Total chlorine free bleaching of arundo donax pulp
a technology of arundo donax and chlorine free bleaching, which is applied in the direction of fibre chemical treatment, vegetable materials, mechanical equipment, etc., can solve the problems of inability to meet the needs of the market, the approach is more difficult, and the world is concerned about large scale deforestation and other problems, to achieve the effect of less binder and lighter color
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
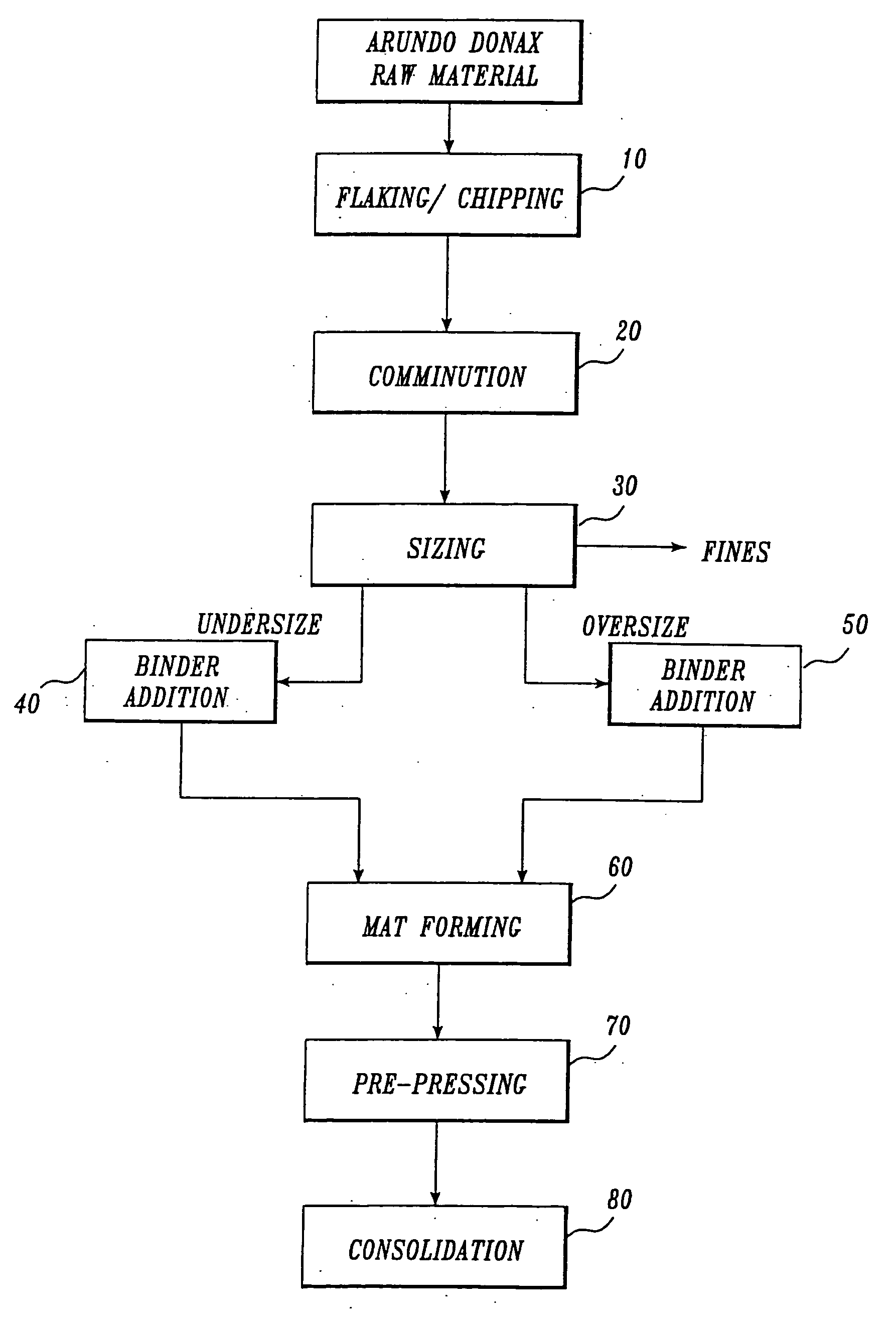
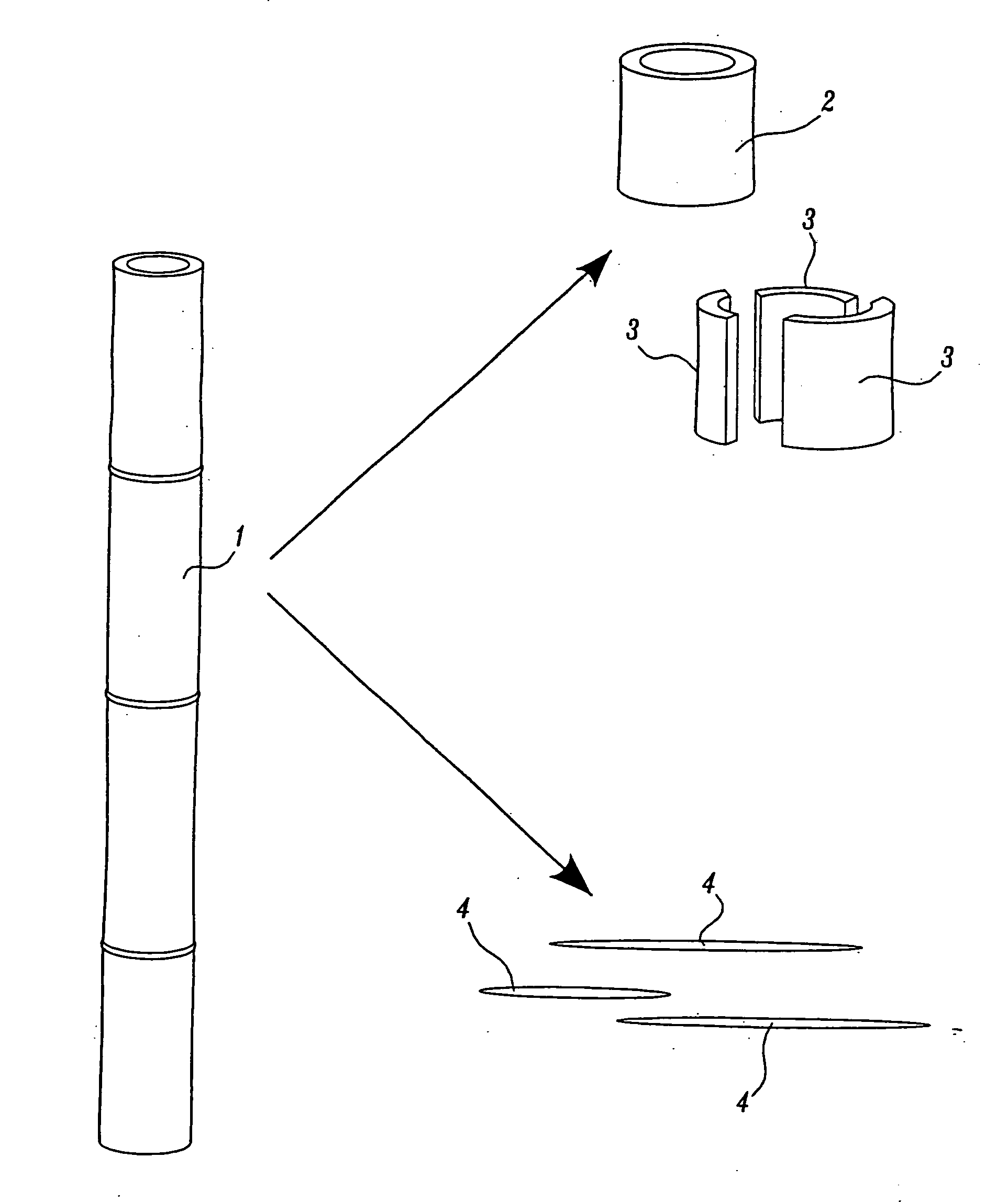
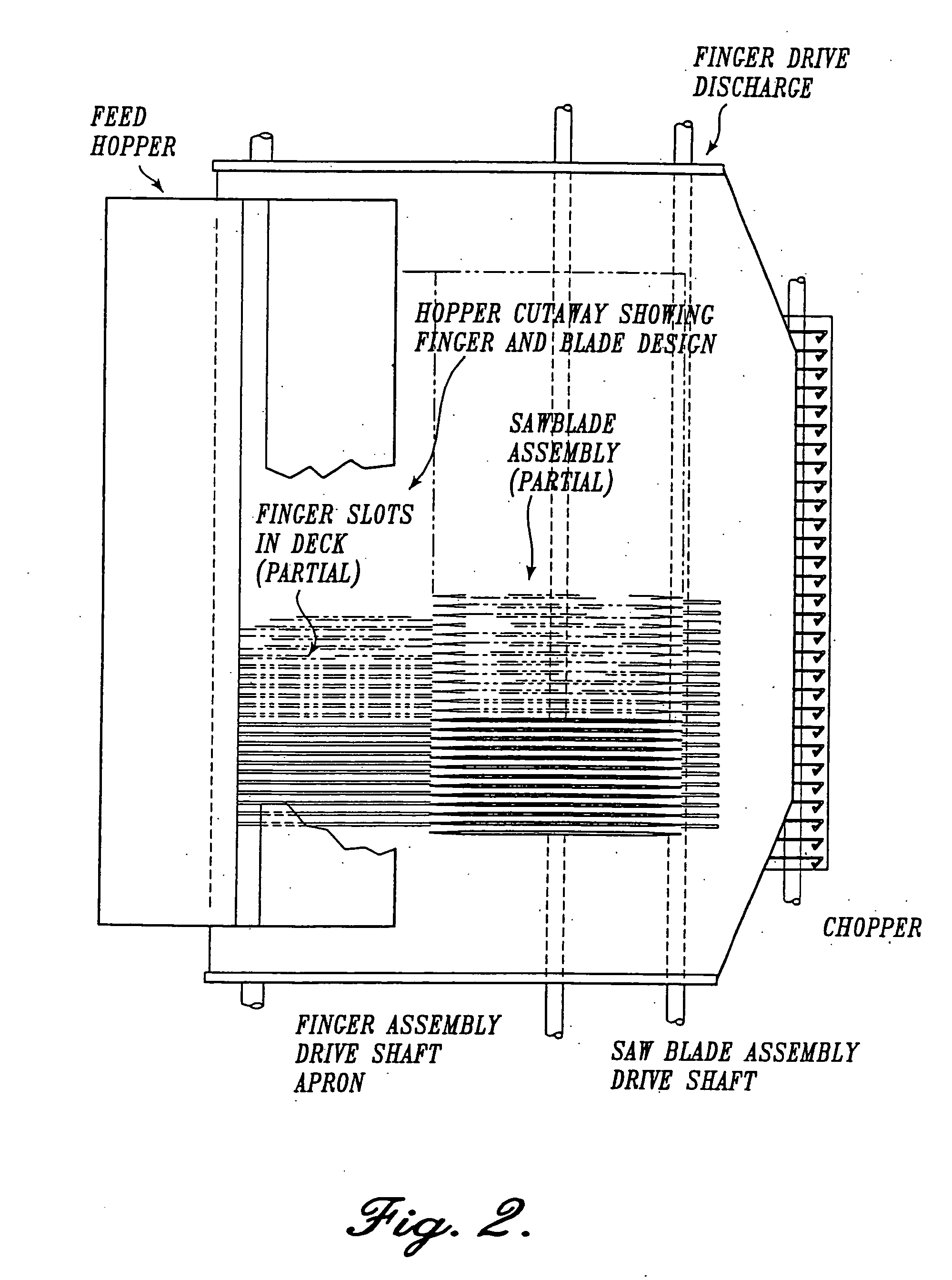
Equipment, Processes, and Methods for Nalgrass Size Reduction
[0090] In this example, cutting or macerating nalgrass, more specifically cutting nalgrass into particles that are suitable for processing into digested pulp or for efficient processing into composite panels and / or engineered wood products, is described.
[0091] Fairly sophisticated processing equipment has been developed over many years, by the forest and wood products industries, for size reduction of logs, sawmill shavings, waste lumber, etc. The equipment and handling methods have been designed to produce particles of specific geometry