Reducing scale factor transmission cost for MPEG-2 AAC using a lattice
A technology of scale factor and audio encoder, which is applied in speech analysis, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of scale factor performance and high bit cost of lowering masking level technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
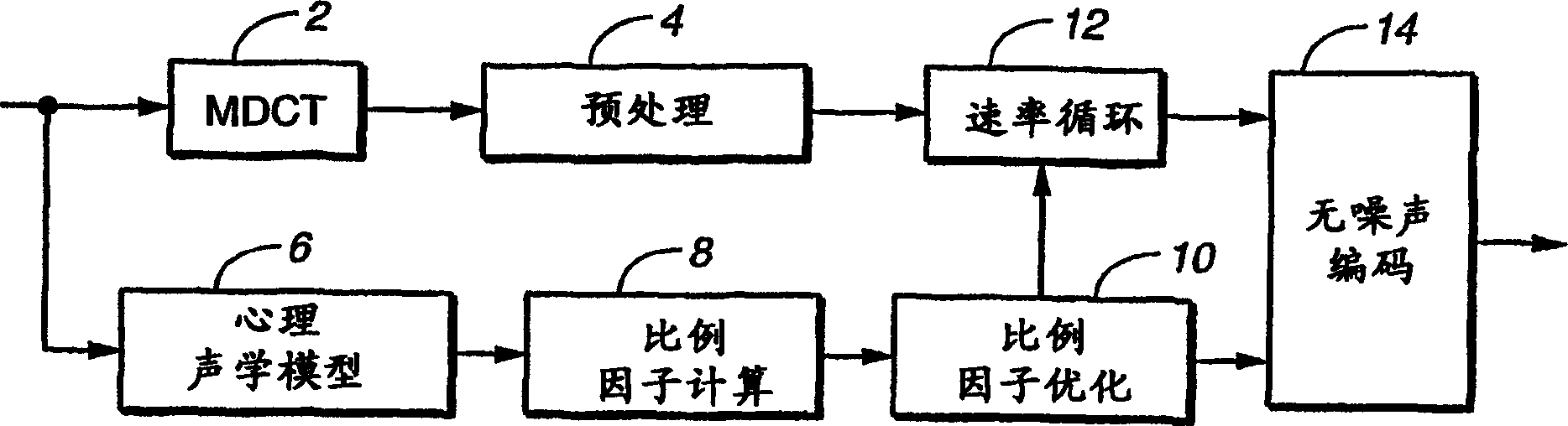
[0022] figure 1 A simple, high-level schematic diagram of the AAC encoding process incorporating dynamic programming scalefactor optimization according to the present invention is shown. The figure shows scalefactor optimization according to the invention combined with direct scalefactor estimation from the above model information. While other scaling factor derivation