Method and apparatus for reducing segregation in metallic ingots
a technology of segregation and ingots, which is applied in the direction of manufacturing tools, moulding machines, and foundation moulding apparatus, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the life of low cycle fatigue (lcf) products, exhibiting significant macro-segregation defects in the ingots produced by esr from such alloys, and reducing the size of the ingot produced by esr, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing macro-segregation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
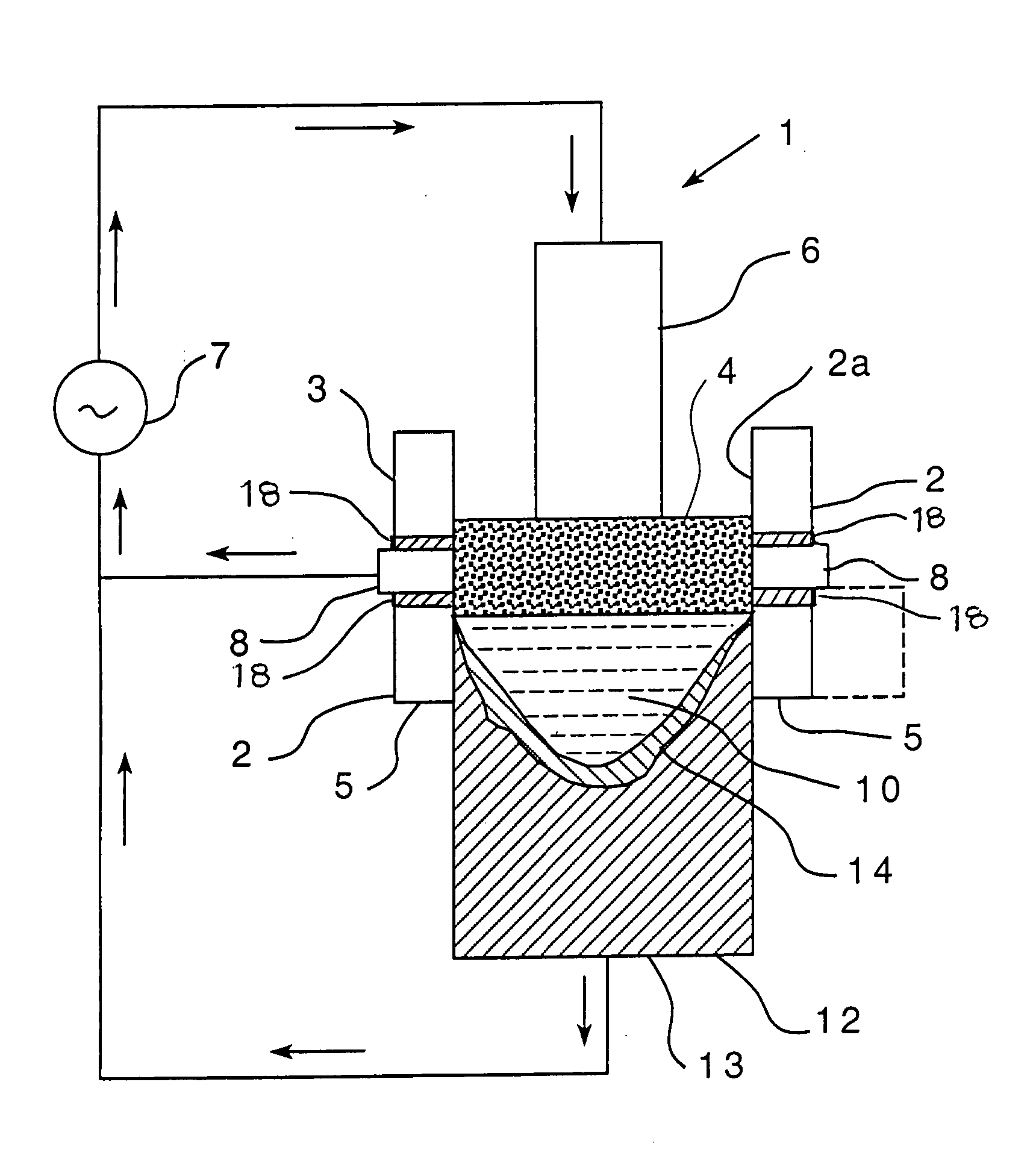
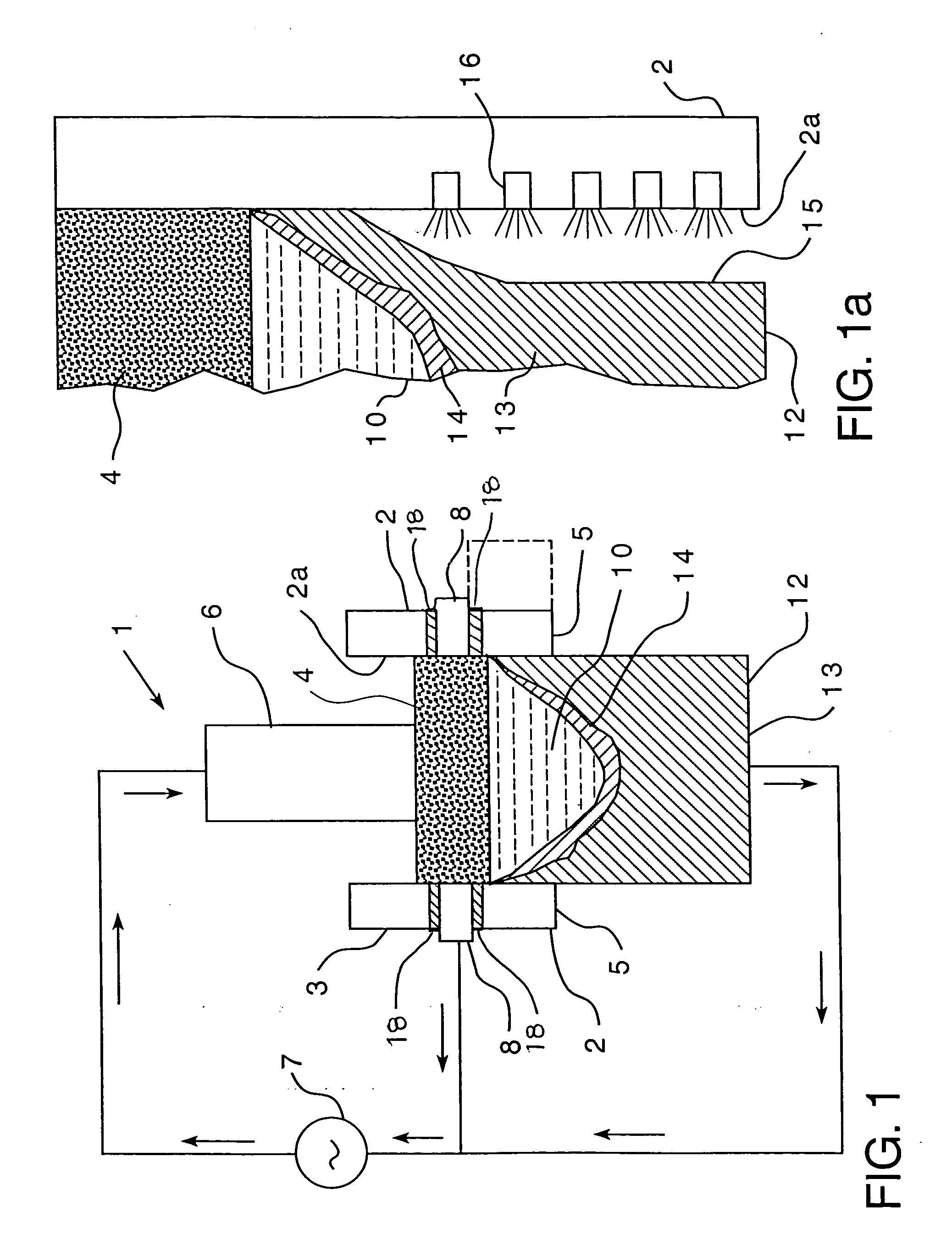
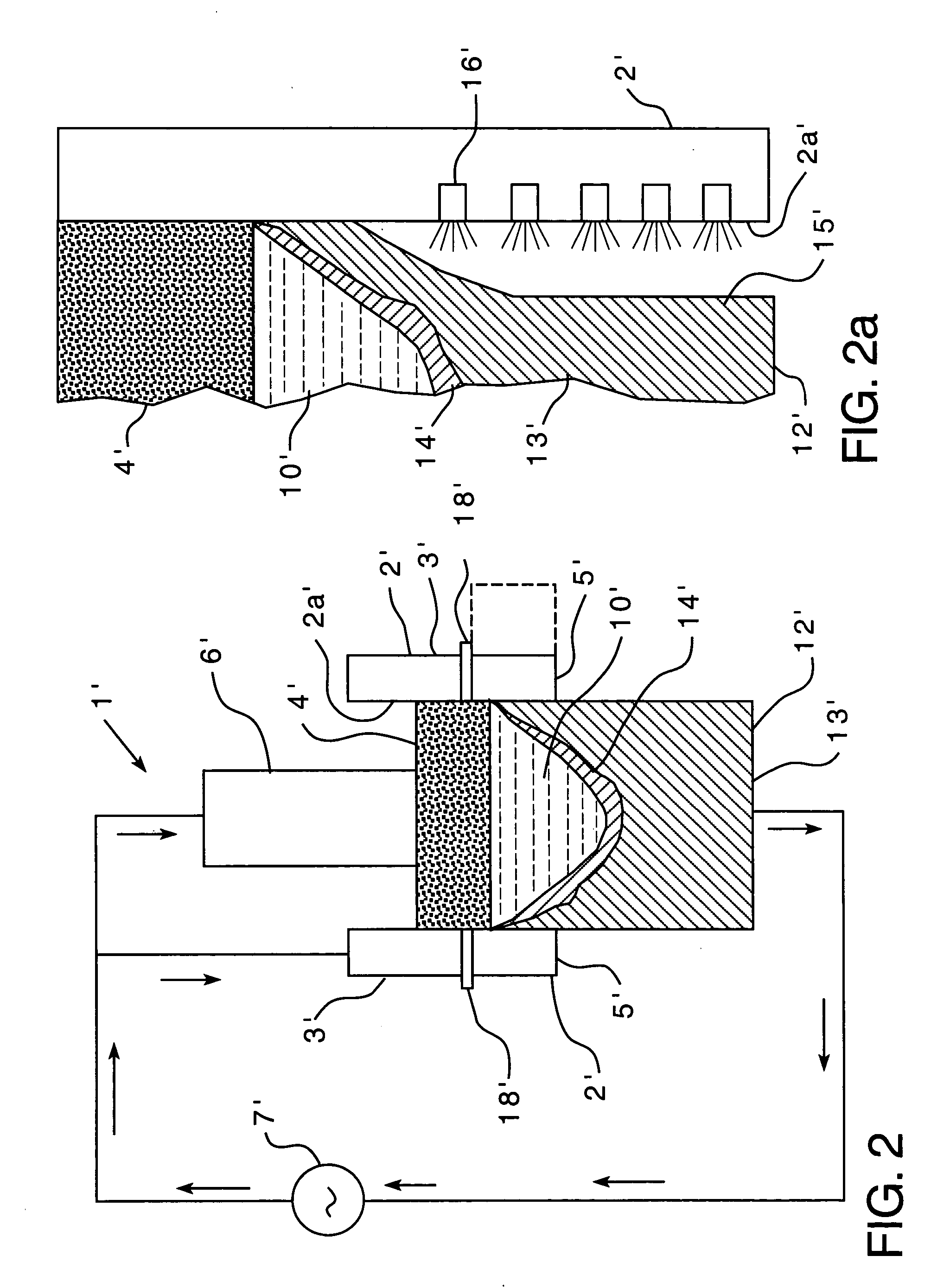
[0022] Each of the non-limiting embodiments described herein is believed to be useful in the manufacture of large diameter ingots of metallic (i.e., metal-containing) alloys, wherein use of conventional ESR methods would result in macro-segregation within the ingot. It will be understood, however, that the use of the embodiments described herein is not so limited, and the embodiments may be employed in, for example, the production of metallic ingots of any size, including large diameter ingots. As noted above, as used herein, “large diameter” refers to diameters greater than 16 inches (about 0.40 m). Thus, for example, and without limiting the present disclosure in any way, ingots having diameters of 20 inches (about 0.508 m) and 38 inches (about 0.965 m) may be made according to methods disclosed herein. Also, as used herein, “metallic ingot” and “metallic alloy” refer to, respectively, an ingot and an alloy that are at least partially composed of metal.
[0023] By way of example on...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameters | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com