Method and apparatus for online sample interval determination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
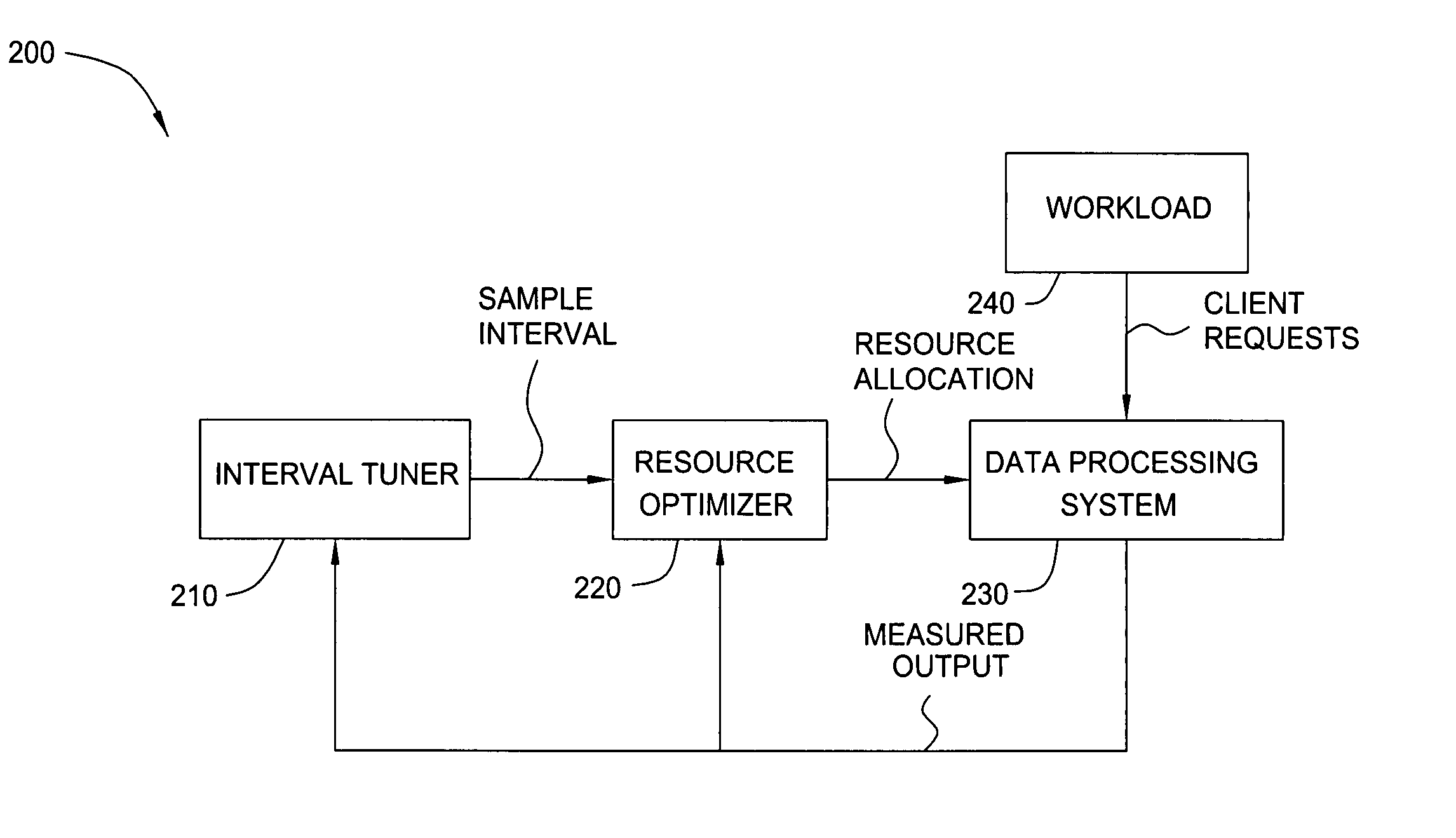
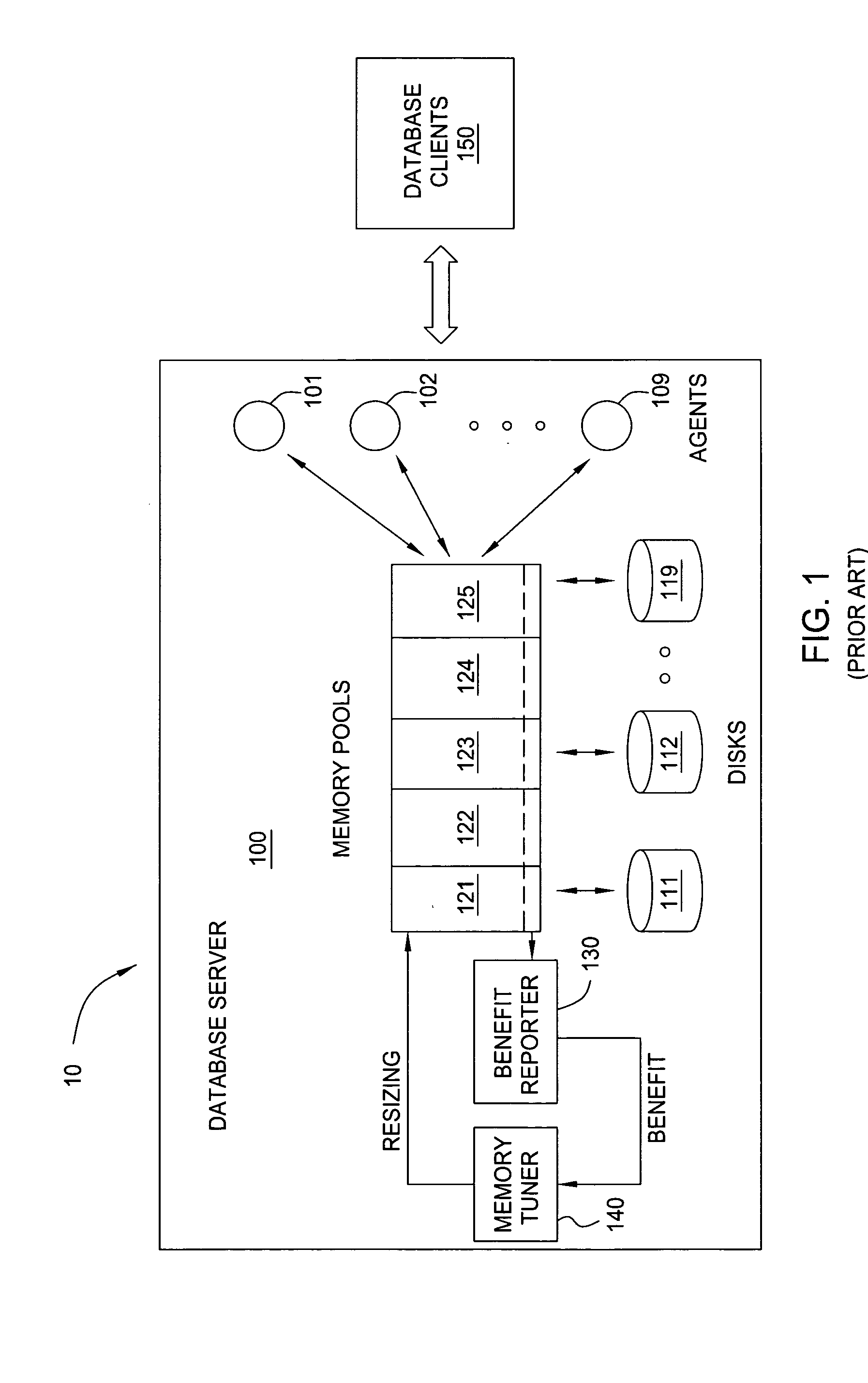
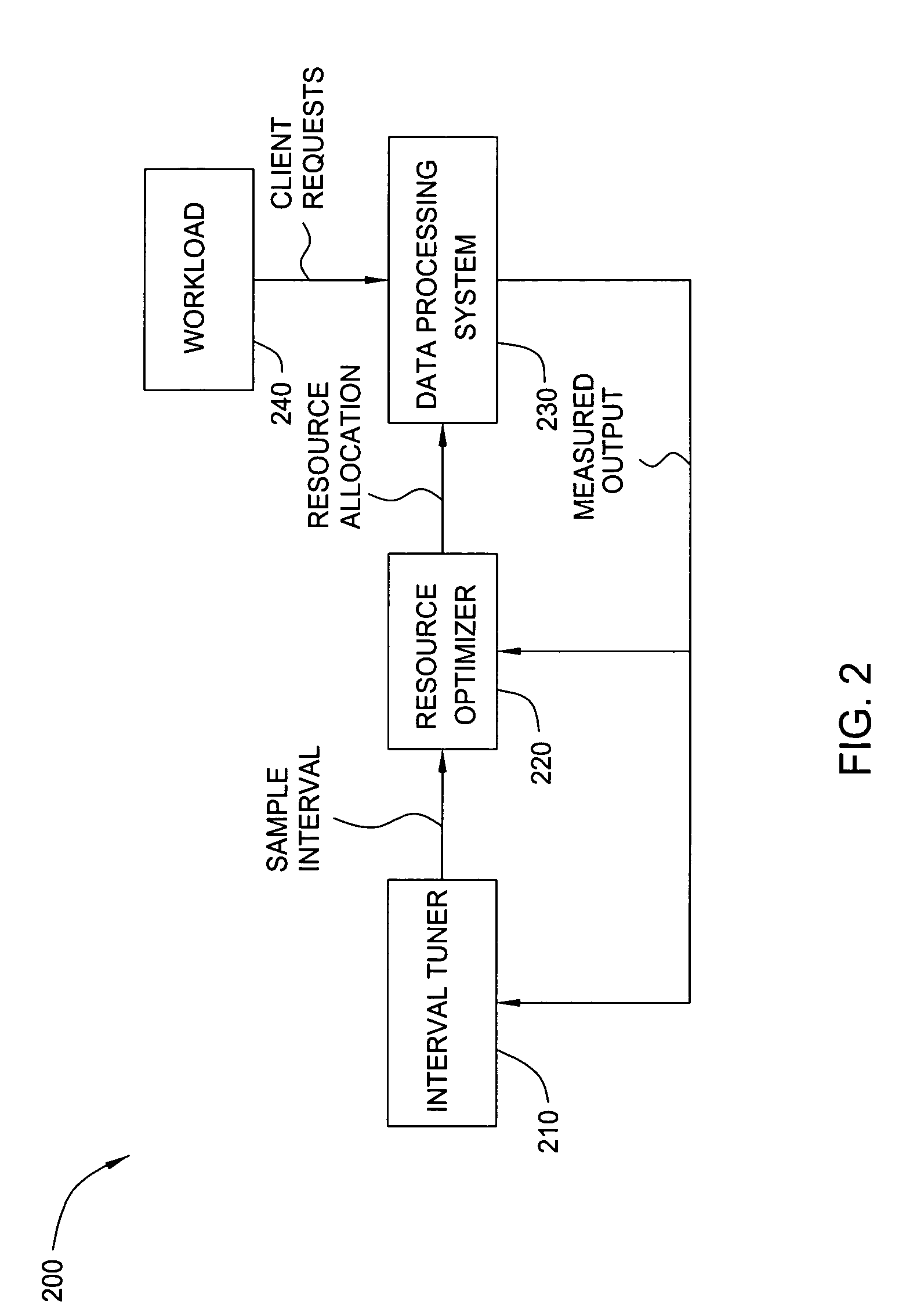
[0018] In one embodiment, the present invention provides a method for online determination of a sample interval for collecting measured output data of computing systems dealing in dynamic (e.g., non-stationary) workloads. In one embodiment, the method is implemented in a data processing system such as that illustrated in FIG. 1, and operates to adjust memory allocation to a plurality of memory pools. Since the total size of a system's memory pools is fixed, increasing the size of one memory pool necessarily means decreasing the size of another pool. Care must be taken in determining when and how frequently to adjust the allocations to the memory pools. If adjustments are made too frequently, the benefit data can be corrupted by substantial random factors in memory usage; however, because, the workload varies over the time and the memory tuner needs to be responsive in determining the optimal memory allocations, memory allocation adjustments must not be made too infrequently either. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com