System, apparatus, and method for user tunable and selectable searching of a database using a weigthted quantized feature vector
a feature vector and database technology, applied in the field of data processing, can solve the problems of difficult to find exact matches of atom-by-atom and bond-by-bond search, affecting the accuracy of database search results, and consuming a lot of time for exact match searching
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
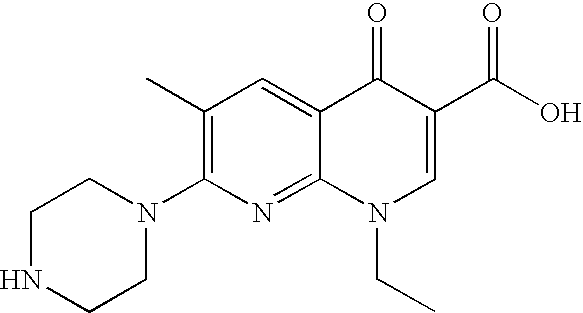
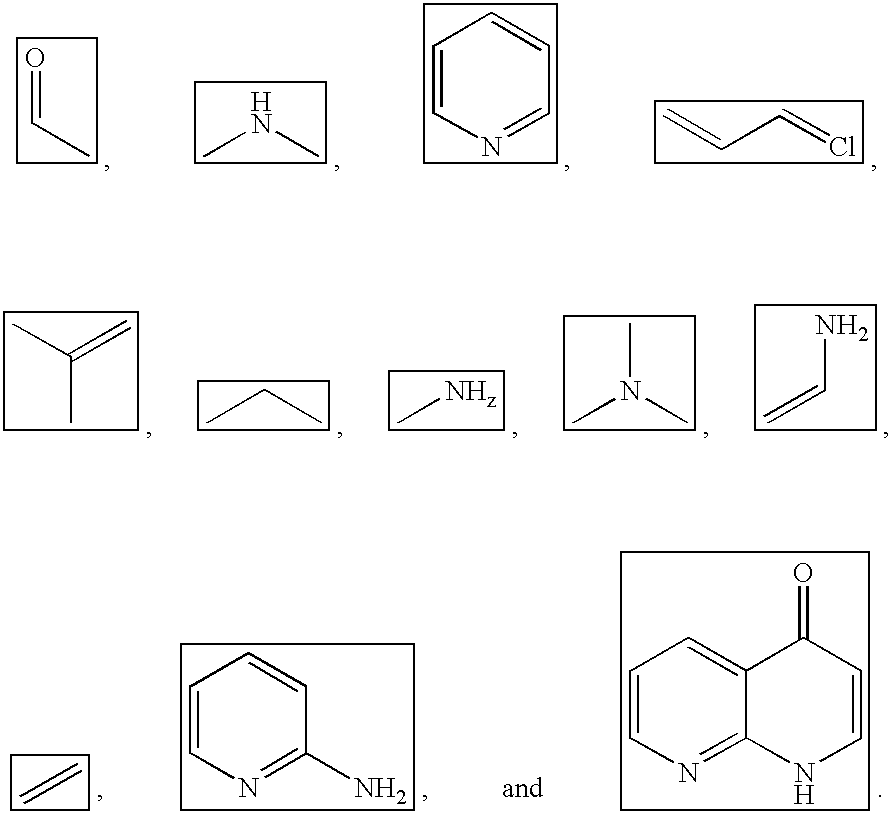
[0038] It is feasible to perform similarity searches in an electronic database of items, wherein said items possess a set of one or more descriptive properties (related to the items) that can be expressed in numeric form. Similarity searching in such a generalized database according to current technology may be performed in a computer using the method shown in FIG. 1.
[0039] 1. A user submits a query to the system. The query may be submitted using different formats, but a query item must be able to be classified according to its descriptive properties. The descriptive properties may have inherent numeric values (e.g., test results, characteristic values, prices, ASCII values, checksums, etc.). Alternatively, they may have binary values (`one` indicating the presence of a feature and `zero` indicating the absence of the feature).
[0040] 2. The query item is parsed according to its descriptive properties. The descriptive properties are analyzed by comparing various elements of the query...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com