Conductive filament
a technology of conductive filament and conductive filament, which is applied in the direction of weaving, transportation and packaging, yarn, etc., can solve the problems of flaking or peeling, severe deterioration of yarn properties, and inability to completely accep
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
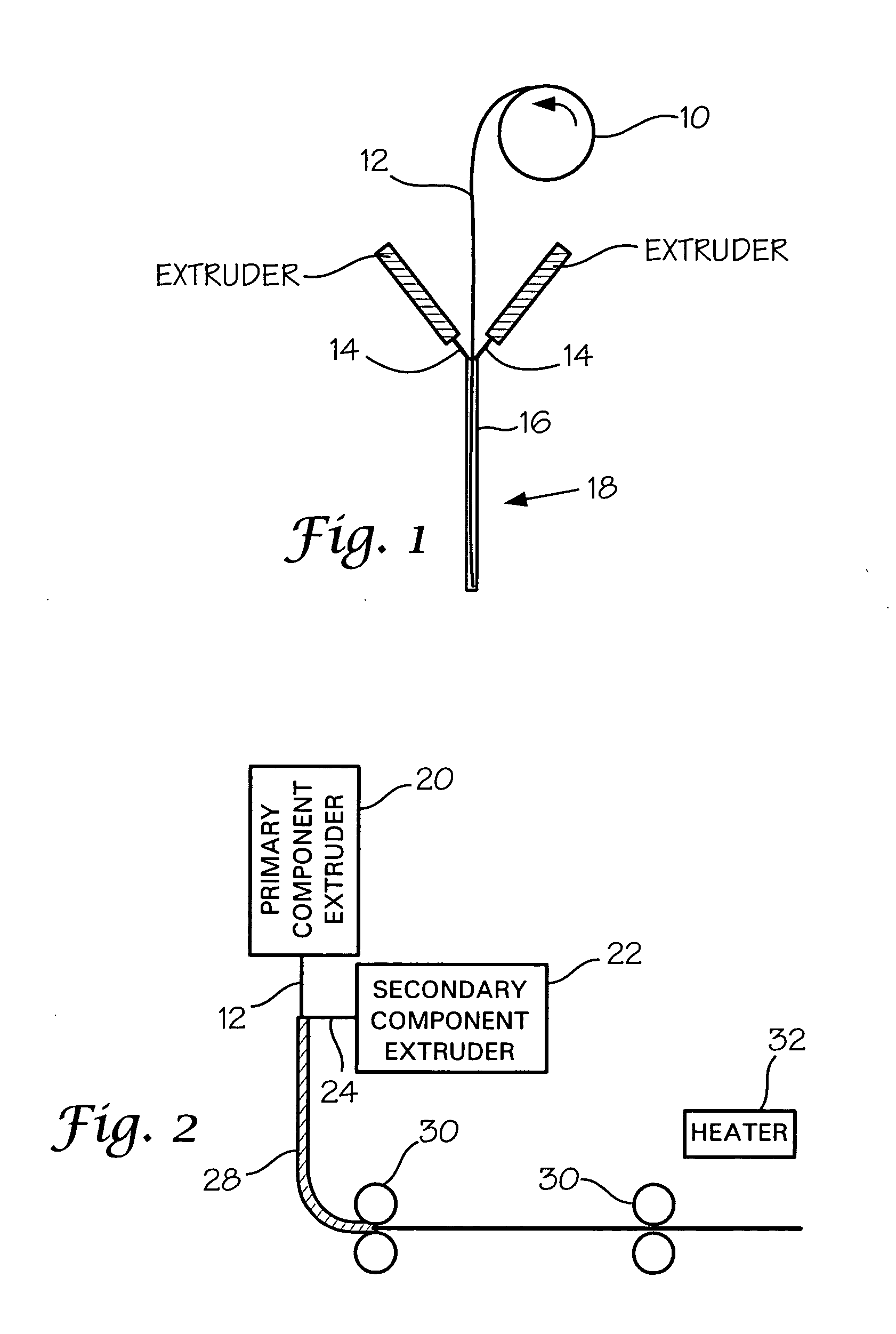
[0035] Referring now in more detail to the drawings, the invention will now be described in more detail.
[0036] Carbon nanotubes are extremely small conductive elements which have found use with polymers as a conductive additive. A primary advantage of carbon nanotubes is that they possess a higher aspect ratio than carbon black particles or chopped carbon which allows for a lower additive loading while maintaining adequate levels of conductivity.