for use in modern digesters for the manufacture of pulp and in milling equipment for wood composites, namely, particleboard, oriented strand board (OSB), and medium density fiberboard (MDF). During the development work, several types and models of wood chippers and flakers were tested. The resulting particles were satisfactory for laboratory and pilot scale work but it quickly became evi...
example 2
The Formation of Representative Nalgrass Particle Boards
[0102] The protocol for manufacturing particle board of nalgrass, and of comparison materials, is described in this example.
[0103] Preparing the Furnish (Particles).
[0104]Arundo donax stalks were chipped into pieces of approximately 2 to 3 in. long×¼ to ⅜ in. wide×0.03 in. thick in a Pallmann Drum Flaker, dried to 8% moisture, and then processed in a Prater Blue Streak hammermill with a ⅛ in. screen. Material from the mill was screened resulting in 32% through the screen to be used for face material and 68% on the screen to be used for core material.
[0105] For wood (southern pine) composite preparation, commercially obtained face and core material was used. The commercial face material was coarser than that used for nalgrass and wheatstraw so a portion of the wood face material was screened, using the same mesh screen as used for nalgrass.
[0106] For wheatstraw, the straw was processed through the Prater Blue Streak hammerm...
example 3
The Formation of Representative Nalgrass / Southern Pine Particleboards
[0133] In this example, the formation of particle boards containing nalgrass / southern pine blends is described. The mechanical and physical properties of the particle boards compared to particle boards formed from (1) nalgrass and (2) southern pine.
[0134] Tests were conducted to compare the mechanical and physical properties of nalgrass, southern pine, and nalgrass / southern pine particleboard. For each furnish type, panels were manufactured with target densities of 42 lb / ft3 and 47 lb / ft3 and resin levels of 2% and 4%. All specimens were tested in static bending, internal bond strength, face and edge screwholding, water sorption, and thickness swell. Mechanical properties were compared with product specifications for medium density particleboard (ANSI A208.1-1993). See Table 2.
TABLE 2Grade Specifications of Medium Density Particleboard(National Particleboard Association ANSI A208.1-1993)MORMOEIBFSPESPGrade(psi)...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com