Method for manufacturing a composite material
a manufacturing method and composite material technology, applied in the field of composite material manufacturing methods, can solve the problems of difficult to predict the dimensions of the final product, difficult to obtain a proper “balance” between the individual components of the composite material, and difficult to achieve the effect of enhancing the e-modulus, improving form stability, and reducing shrinkag
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
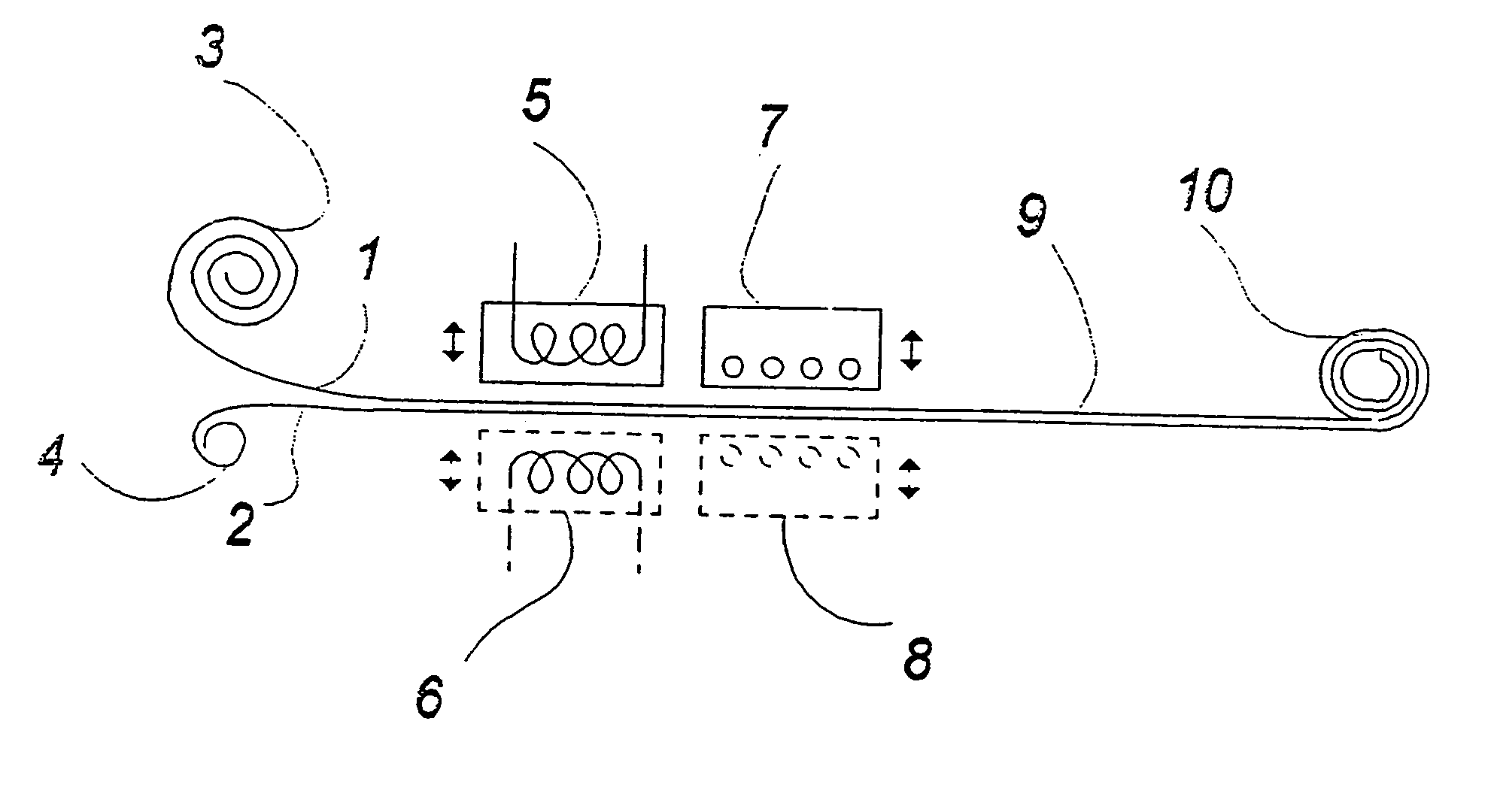
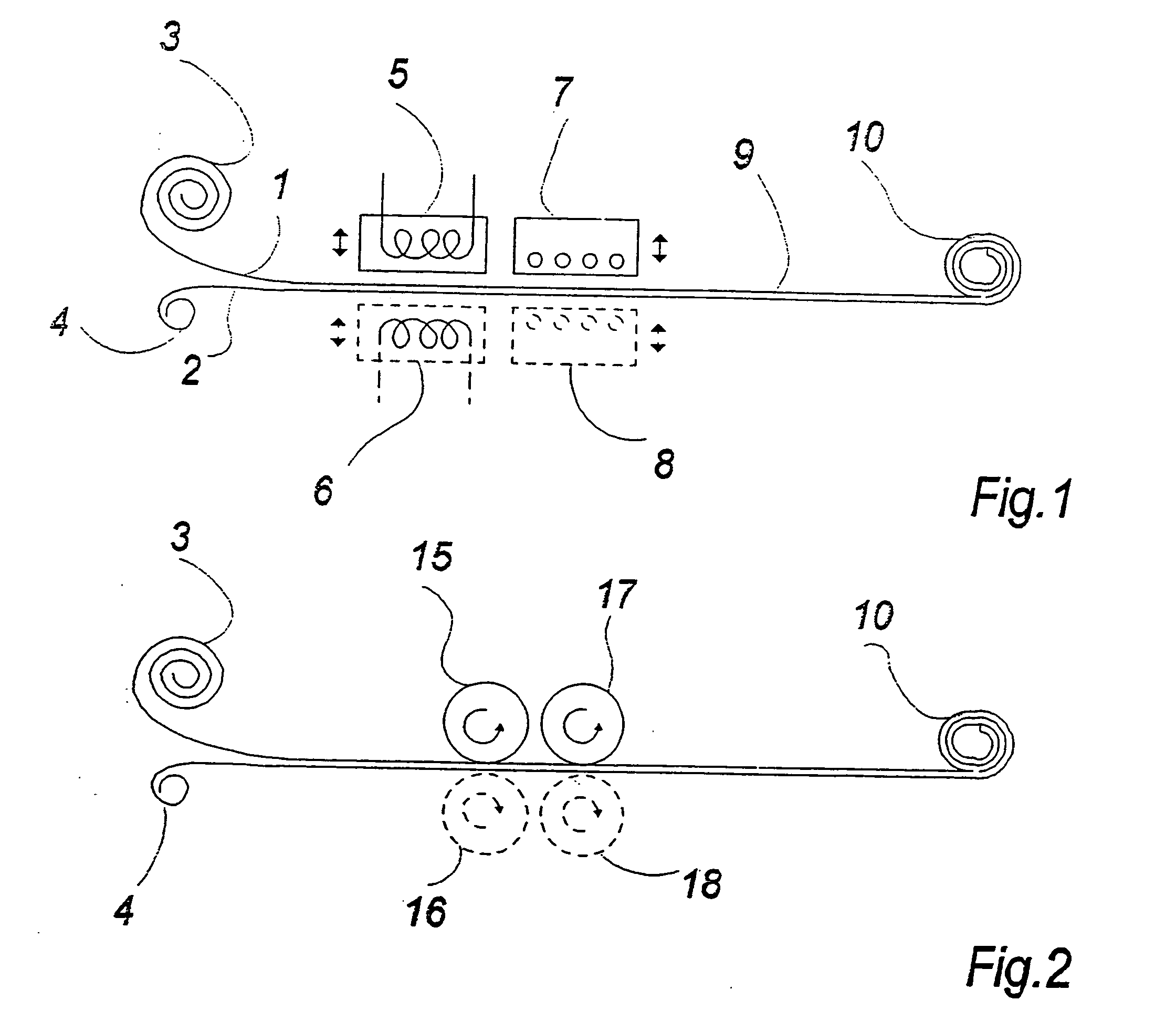
[0044] In FIG. 1 a schematic view of a preferred automated embodiment according to the invention is shown.
[0045] In this embodiment, the apparatus is fed by endless webs of PTFE foil 1 and PTFE coated glass fibre fabric 2 from a roll of PTFE foil 3 and a roll of PTFE coated glass fibre fabric 4. The finished composite 9 is wound up on a roll 10.
[0046] According to this embodiment the webs 1 and 2 move relative to the apparatus. The rollers 3, 4 and 10 are rotated by forwarding means (not shown in FIG. 1) in an intermittent movement between two cooperating heated pressure surfaces 5 and 6. These pressure surfaces 5, 6 are connected to hydraulic pressure- and movement means (not shown in FIG. 1) and adapted to perform a relative movement to and from the two webs 1 and 2.
[0047] The above stepwise movement in the longitudinal direction essentially corresponds to the pressure surfaces 5, 6.
[0048] When the stepwise movement has fed two new partial lengths of foil 1 and glass fabric 2 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| shrinkage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com