Chemically reinforced glass and method for production thereof
A technology for strengthening glass and manufacturing methods, which is applied in the field of chemical strengthening glass, and can solve the problems of high destructive strength of glass, impossible cutting, difficult cutting, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
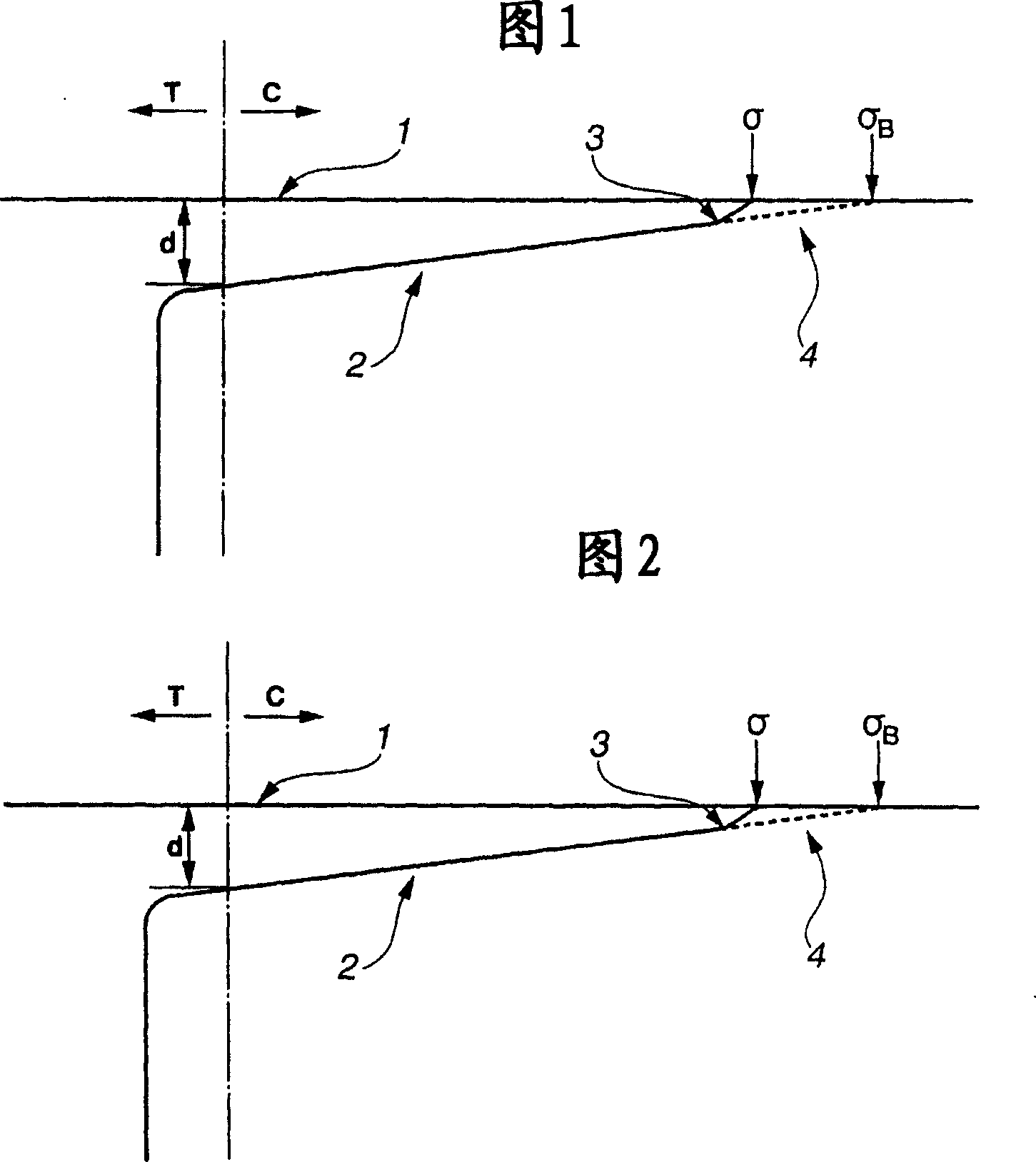
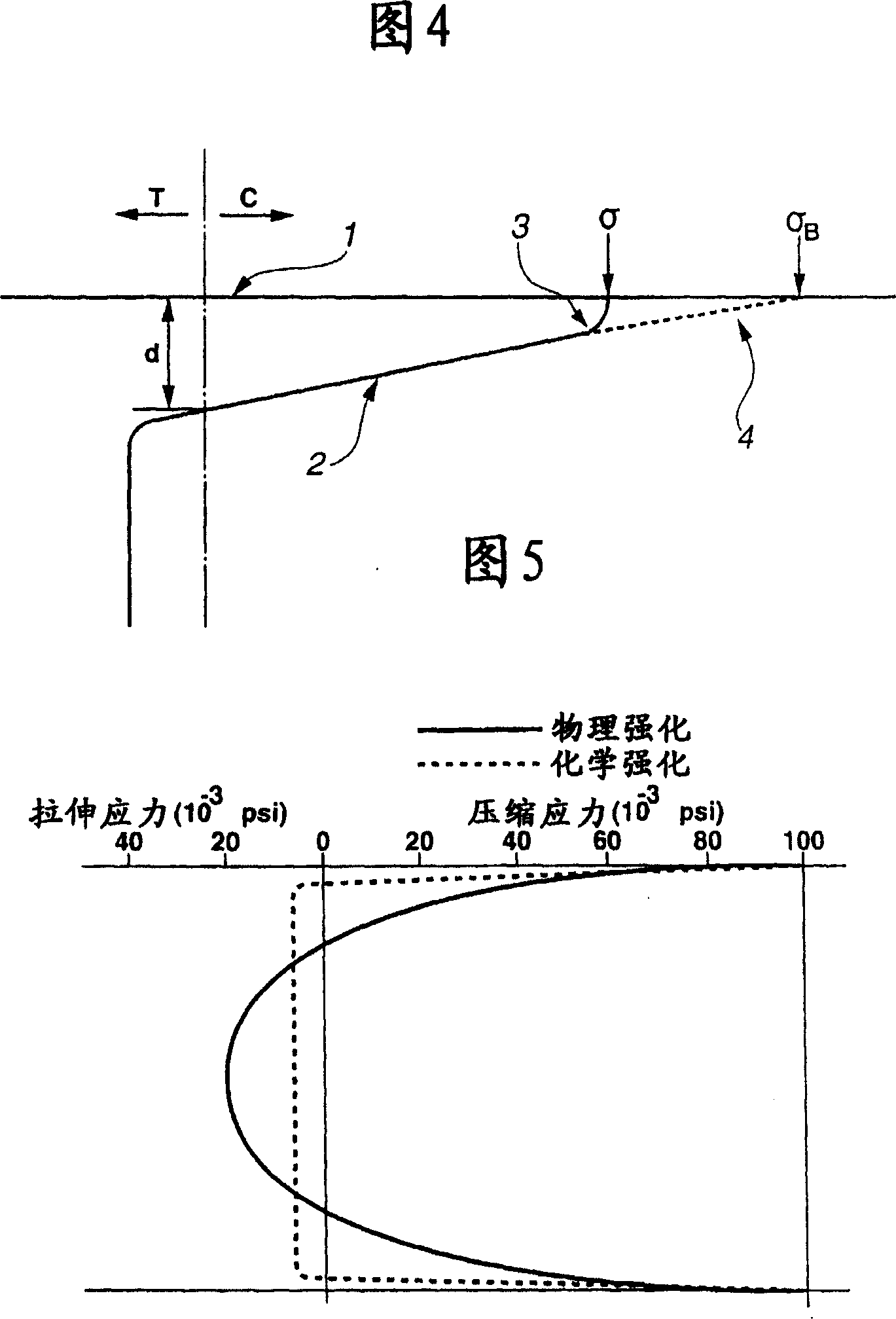
[0065] Soda-lime float glass with a thickness of 0.7mm is immersed in potassium nitrate molten salt at 460°C for 10 hours for ion exchange treatment, then the chemically strengthened glass is moved to a cooling tank set at 510°C, and then placed in the cooling tank Hold for 60 minutes. Then, it is cooled at a usual cooling rate (about 10° C. / minute) to obtain a predetermined chemically strengthened glass. The stress curve of this glass is shown in FIG. 1 . C in the figure represents compressive stress, and T represents tensile stress. In this way, it is a chemically strengthened glass characterized by two types of curves, the compressive stress curve A on the glass surface side and the compressive stress curve B on the glass inner layer side, in the compressive stress layer. In addition, this stress curve is a stress curve showing the result of cutting out chemically strengthened glass, grinding it, and observing it using a Babinet compensator and an optical microscope. The...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Soda-lime float glass with a thickness of 0.55mm is immersed in potassium nitrate molten salt at 470°C for 4 hours for the first ion exchange treatment, then immersed at 510°C for 20 minutes for the second ion exchange treatment, and then proceed as usual Cool at a certain