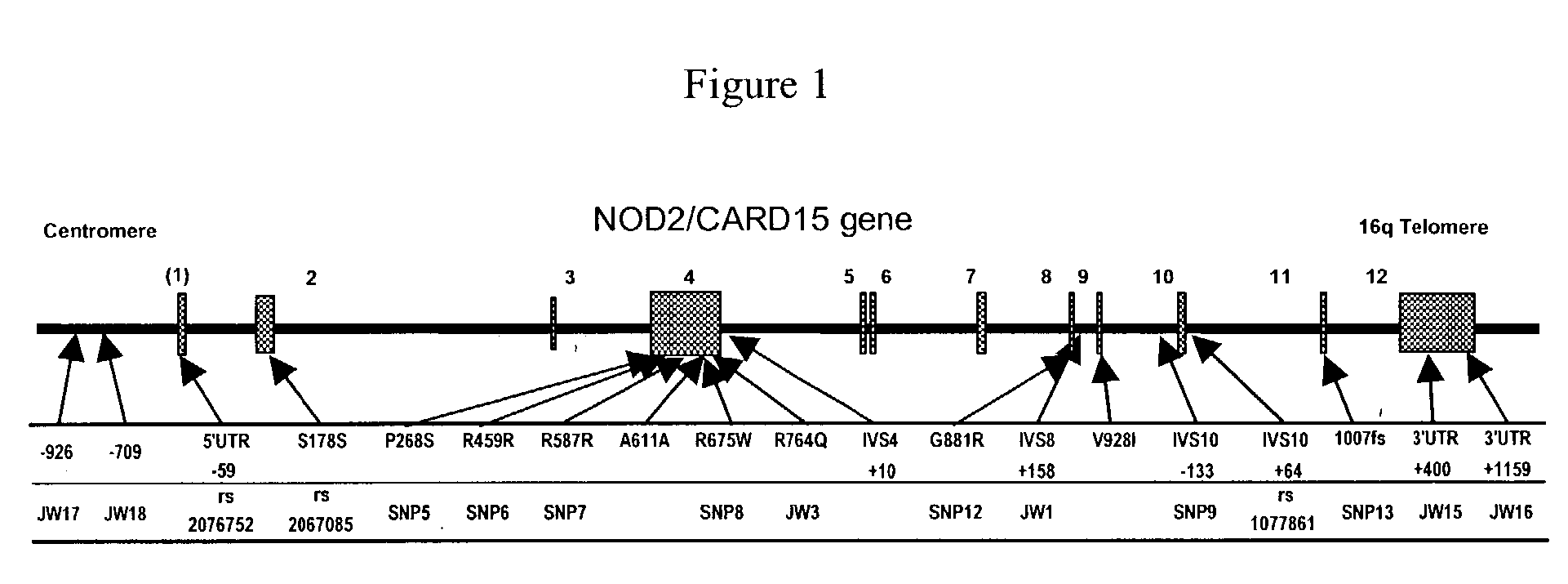
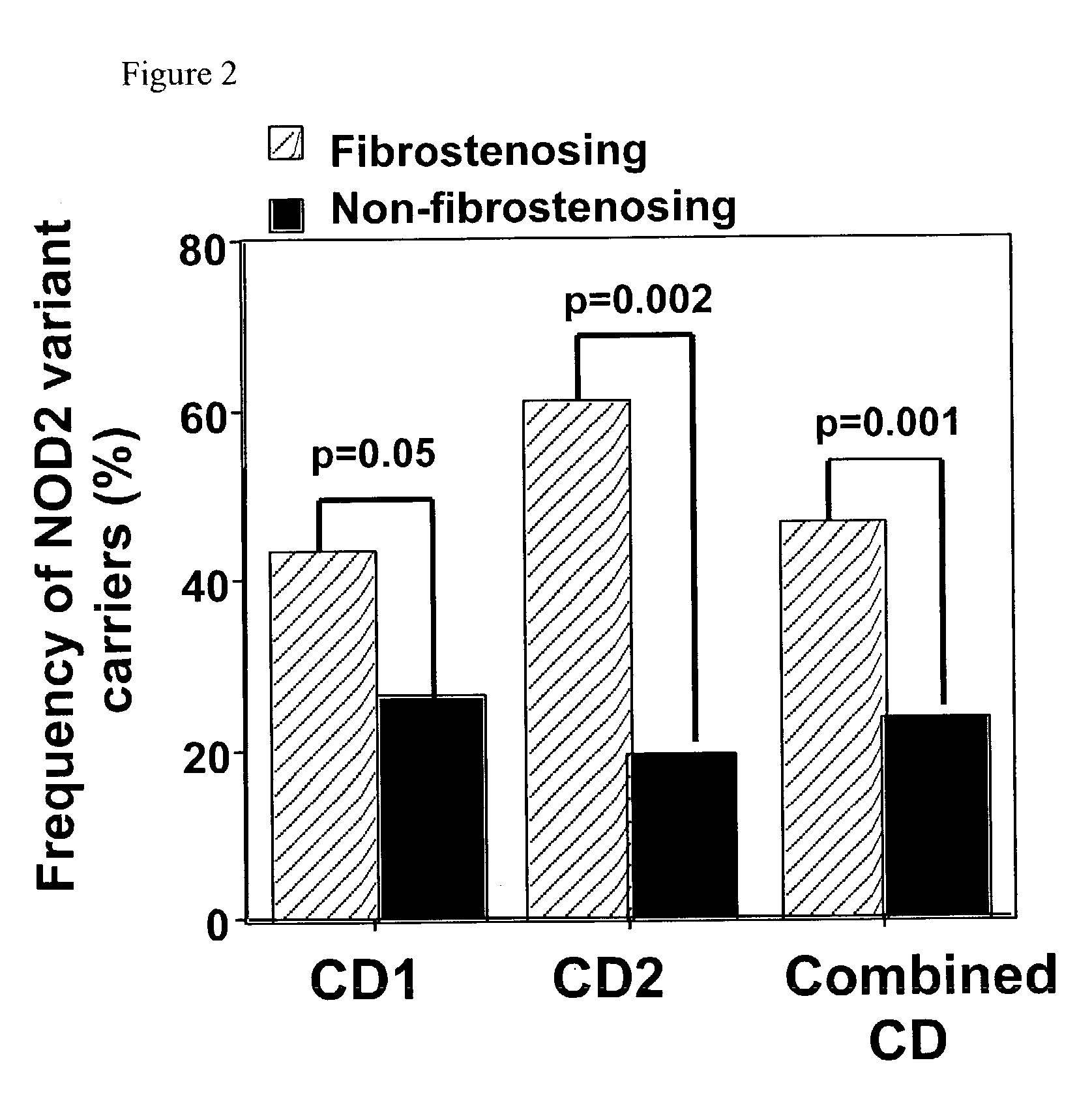
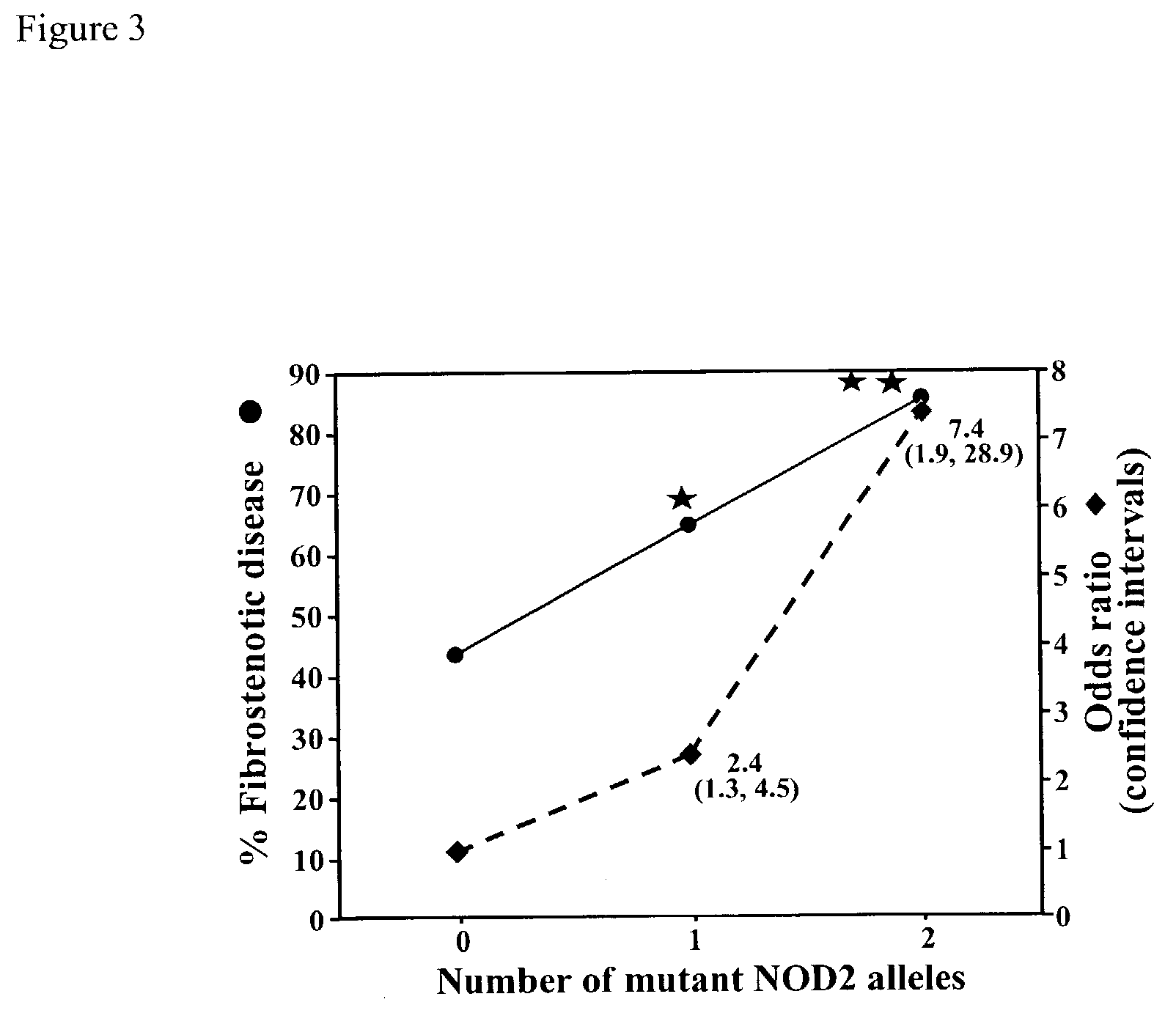
Mutations in NOD2 are associated with fibrostenosing disease in patients with Crohn's disease
a technology of fibrostenosis and mutations, which is applied in the field of mutations in nod2 that are associated with fibrostenosis in patients with crohn's disease, can solve the problems of delayed optimal treatment, increased risk of intestinal cancer, and increased risk of ibd
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example ii
Patients with Crohn's Disease Have an Increased Frequency of Rare Allelic Variants of NOD2 / CARD15
[0100] This example describes the association of a "2" allele at SNP 8, SNP 12, or SNP 13 within the NOD2 / CARD15 locus (rare allelic variants of NOD2 / CARD15) with Crohn's disease in a North American population.
[0101] In order to determine whether the North American Crohn's disease patient populations in Cohorts 1 and 2 expressed allelic variants of NOD2 / CARD15, Cohort 1 (hypothesis-generating) and Cohort 2 (hypothesis-confirming) were genotyped for the rare allelic variant of SNP 8 (R675W), SNP 12 (G881R) and SNP 13 (3020insC). A cohort of ulcerative colitis patients was used for comparison.