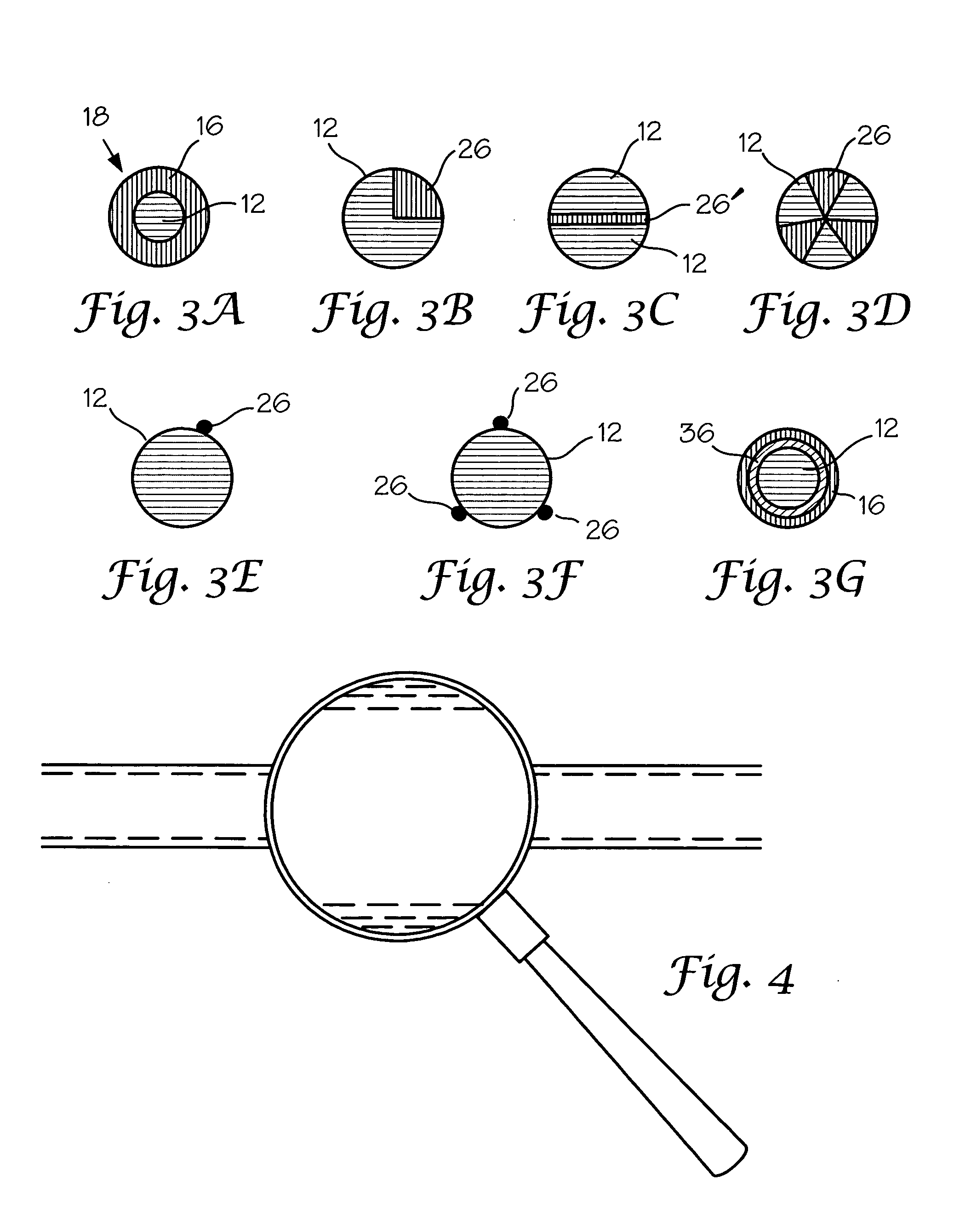
[0037] Carbon nanotubes comprise elongated particles which tend to intertwine and have a low sensitivity to shear fields. This provides the capability of elongating the polymeric resin containing carbon nanotubes without entirely severing the carbon nanotube agglomerates which are formed within the polymer. FIG. 4 schematically shows generally the manner in which carbon nanotubes can be distributed in a polymeric resin.
[0038] In a conductive yarn it has been most difficult to produce a yarn which retains most of the desired fiber characte...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com