Quasi crystal phase fortified magnesium lithium alloy and its preparation method
A technology of magnesium-lithium alloy and quasi-crystalline phase, which is applied in the field of high-strength magnesium-lithium alloy and its preparation, can solve the problems of low density and strength, and achieve good plasticity and simple processing technology.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] I), alloy composition
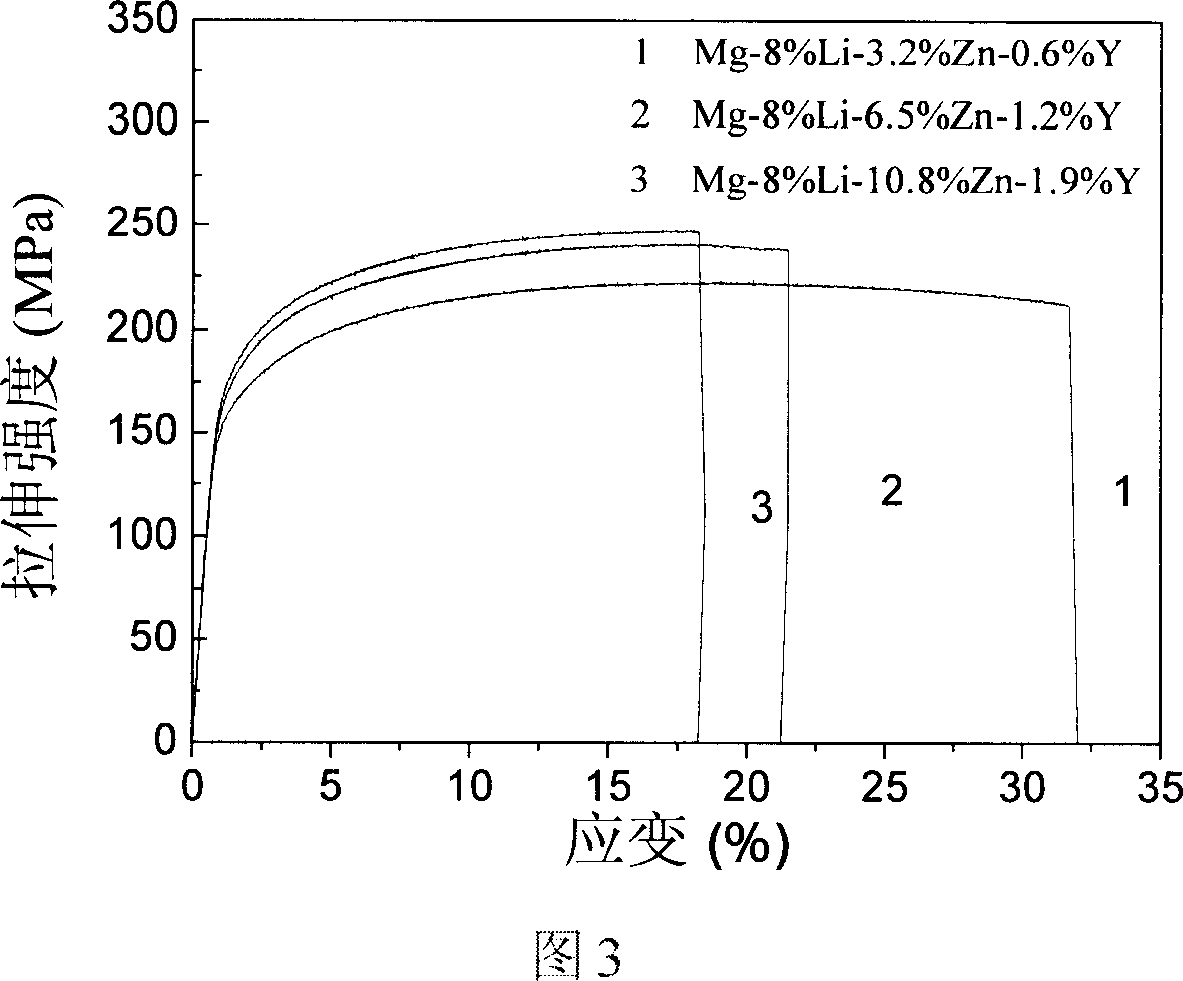
[0031] Configure 15 kilograms of lithium-containing magnesium alloy materials according to the following proportions, and the elements taken out are: 1200 grams of lithium (Li), 480 grams of zinc (Zn), 375 grams of magnesium-yttrium master alloy (Mg-24%Y) and the balance Magnesium (Mg). In terms of weight percentage, the alloy composition is Mg-8%Li-3.2Zn-0.6Y.
[0032] II), alloy smelting and casting
[0033] The alloy is smelted in a 15 kg capacity crucible and electric resistance furnace. The crucible and casting molds are made of mild steel. Taking Example 1 as an example, the smelting and casting process of the alloy will be described in detail below.