techniques can be improved using the techniques of the present invention, the present invention is particularly well suited to use of this direct estimation technique.
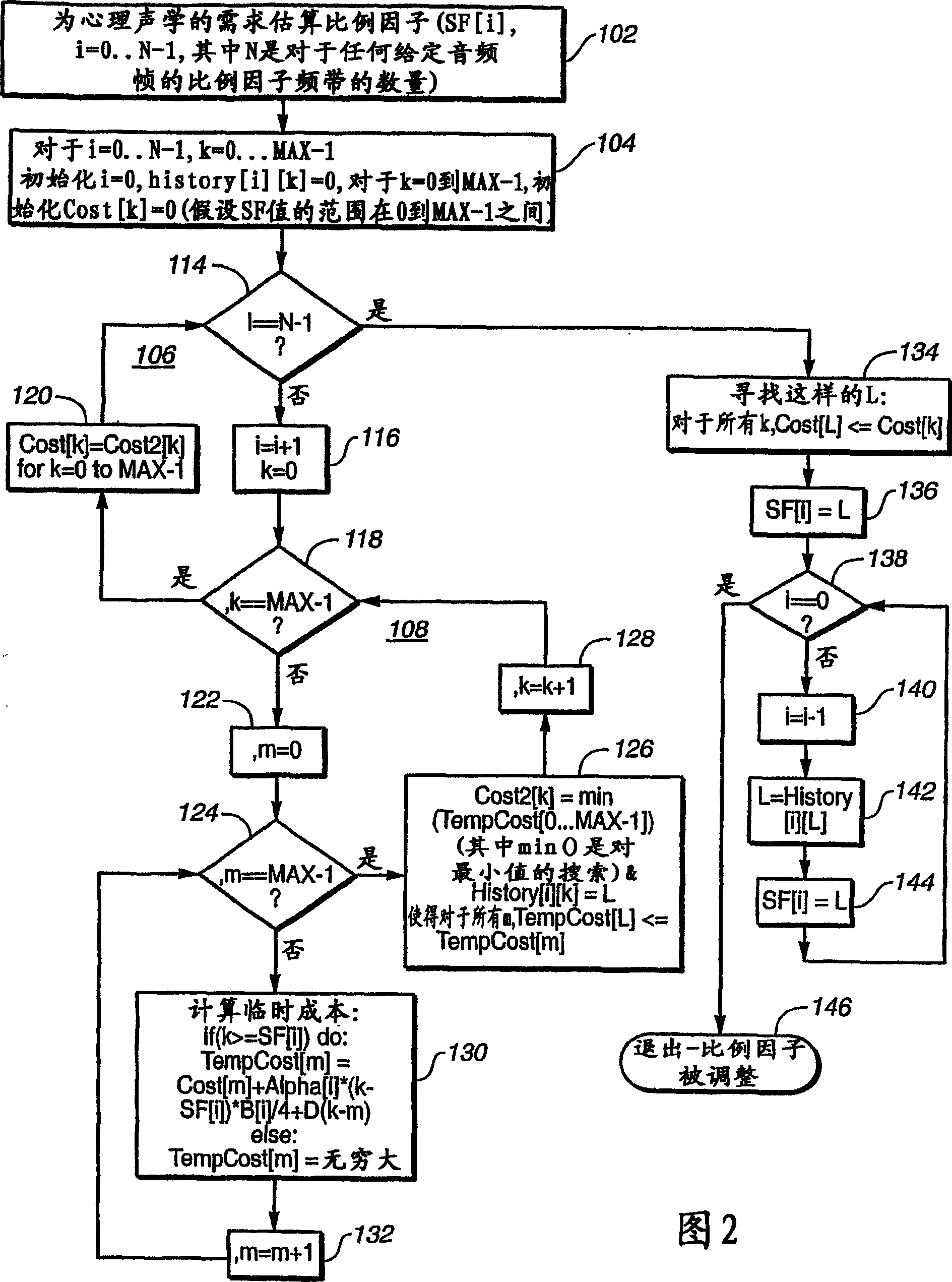
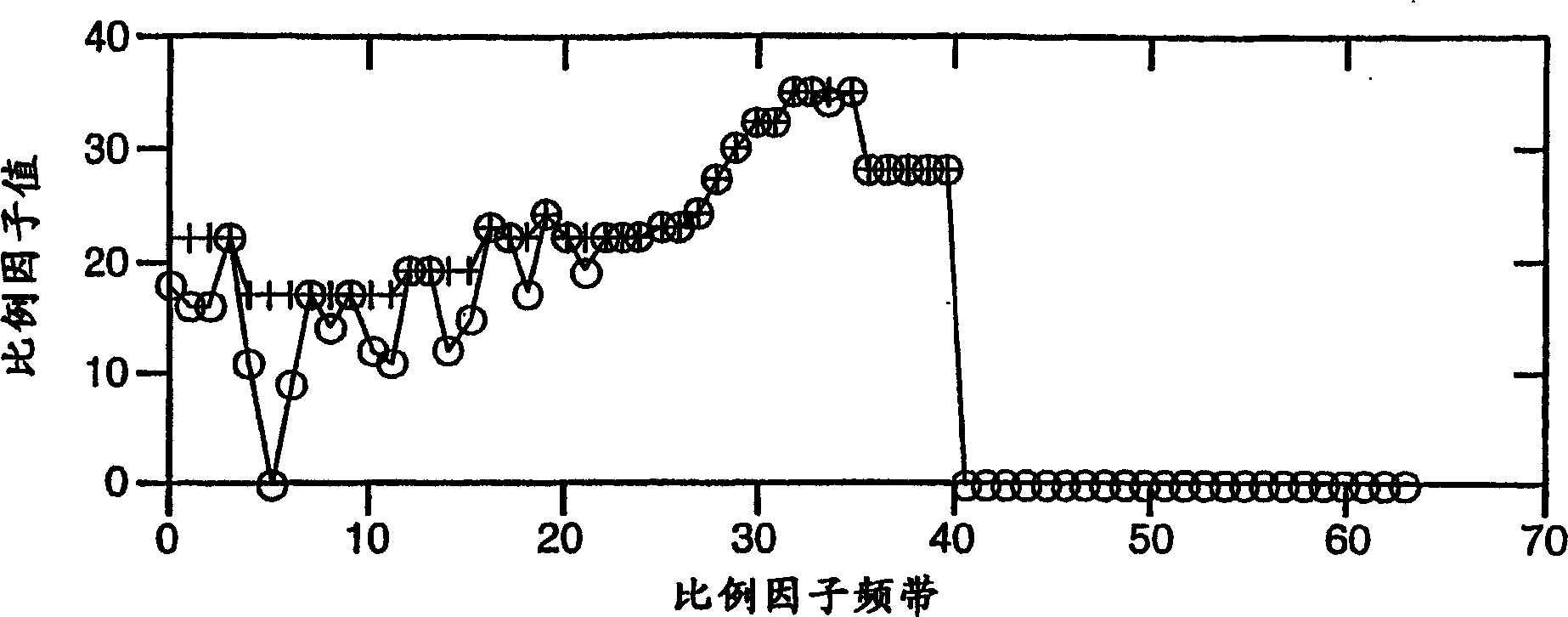
[0023] existfigure 1 In , the input audio is transformed using MDCT2, followed by preprocessing4 (eg: temporal noise shaping (TNS), prediction and mid-side coding (MS) in stereo applications). This input can also be passed to the psychoacoustic model 6, which calculates the masking level. As mentioned above, the masking model is used directly to calculate the scale factor for each frequency band ("Scale Factor Computation" 8). Although the in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com