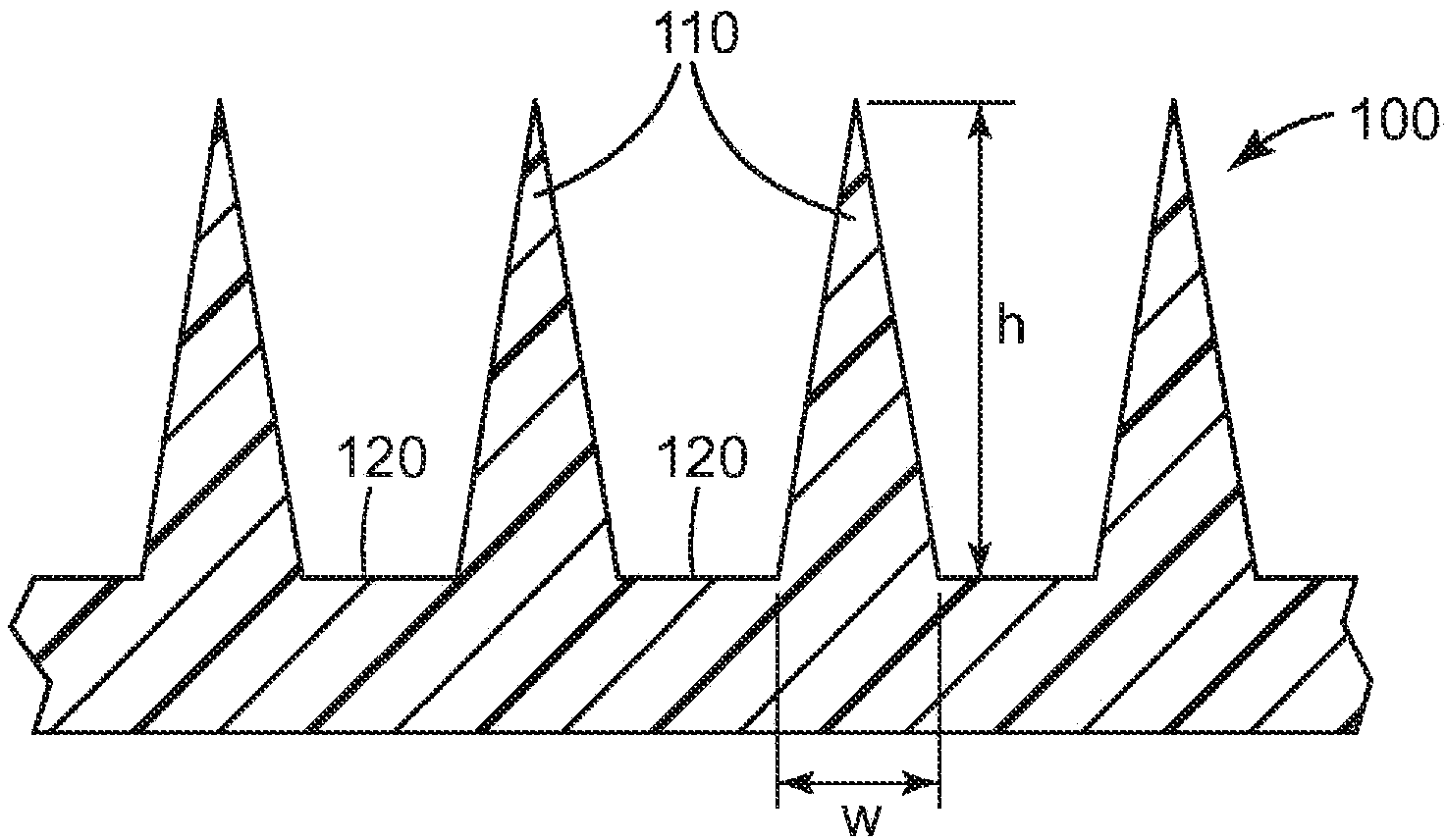
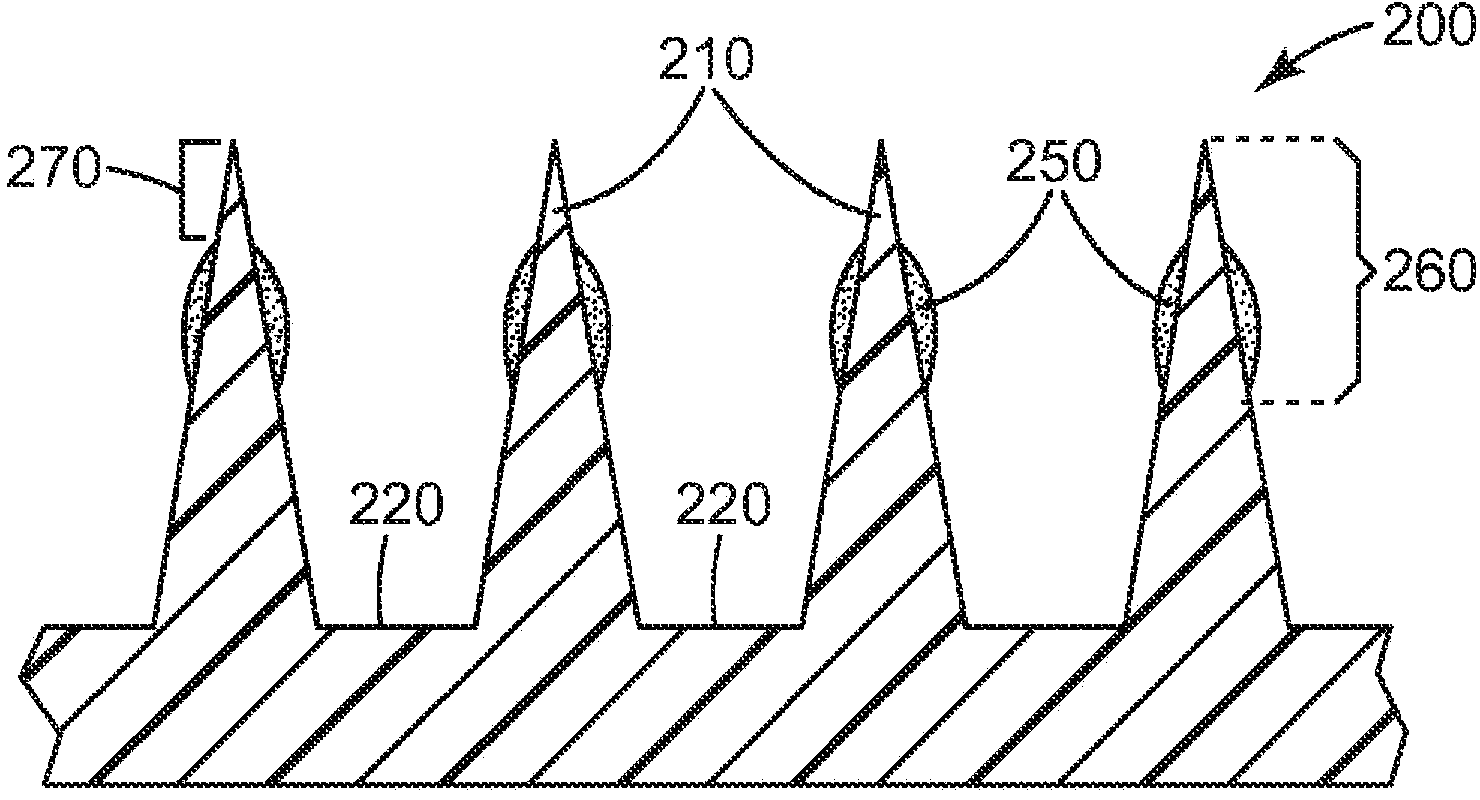
[0172] The microneedle array uses a surface area of about 1.27 cm 2 Class VI medical grade liquid crystal polymer (LCP) ( Injection molded from Ticona Plastics, Auburn Hills, Michigan, USA (3M Company, St. Paul, MN, USA). Each microneedle array is characterized by 316 quadrangular pyramid-shaped microneedles arranged in an octagonal pattern, where the height of the microneedles is nominally 500 microns, the aspect ratio is about 3:1, and the tips between adjacent microneedles reach to The tip distance is nominally 550 microns.
[0173]Using the dip coating method, a mixture of 30% dextran (Pharmacosmos, Holbaek, Denmark), 20% lidocaine hydrochloride (Sigma, St. Louis, Missouri, USA) was used. Company (Sigma, St.Louis, MO)) and tetracaine hydrochloride 10% (Spectrum Chemical & Laboratory Products, New Brunswick, NJ, U.S.A. (Spectrum Chemical & Laboratory Products, New Brunswick, NJ)) & Laboratory Products (Spect...
example 2
[0184] Preparations containing prilocaine and tetracaine
[0185] The microneedle array uses a surface area of about 1.27 cm 2 Class VI medical grade liquid crystal polymer (LCP) ( MT1300 was obtained from Ticona Plastics, Auburn Hills, Michigan, USA and was injection molded (3M Company, St. Paul, MN, USA). Each microneedle array is characterized by 316 quadrangular pyramid-shaped microneedles arranged in an octagonal pattern, where the height of the microneedles is nominally 500 microns, the aspect ratio is about 3:1, and the tips between adjacent microneedles reach to The tip distance is nominally 550 microns.