[0034] 1) Set the target temperature of the crucible to 720°C and start heating; then preheat various ingredients such as pure magnesium, pure zinc, magnesium-yttrium intermediate alloy, pure lithium, etc. 2% covering agent (LiCl and LiF, weight ratio of 3:1) was baked in an oven; the ca...
Embodiment 2
[0050] I), alloy composition
[0051] Configure 15 kilograms of lithium-containing magnesium alloy materials according to the following proportions, and the elements taken out are: 1200 grams of lithium (Li), 975 grams of zinc (Zn), 750 grams of magnesium-yttrium master alloy (Mg-24%Y) and the balance Magnesium (Mg). In terms of weight percentage, the alloy composition is Mg-8%Li-6.5Zn-1.2Y.
[0052] II), alloy smelting and casting
[0053] The smelting and casting of reference embodiment 1. The difference is that the zinc (Zn) and yttrium (Y) contents of the two are different.
[0054] III), hot extrusion processing
[0055] Referring to the extrusion process of Example 1.
[0056] IV), microstructure characterization
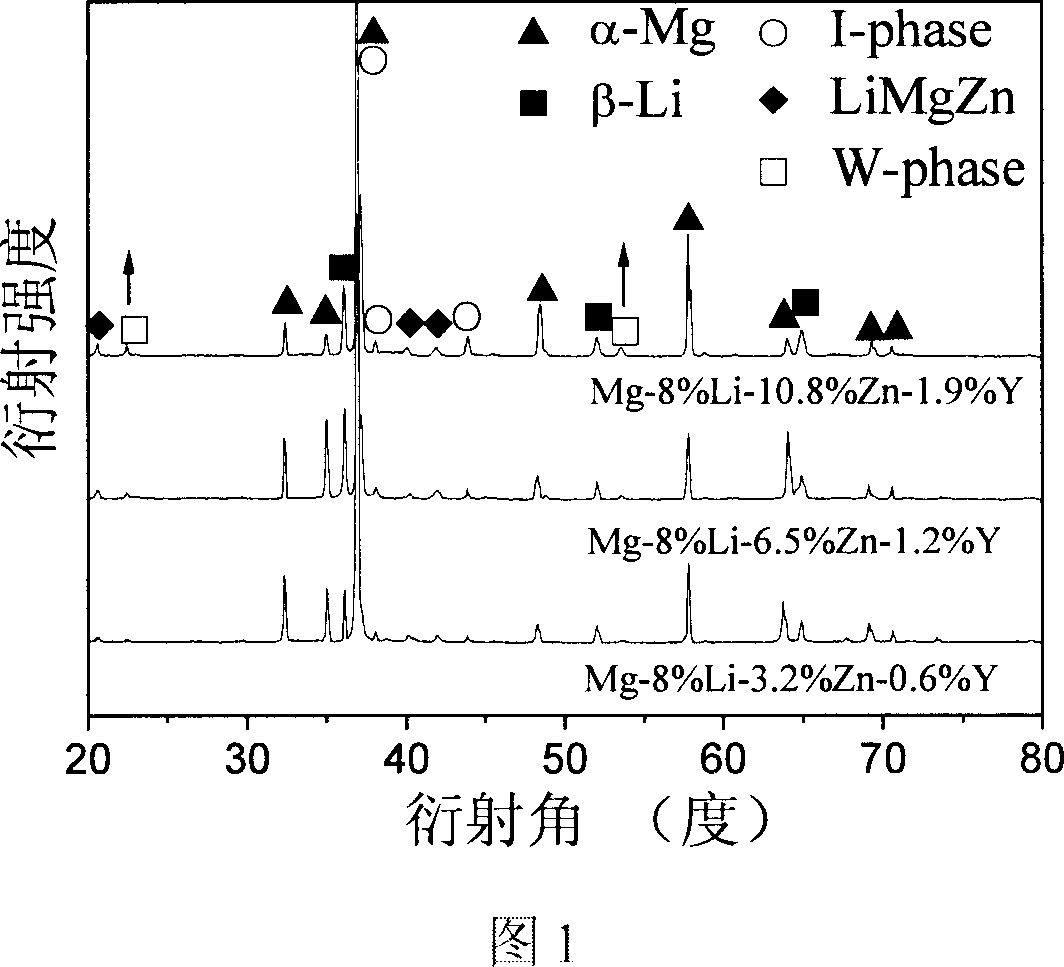
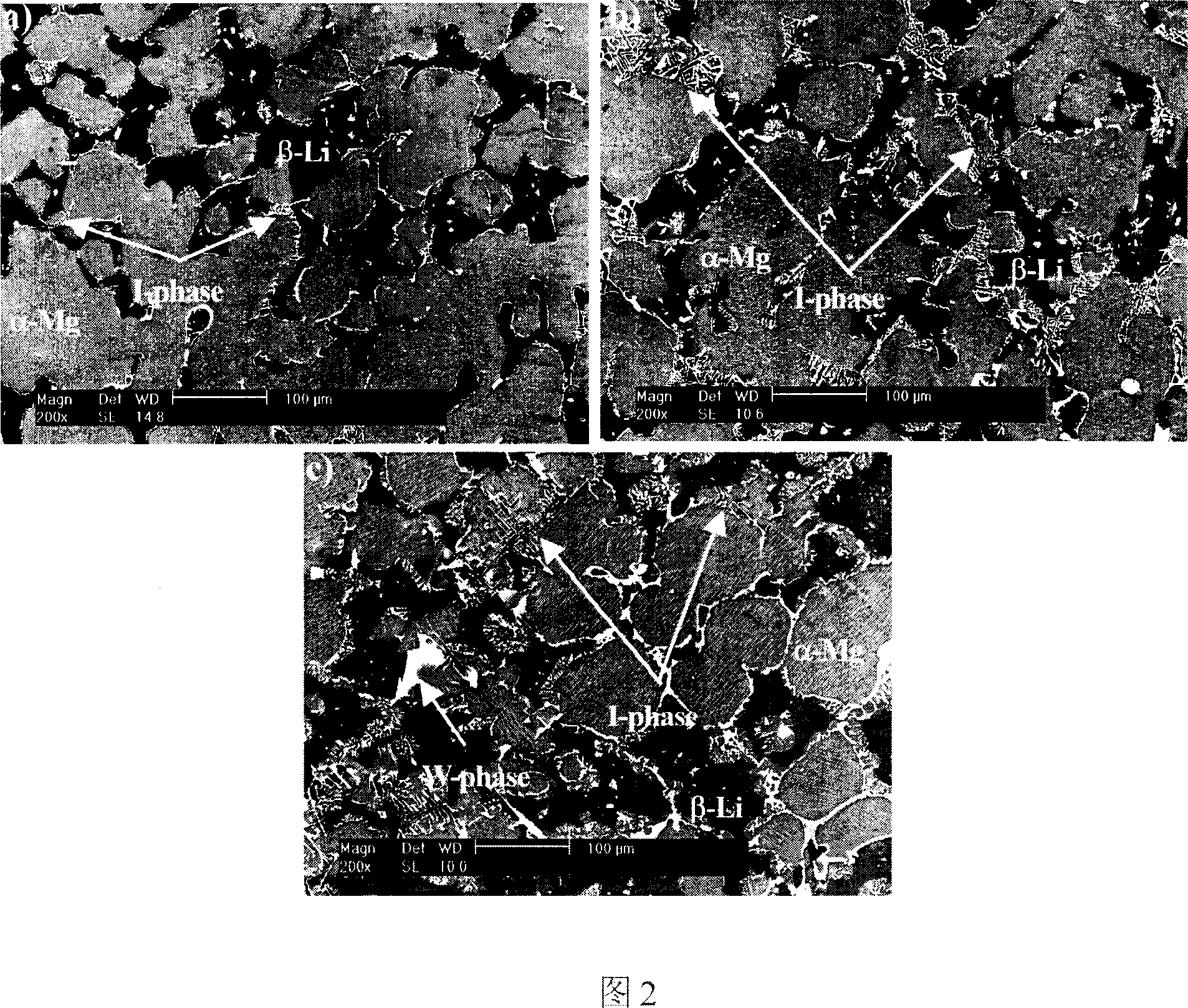
