Reinforcement material and reinforcement structure of structure and method of designing reinforcement material
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
eighth embodiment
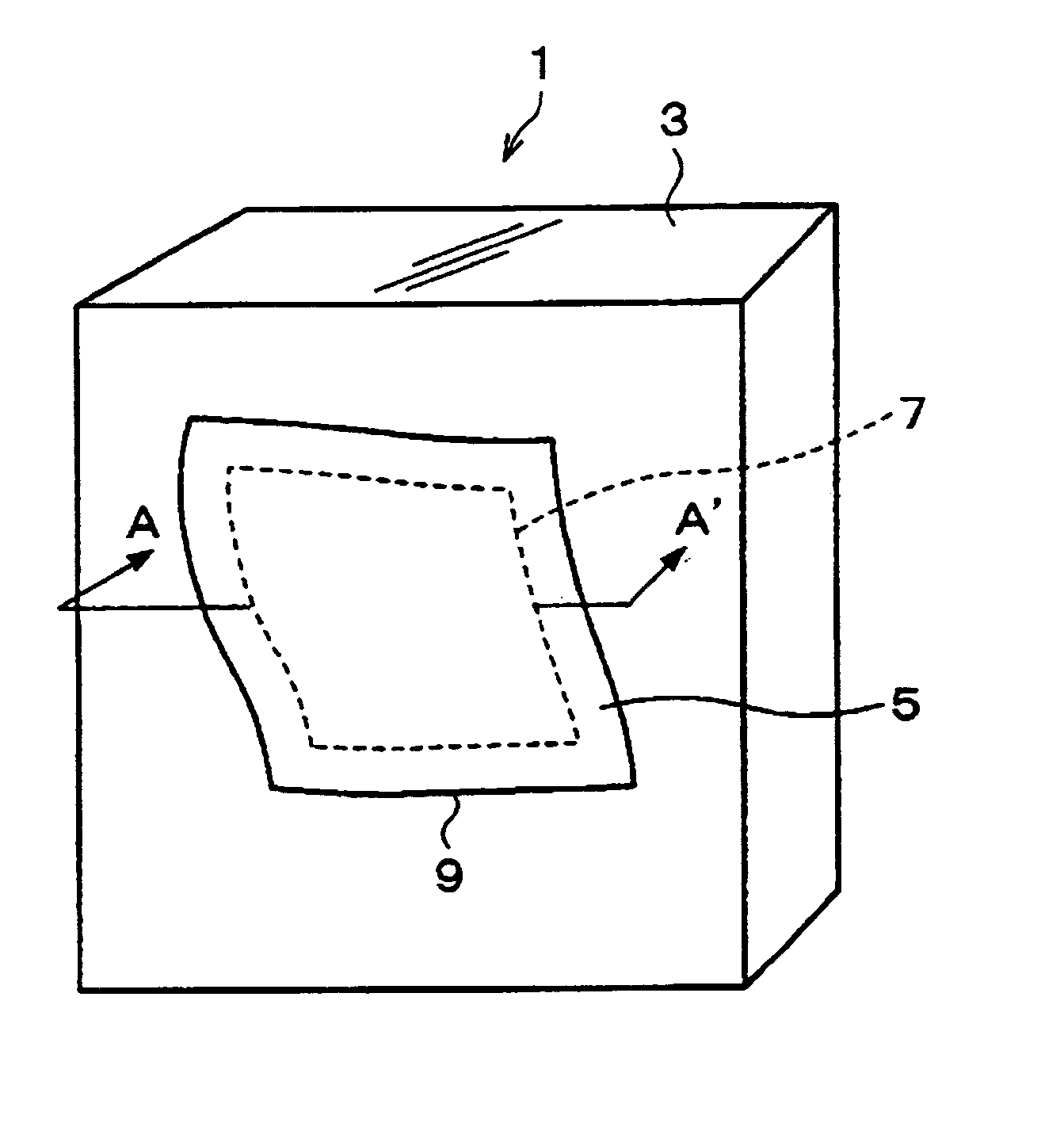
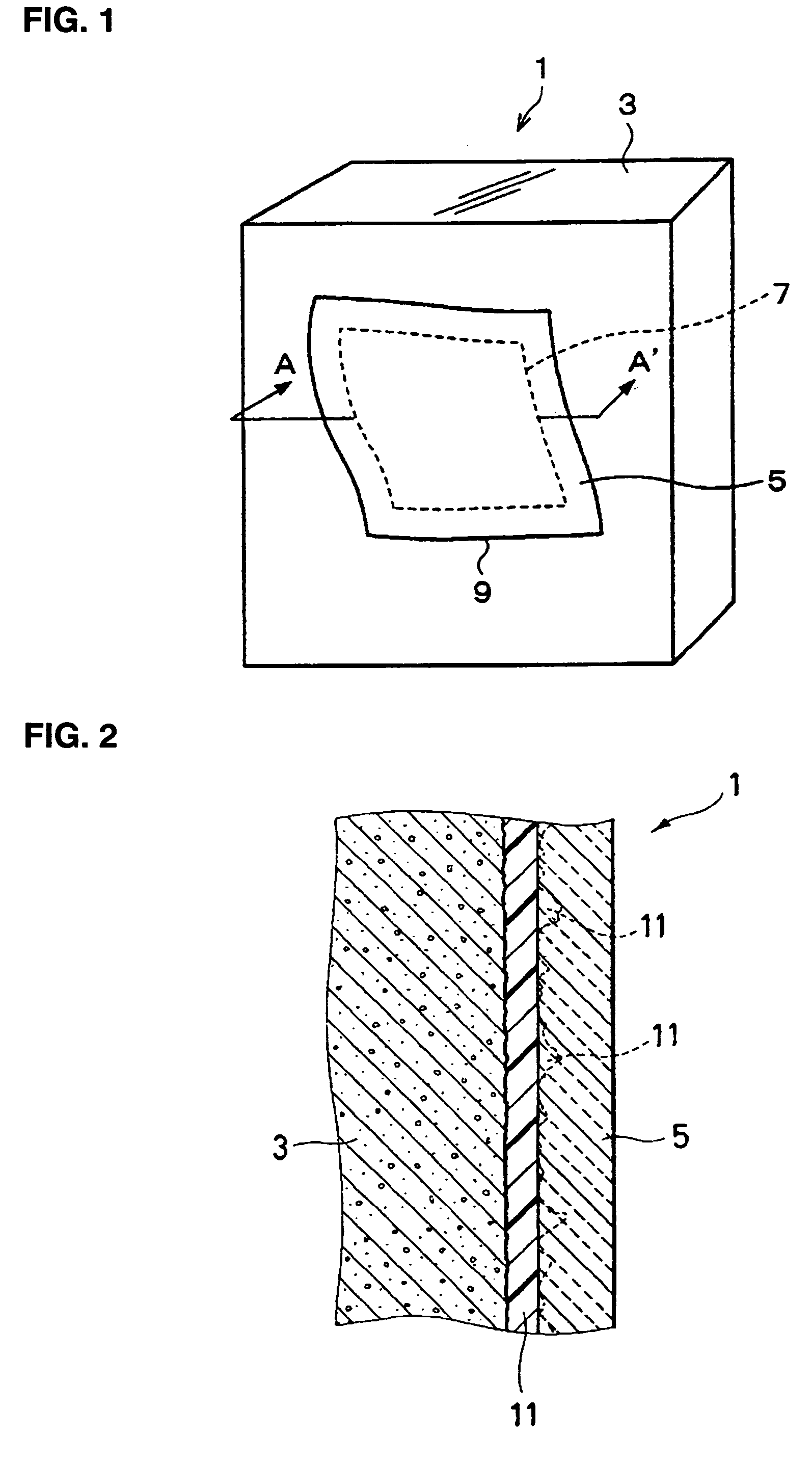
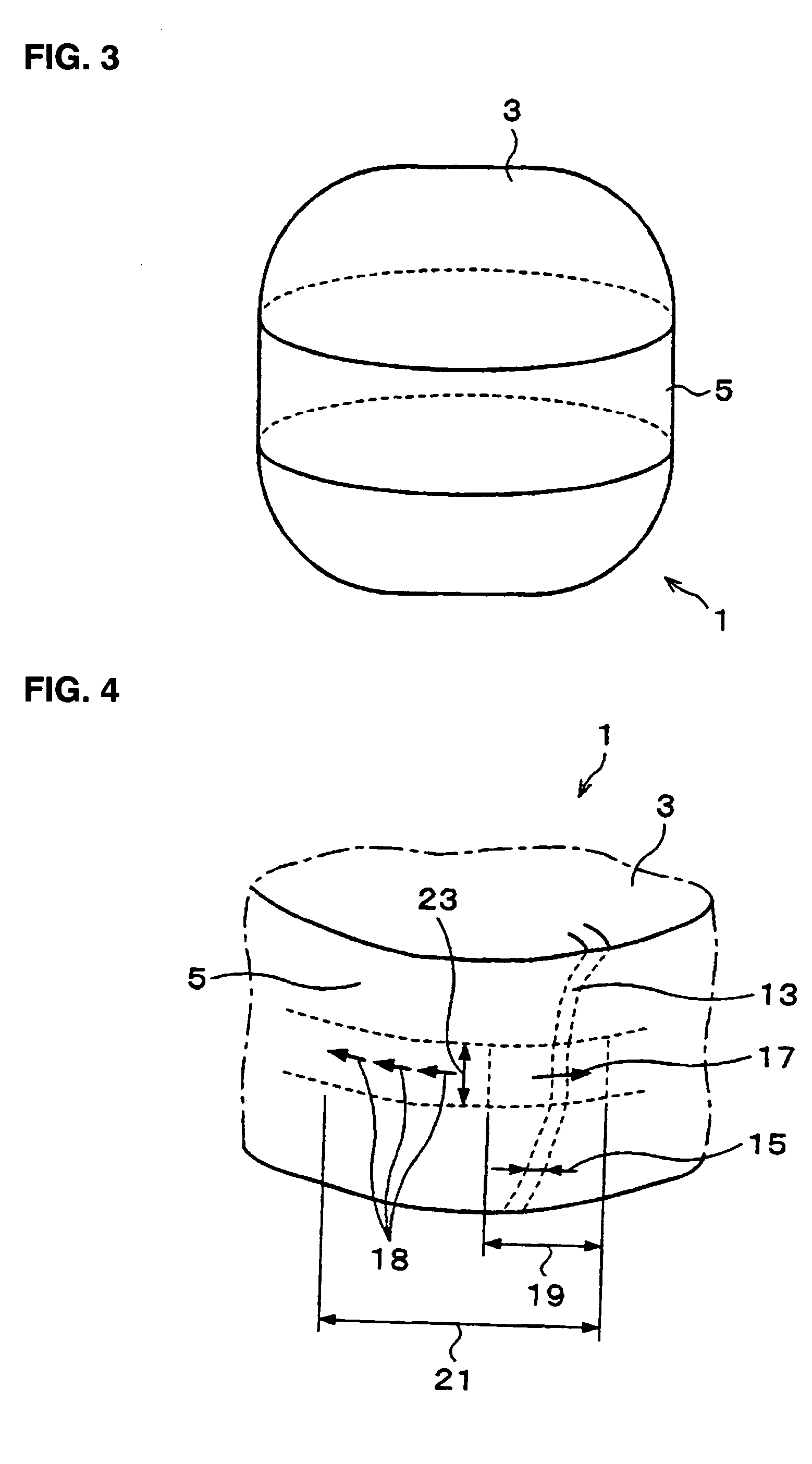
When the polyester belt 199 is used as the reinforcement 185, a column 205 shown in FIGS. 22 to 25 corresponds to the member 181 of FIG. 19. A reinforcement method by use of the polyester belt 199 as shown in FIGS. 22 to 25 will be described in the subsequent section of an
FIG. 21 is a plan view of the polyester belt 199; FIGS. 22 and 23 are perspective views showing examples of the column 205 reinforced by use of a beltlike reinforcement 201; and FIG. 24 is an elevation of the column 205 shown in FIG. 23.
First, reinforcement shown in FIG. 22 will be described. In FIG. 22, a plurality of beltlike reinforcements 201 are disposed at predetermined intervals on the column 205 in such a manner as to be wound about the column 205. End portions of each of the beltlike reinforcements 201, which are wound about the column 205, can be connected together by means of bonding and / or a clasp, which are mechanical joints. Use of mechanical joints can implement reinforcement in a short period of t...
ninth embodiment
The beltlike reinforcement 201 used in the ninth embodiment is not limited to the polyester belt 199. Any material having strength and rigidity equivalent to those of the polyester belt 199 can be used.
The reinforcement method is such that, through control of an increase in crack width 217, the expansion of an apparent volume of a member is restrained. Thus, in principle, the method is identical to that of the previous application. However, the method employs the mechanism of restraining variation in shape and axial strain and is verified theoretically and experimentally, thereby indicating high practical viability thereof.
Next, a structure for enhancing a reinforcement effect for a member involving an irregular profile and a member-to-member joint of the present invention will be described. FIG. 36 is a perspective view showing a state in which connecting reinforcements 269a and 269b are disposed on the joint between a column 261 and a beam 263. The beam 263 is joined to the col...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fracture strain | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fracture strain | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com