[0186] Using the dip coating method, a mixture of 30% dextran (Pharmacosmos, Holbaek, Denmark), 12% prilocaine hydrochloride (New Browns, New Jersey, USA) was used. Wake City Spectrum Chemical & Laboratory Products Company (Spectrum Chemical & Laboratory Products, New Brunswick, NJ)) and 8% tetracaine hydrochloride (U.S. New Brunswick, New Jersey Spectrum Che...
example 3
[0197] Preparations containing lidocaine and bupivacaine
[0198] The microneedle array uses a surface area of about 1.27 cm 2 Class VI medical grade liquid crystal polymer (LCP) ( MT1300 was obtained from Ticona Plastics, Auburn Hills, Michigan, USA and was injection molded (3M Company, St. Paul, MN, USA). Each microneedle array is characterized by 316 quadrangular pyramid-shaped microneedles arranged in an octagonal pattern, where the height of the microneedles is nominally 500 microns, the aspect ratio is about 3:1, and the tips between adjacent microneedles reach to The tip distance is nominally 550 microns.
[0199] Using the dip coating method, a mixture of 30% dextran (Pharmacosmos, Holbaek, Denmark), 30% lidocaine hydrochloride (Sigma, St. Louis, Missouri, USA) was used. Company (Sigma, St.Louis, MO)) and 1.7% bupivacaine hydrochloride (MP Biomedicals LLC, Solon, OH) onto the microneedle array. Prior to coating, microneedle arrays were cleaned with 70% isopro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com