Method for preparing nanometer zero-valent iron grain using improved liquid phase reduction method
A technology of nano-zero-valent iron and reduction method is applied in the field of preparation of nano-zero-valent iron particles, which can solve the problems of easy agglomeration and uneven particle distribution, and achieve the effects of low production cost, easy operation and fast preparation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Weigh 0.139 g FeSO 4 .7H 2 O, dissolved in distilled water, made into 0.01M FeSO 4 .7H 2 O aqueous solution 50ml, electromagnetic stirring to make it fully mixed. The solution was then poured into an Erlenmeyer flask and placed on a mechanical stirrer. Weigh 0.0567g NaBH 4 , dissolved in distilled water, made into 0.03M NaBH 4 Aqueous solution 50ml. Under the condition of mechanical stirring, the NaBH 4 The aqueous solution is rapidly added to the FeSO 4 .7H 2 O aqueous solution, continue stirring for 5-15 seconds, and stop stirring when the solution turns black. Selected by magnetic separation, first washed three times with distilled water, then fully washed three times with acetone, and stored in acetone.
[0040] The test results of TEM show that the particle size range is 10-100nm, and the particle size distribution is not uniform.
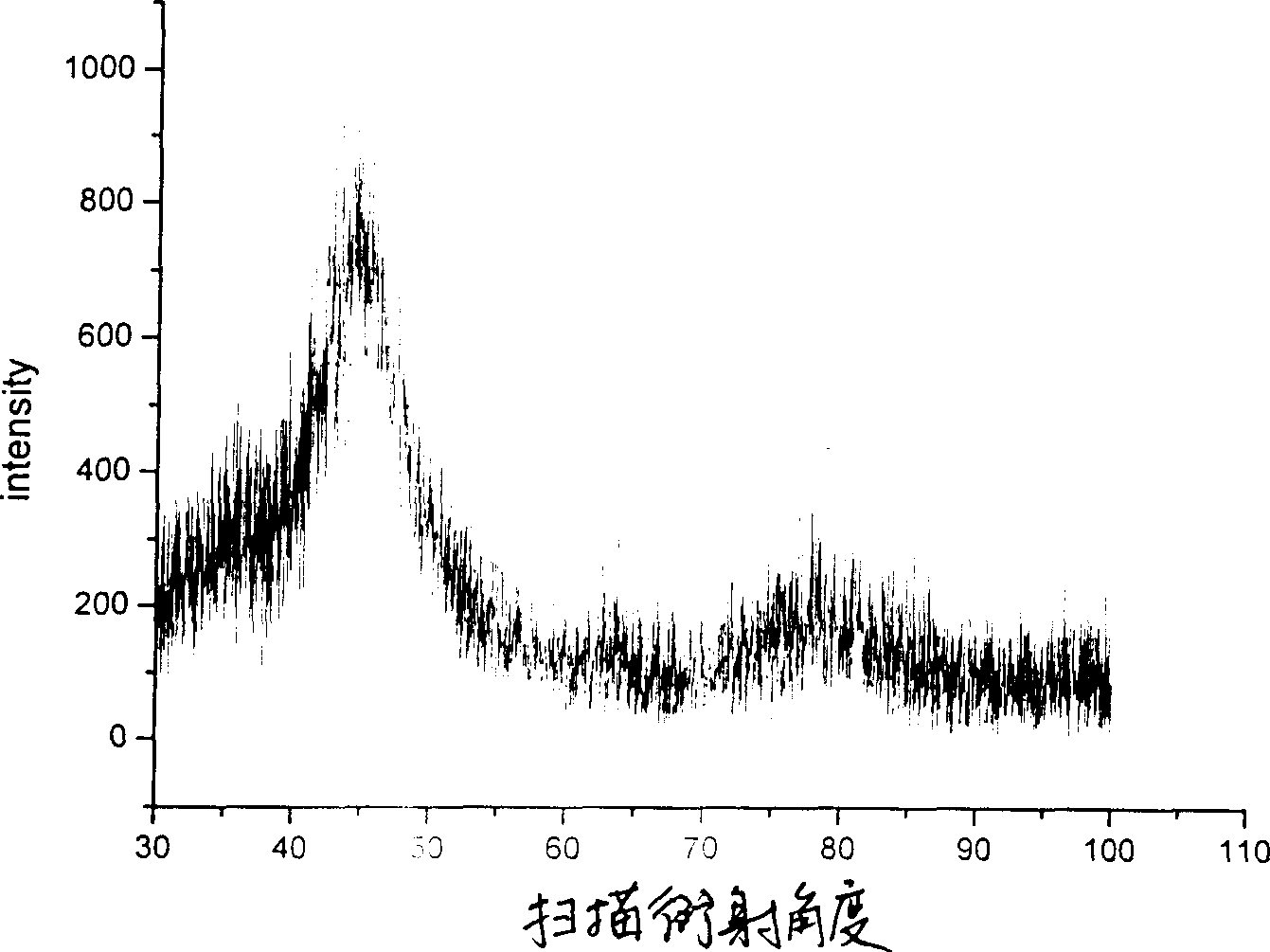
[0041] The XRD test results show that: when the scanning diffraction angle (2θ) is 30°-100°, the corresponding 2θ when the ...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Weigh 0.139 g FeSO 4 .7H 2 O, dissolved in distilled water, made into 0.01M FeSO 4 .7H 2 O aqueous solution 50ml, then add 0.1g polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP K-30), electromagnetic stirring to make it fully mixed. The solution was then poured into an Erlenmeyer flask and placed on a mechanical stirrer. Weigh 0.0567g NaBH 4 , dissolved in distilled water, made into 0.03M NaBH 4 Aqueous solution 50ml. Under the condition of mechanical stirring, 50mlNaBH 4 The aqueous solution was quickly poured into the FeSO 4 .7H 2 O aqueous solution, continue to stir for a few seconds, stop stirring when the solution turns black. Selected by magnetic separation, first washed three times with distilled water, then fully washed three times with acetone, and stored in acetone.
[0045] The test result of TEM shows that: the particle size range is 44-96nm, and the average particle size is 780nm.
[0046] The XRD test results show that: when the scanning angle (2θ) is 30°-100°, the co...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Weigh 0.139 g FeSO 4 .7H 2 O, dissolved in distilled water, made into 0.01M FeSO 4 .7H 2 O aqueous solution 50ml, then add 0.2g polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP K-30), electromagnetic stirring to make it fully mixed. The solution was then poured into an Erlenmeyer flask and placed on a mechanical stirrer. Weigh 0.0567g NaBH 4 , dissolved in distilled water, made into 0.03M NaBH 4 Aqueous solution 50ml. Under the condition of mechanical stirring, 50mlNaBH 4 The aqueous solution was quickly poured into the FeSO 4 .7H 2 O aqueous solution, continue to stir for a few seconds, stop stirring when the solution turns black. Selected by magnetic separation, first washed three times with distilled water, then fully washed three times with acetone, and stored in acetone.
[0050] The test result of TEM shows that: the particle size range is 43-76nm, and the average particle size is 60nm.
[0051] The XRD test results show that: when the scanning angle (2θ) is 30°-100°, the cor...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com