[0102] Genotyping was performed using a genotyping assay employing 5'-exonuclease technology, the TaqMan MGB.TM. assay (PE Biosystems; Foster City, Calif.). Primers were designed using the software PrimerExpress 1.5.TM. (PE Biosystems) and sequence information found in dbSNP for NOD2 / CARD15 SNP 5, 8, ...
example iii
Rare Variant Alleles in the NOD2 / CARD15 Locus are Associated with the Fibrostenosing Subtype of Crohn's Disease in Cohort 1
[0106] This example demonstrates that a "2" allele at SNP 8, SNP 12, or SNP 13 is significantly associated with fibrostenosing disease in Cohort 1.
[0107] Patients with Crohn's disease express diverse clinical phenotypes that can be due to differences in underlying genetic factors. In order to determine whether rare variant alleles at the NOD2 / CARD15 locus were associated with specific Crohn's disease-related clinical phenotypes or disease-related serum immune markers, univariate analysis was performed. The univariate analysis evaluated the association between NOD2 / CARD15 allelic variants at SNP 8, SNP 12, or SNP 13 and predefined clinical characteristics, including age of onset, disease location, and disease phenotype (fibrostenosing disease, internal-perforating disease, perianal fistulizing disease or ulcerative colitis-like disease). The association between N...
example iv
Rare Variant Alleles in the NOD2 / CARD15 Locus are Associated with the Fibrostenosing Subtype of Crohn's Disease in Cohort 2
[0110] This example demonstrates that a "2" allele at SNP 8, SNP 12, or SNP 13 of the NOD2 / CARD15 locus is significantly associated with fibrostenosing disease in Cohort 2.
[0111] The results obtained with Cohort 1 in Example III indicated that NOD2 / CARD15 rare variant alleles were positively associated with fibrostenosing Crohn's disease, small bowel involvement, ASCA positivity, and younger age of onset, and negatively associated with UC-like disease (see Table 5). These hypotheses were further tested using Cohort 2; the results are shown in Table 6. As with Cohort 1, Cohort 2 demonstrated a significant association between a "2" allele at SNP 8, SNP 12, or SNP 13 of the NOD2 / CARD15 locus and fibrostenosing disease (p=0.002, with Bonferroni correction p=0.01; see Table 6). These results indicate that a "2" allele at SNP 8, SNP 12, or SNP 13 of the NOD2 / CARD15 lo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com