[0057] Refer to the microstructure characterization of Example 1. The main phases in the alloy are α-Mg, β-Li, LiMgZn, Mg 3 Zn 6 Y (quasicrystalline phase I-phase) and Mg 3 Zn 3 Y (W-phase), the corresponding X-ray spectrum is listed on the accompan...
Embodiment 3
[0061] I), alloy composition
[0062] Configure 15 kilograms of lithium-containing magnesium alloy materials according to the following proportions. The elements taken out are: lithium (Li) 1200 grams, zinc (Zn) 1620 grams, magnesium yttrium master alloy (Mg-24%Y) 1187 grams and the balance Magnesium (Mg). In terms of weight percentage, the alloy composition is Mg-8%Li-10.8Zn-1.9Y.
[0063] II), alloy smelting and casting
[0064] The smelting and casting of reference embodiment 1. The difference is that the zinc (Zn) and yttrium (Y) contents of the two are different.
[0065] III), hot extrusion processing
[0066] Referring to the extrusion process of Example 1.
[0067] Iv), microstructure characterization
[0068] Refer to the microstructure characterization of Example 1. The main phases in the alloy are α-Mg, β-Li, LiMgZn, Mg 3 Zn 6 Y (quasicrystalline phase I-phase) and Mg 3 Zn 3 Y(W-phase), the corresponding X-ray spectrum is listed on accompanying drawing 1;...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Strain rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com