Piston compressor
a compressor and piston technology, applied in the field of piston compressors, can solve the problems affecting the performance of the compressor, and easily generating noise due to self-excited vibration, and achieving the effect of reducing the suction resistance of gas
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
[0034] The invention of claim 1 will now be described. A swash plate type variable displacement compressor 10 will now be described.
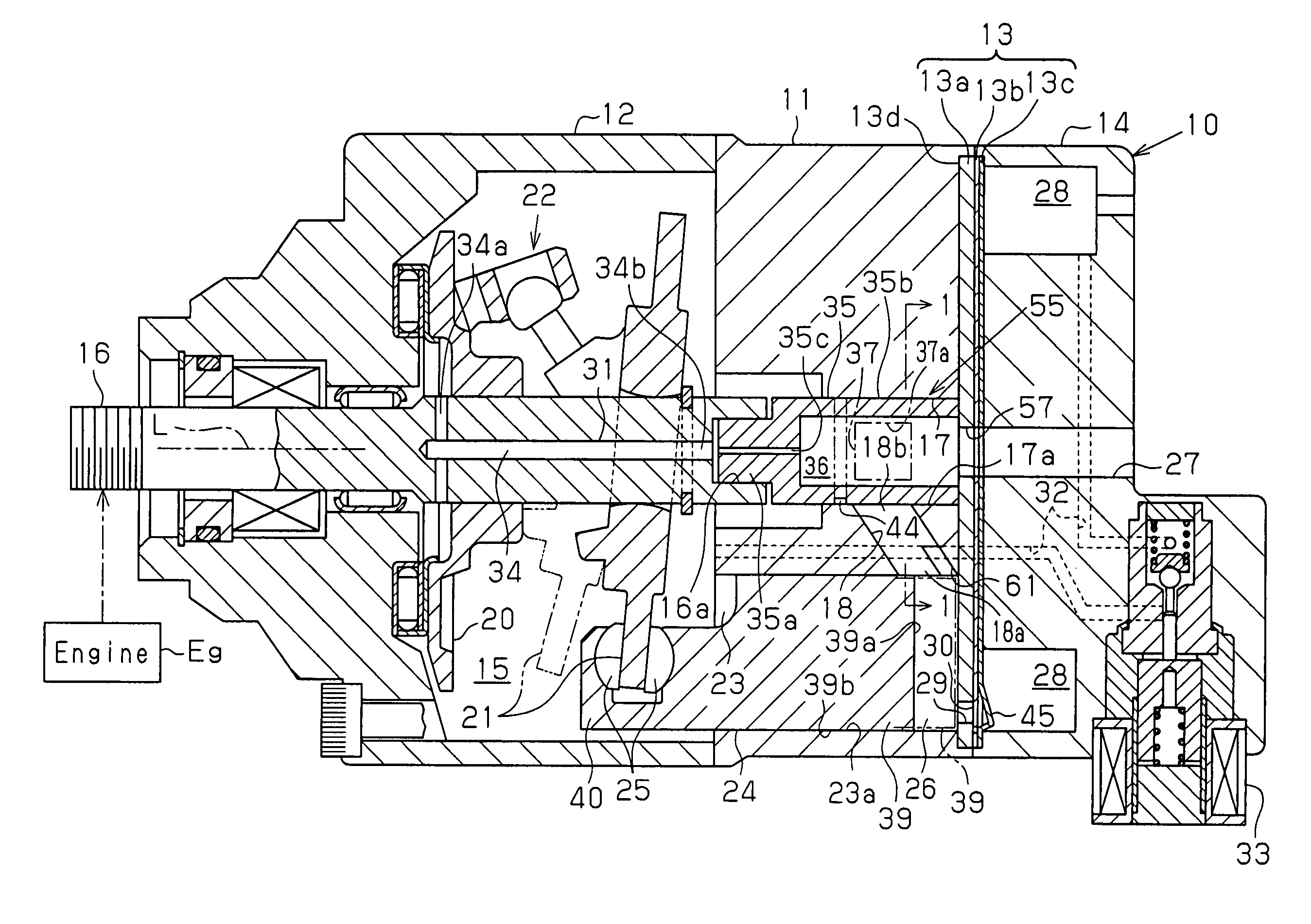
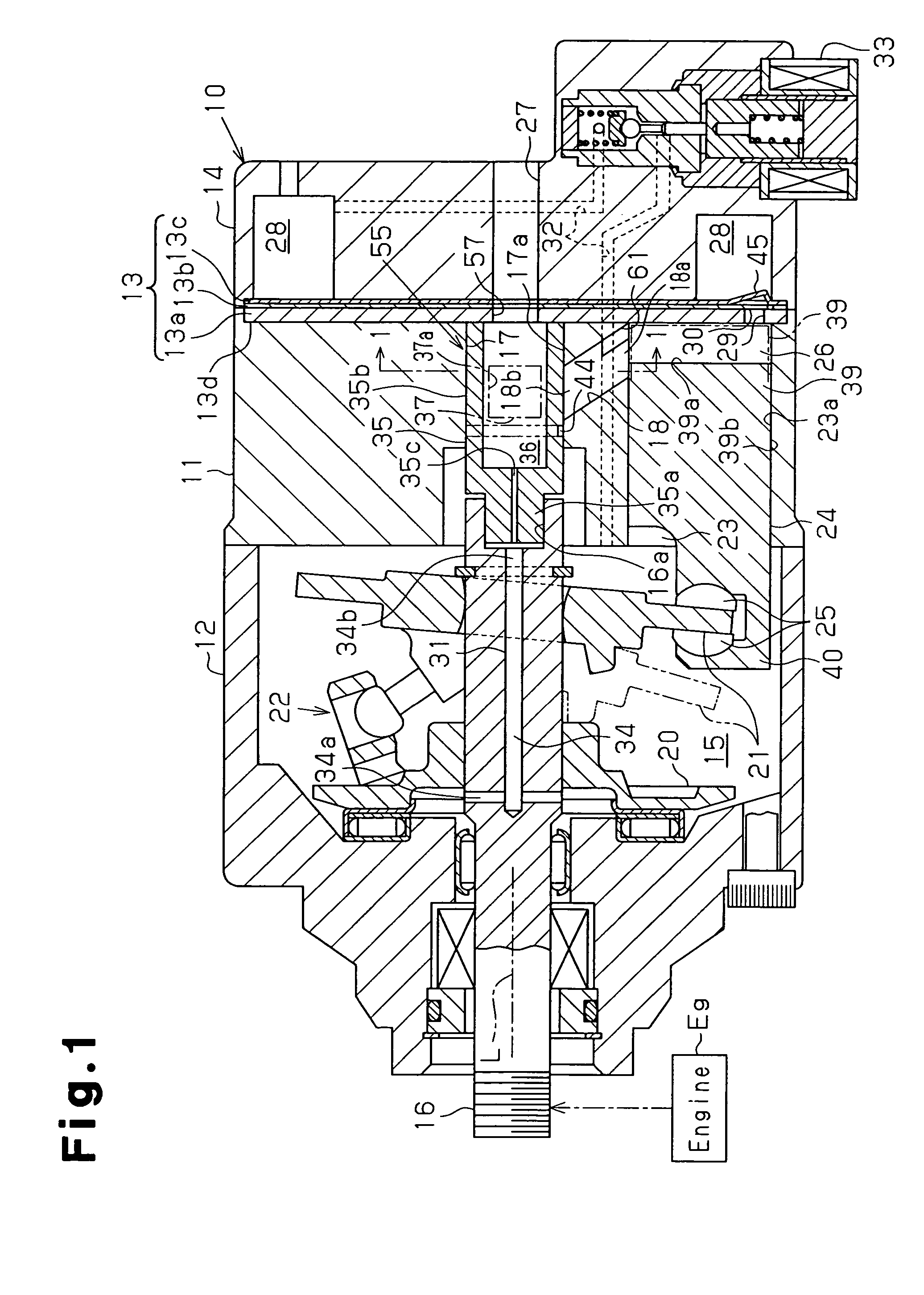
[0035]FIG. 1 shows a longitudinal cross-section of the compressor 10: The left end of the compressor 10 in FIG. 1 is defined as the front of the compressor 10, and the right end is defined as the rear of the compressor 10. As shown in FIG. 1, the compressor 10 includes a cylinder block 11, a front housing member 12, a valve assembly 13, and a rear housing member 14. The front housing member 12 is secured to the front end of the cylinder block 11. The rear housing member 14 is secured to the rear end of the cylinder block 11 with the valve assembly 13 in between. The valve assembly 13 includes a port plate 13a, a discharge valve flap plate 13b, and a retainer plate 13c, which are laminated from the cylinder block 11 toward the rear housing member 14 in this order. The cylinder block 11, the front housing member 12, and the rear housing member 14 form a ...
fourth embodiment
[0079] Since the compressor 10 of the fourth embodiment includes the discharge ports 29, 51 for each compression chamber 26, refrigerant gas is smoothly discharged to the discharge chamber 28 from the compression chamber 26. Therefore, excess compression of refrigerant gas is prevented and power loss of the compressor 10 is reduced. The two discharge ports 29, 51 are selectively opened and closed by one discharge valve 30. Specifically, each second discharge port 51 is selectively opened and closed by the proximal end of the corresponding discharge valve 30. Flow of refrigerant gas is thus generated at the proximal portion of the discharge valve 30 during the discharge stroke, which prevents clogging of a foreign object in the second discharge port 51. Accordingly, during the suction stroke and the compression stroke, the first and second discharge ports 29, 51 are reliably closed by the corresponding discharge valve 30. This improves the efficiency of the compressor 10.
