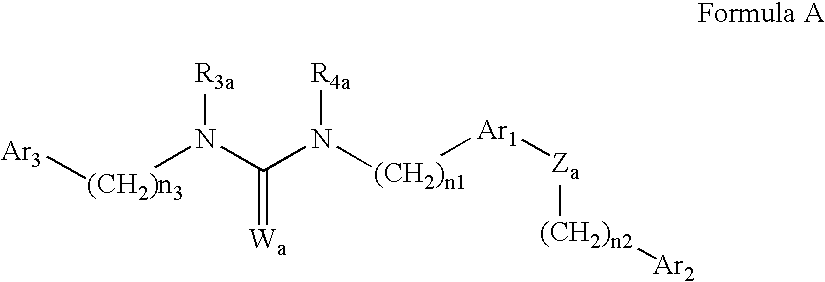
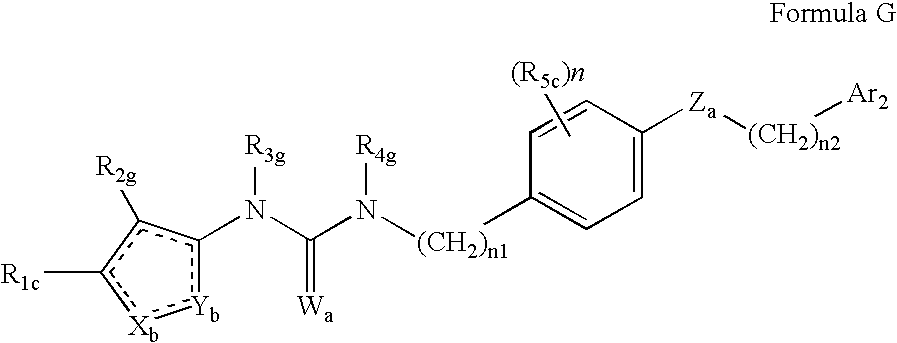
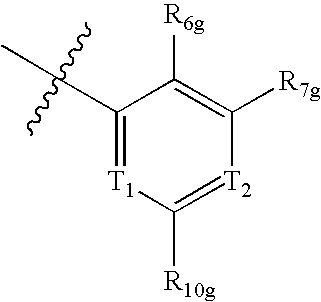
Urea derivatives as ABL modulators
a technology of urea derivatives and modulators, applied in the field of compounds, can solve problems such as poor patient prognosis, and achieve the effects of reducing the toxicity of inhibitory compounds, accurate targeting, and inhibiting kinase activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example a
Synthesis of Isoxazole-Ureas
[0201]
[0202] A mixture of amine 1 (1 eq) in dry THF is stirred at room temperature under argon for an hour. Then the stirred suspension is cooled to 0° C. and to it is added dropwise a solution of phosgene or disuccinimidyl carbonate or carbonyl diimidazole (1.2 eq). The reaction is stirred at 0° C. for half an hour. An isoxazol-amine 2 in THF is added dropwise and the reaction is allowed to warm to room temperature and stirred overnight. The solvent is removed and extracted with ethyl acetate and water. The organic layer is dried over magnesium sulfate and solvent removed, and the product 3 purified by HPLC.
[0203] Alternatively, to a stirring solution of an isoxazol-amine 2 (1 eq) in THF, a mixture of 4-nitrophenyl chloroformate (1.2 eq) and triethyl amine (1.2 eq) is added dropwise at 0° C. The reaction is stirred for two hours at room temperature and the aniline 1 is added. The reaction is refluxed to 80° C. for six hours. The mixture is cooled to r...
example b
Synthesis of alkyl-ureas
Synthesis of Compound B1: 1-(4-methoxybenzyl)-3-(5-tert-butylisoxazol-3-yl)urea
[0209]
[0210] To a flask 5-tert-Butyl-3-isocyanato-isoxazole (242 mg, 1 eq) and substituted benzylamine (1 eq) was added and dissolved in toluene. The reaction was allowed to stir at 50° C. for three hours. The solvent removed and the mixture was purified by HPLC. Yield: 188 mg (47%).
[0211] Compounds B2 through B8 were synthesized in a manner analogous to Compound B1 using similar starting materials and reagents. The structures are shown below in Table B:
TABLE BNO.CHEMICAL STRUCTUREB1B2B3B4B5B6B7B8
example c
Synthesis of Reactive Ureas
Synthesis of Compound C1: 1-(5-tert-butylisoxazol-3-yl)-3-(4-aminophenyl)urea
[0212]
[0213] To a flask 5-tert-Butyl-3-isocyanato-isoxazole (242 mg, 1 eq) and substituted aniline (159 mg, 1 eq) was added and dissolved in toluene. The reaction was allowed to stir at 50° C. for three hours. The solvent removed and the mixture was purified by HPLC. Yield: 188 mg (47%).
[0214] Compounds C2 through C3 were synthesized in a manner analogous to Compound C1 using similar starting materials and reagents. The structures are shown below in Table C:
TABLE CNO.CHEMICAL STRUCTUREC1C2C3
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length of time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com