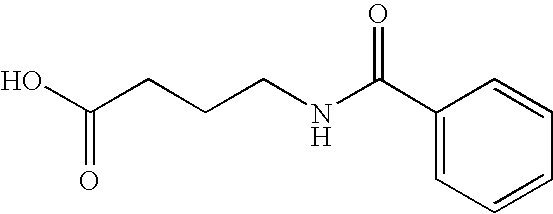
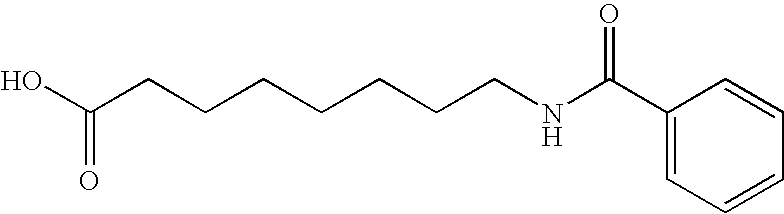
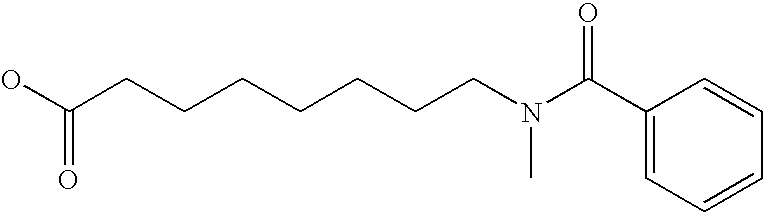
Method for administering glp-1 molecules
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Insulinotropic Activity Determination
[0331] A collagenase digest of pancreatic tissue is separated on a Ficoll gradient (27%, 23%, 20.5%, and 11% in Hank's balanced salt solution, pH 7.4). The islets are collected from the 20.50% / 11% interface, washed and handpicked free of exocrine and other tissue under a stereomicroscope. The islets are incubated overnight in RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine plasma and containing 11 mM glucose at 37° C. and 95% air / 5% CO2. The GLP-1 compound to be studied is prepared at a range of concentrations, preferably 3 nanomolar to 30 nanomolar in RPMI medium containing 10% fetal bovine plasma and 16.7 mM glucose. About 8 to 10 isolated islets are then transferred by pipette to a total volume of 250 μL of the GLP-1 compound containing medium in 96-well microtiter dishes. The islets are incubated in the presence of the GLP-1 compound at 37° C., 95% air, 5% CO2 for 90 minutes. Then aliquots of islet-free medium are collected and 100 μl t...
example 2
Glp-1 Stability in the Presence of Dpp IV
[0332] The stability of each GLP-1 molecule can be determined by incubation of the GLP-1 molecule in human plasma. Plasma (800 μL), obtainable from healthy human volunteers, is incubated at 37° C. with 300 pmol / L of a GLP-1 molecule for up to six hours. This is followed by reversed phase HPLC and RIA according to Deacon, et al., in J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 80: 952-957 (1995).
example 3
Formulation of Delivery Agent Number 15
[0333] Approximately 600 mg of delivery agent number 15 was weighed into Type I glass vials to which 3 mL of base (0.1 N NaOH, pH 12.7) was added to achieve a final concentration of 200 mg / mL. The pH was adjusted to 7.1 and the concentration was estimated to be 171 mg / mL. Delivery agent number 15 was then diluted to 150 mg / mL with Milli-Q® water.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com