Method of localizing fluorescent markers
A labeling and fluorescence radiation technology, applied in fluorescence/phosphorescence, measurement devices, material analysis through optical means, etc., can solve problems such as the inability to freely select wavelengths and limited spatial resolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
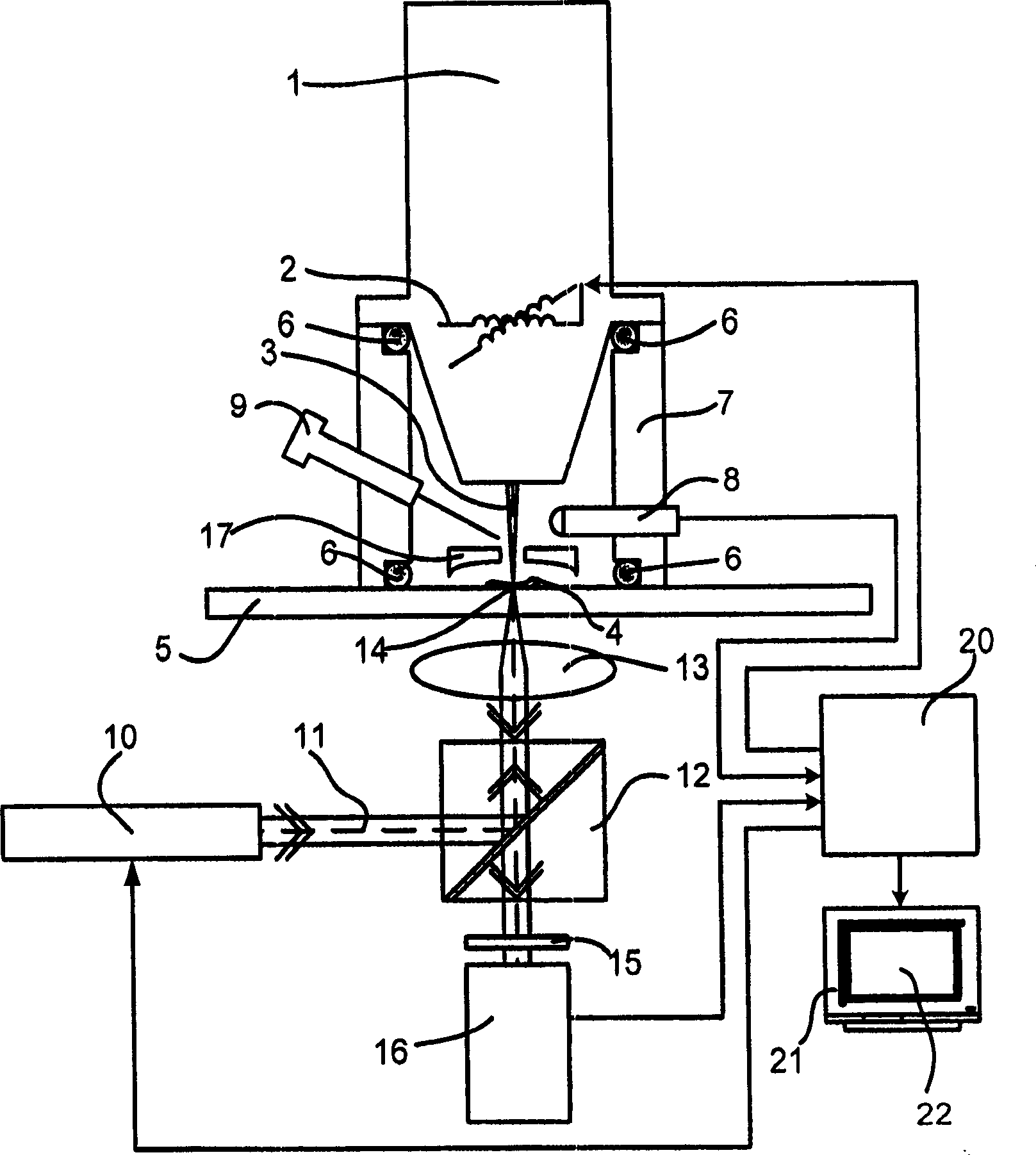
[0044] figure 1A schematic diagram of an apparatus for performing the method of the invention is shown. A particle-optical column 1 , such as an ion column, generates a focused particle beam 3 of charged particles. The particle beam 3 is focused onto a sample 4 on a sample holder 5 . A focused particle beam 3 is scanned over a sample 4 by means of a deflection unit 2 .
[0045] Charged particles (eg secondary electrons) emitted from the sample are detected by a particle detector 8 (eg Everhardt-Thornley detector).
[0046] The vacuum required to focus the particle beam 3 is obtained by sealing the vacuum chamber 7 with the aid of the sealing device 6 and then evacuating the vacuum chamber with a vacuum pump (not shown).
[0047] It should be pointed out that, in the case of biological samples, it is advantageous to maintain a small residual pressure of water vapor so that the sample does not dry out too much. This technique is a known technique and is used, for example, in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com