[0080] In th...
second embodiment
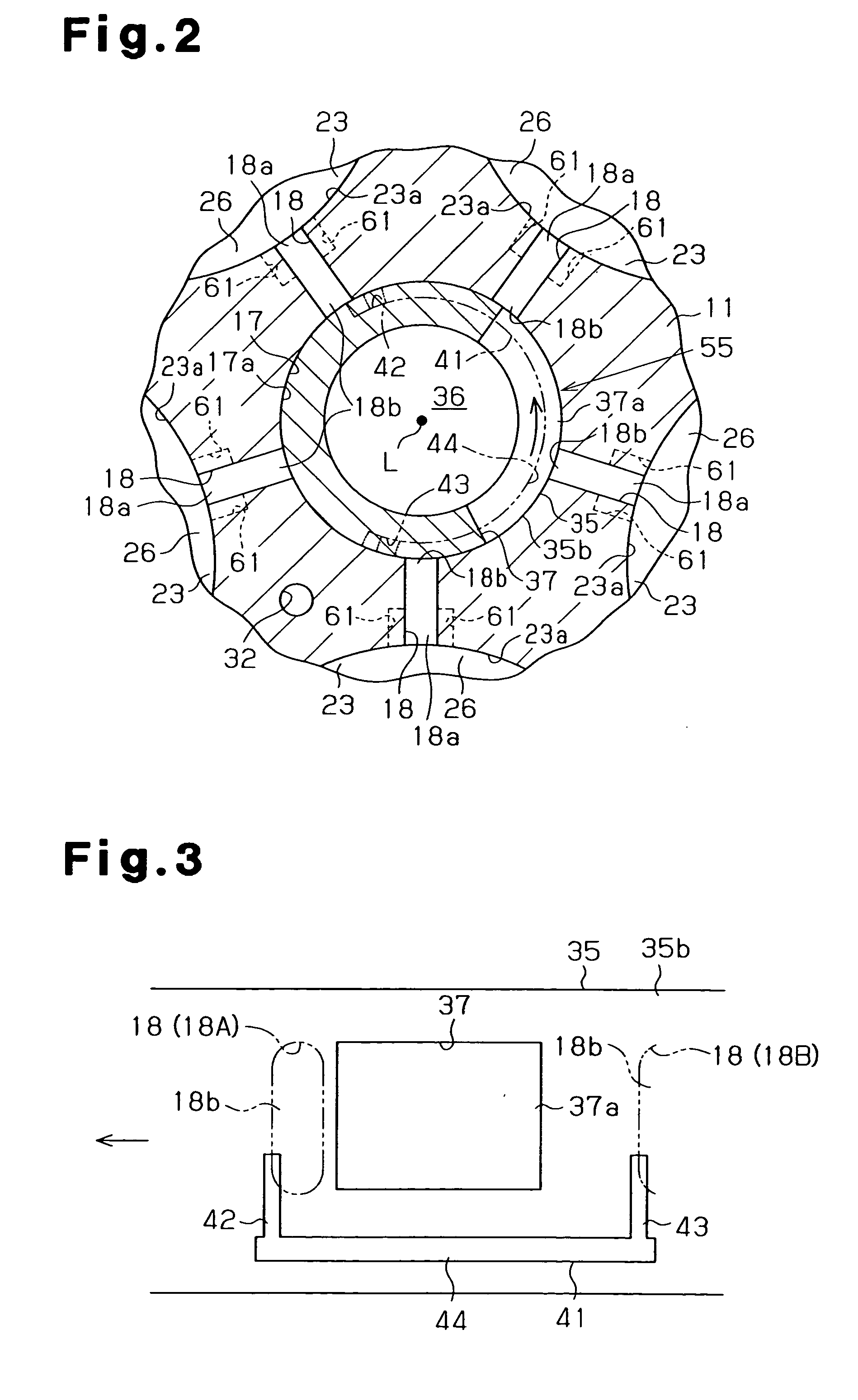
[0085] In the second embodiment, the suction auxiliary portion 64 is formed by cutting off part of the periphery of the end face 39a of each piston 24 (see FIG. 6). This is possible since the compressor 10 has a structure for preventing rotation of each piston 24 about its own axis by the abutment between the neck 40 of the piston 24 and the swash plate 21 or the abutment between the neck 40 and the housing (for example, the front housing member 12). That is, each suction auxiliary portion 64 will not be displaced from the outlet 18a of the corresponding introducing passage 18 by a large amount about the axis of the piston 24.
[0086] However, in a case with a piston compressor that does not have the structure for preventing rotation of the pistons 24 (such as a wobble type compressor), the entire periphery of the end face 39a of each piston 24 is cut off (chamfered) to form the suction auxiliary portion 64 so that the suction auxiliary portion 64 faces the outlet 18a of the correspon...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com