cooling rate (about 10°C / min) to produce a set chemically strengthened glass. The stress curve of this glass is shown in FIG. 2 . The ratio of the surface stress value obtained from the stress curve A to the hypothetical surface stress value obtained from the line extending from the compressive stress curve B to the glass surface was 0.89. In addition, the thickness of the compressive stress layer formed by the stress curve A is 5 μm.
[0069] Using a commercially available superhard wheel cutter, the chemically strengthened glass was subjected to scribing (load weight: 2 kg) and a cutting test according to a general cutting operation, and it was possible to cut without any problem.
Embodiment 3
[0078] Soda-lime float glass having a thickness of 0.7 mm was immersed in molten potassium nitrate salt at 460° C. for 10 hours to perform ion exchange treatment. Immediately after the treatment, the chemically strengthened glass was moved to a cooling tank set at 510° C., and kept in the cooling tank for 60 minutes. Then, it is cooled according to the usual cooling rate (about 10° C. / minute) to produce a set chemically strengthened glass product. In addition, the surface hardness of the chemically strengthened glass product is 570kgf / cm 2 .
[0079] Using a commercially available superhard wheel cutter, the chemically strengthened glass was subjected to scribing (load weight: 2 kg) and a cutting test according to a general cutting operation, and it was possible to cut without any problem.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Surface hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Surface hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Surface hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com