Flip-flop circuit
a flip-flop circuit and circuit technology, applied in the field of flip-flop circuits, can solve the problems of difficult design and development of circuits including such flip-flop circuits, difficult to extract physical characteristics that are to be registered in a library as those of standard cells, and processing becomes very complicated, so as to achieve the effect of easy holding and outpu
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
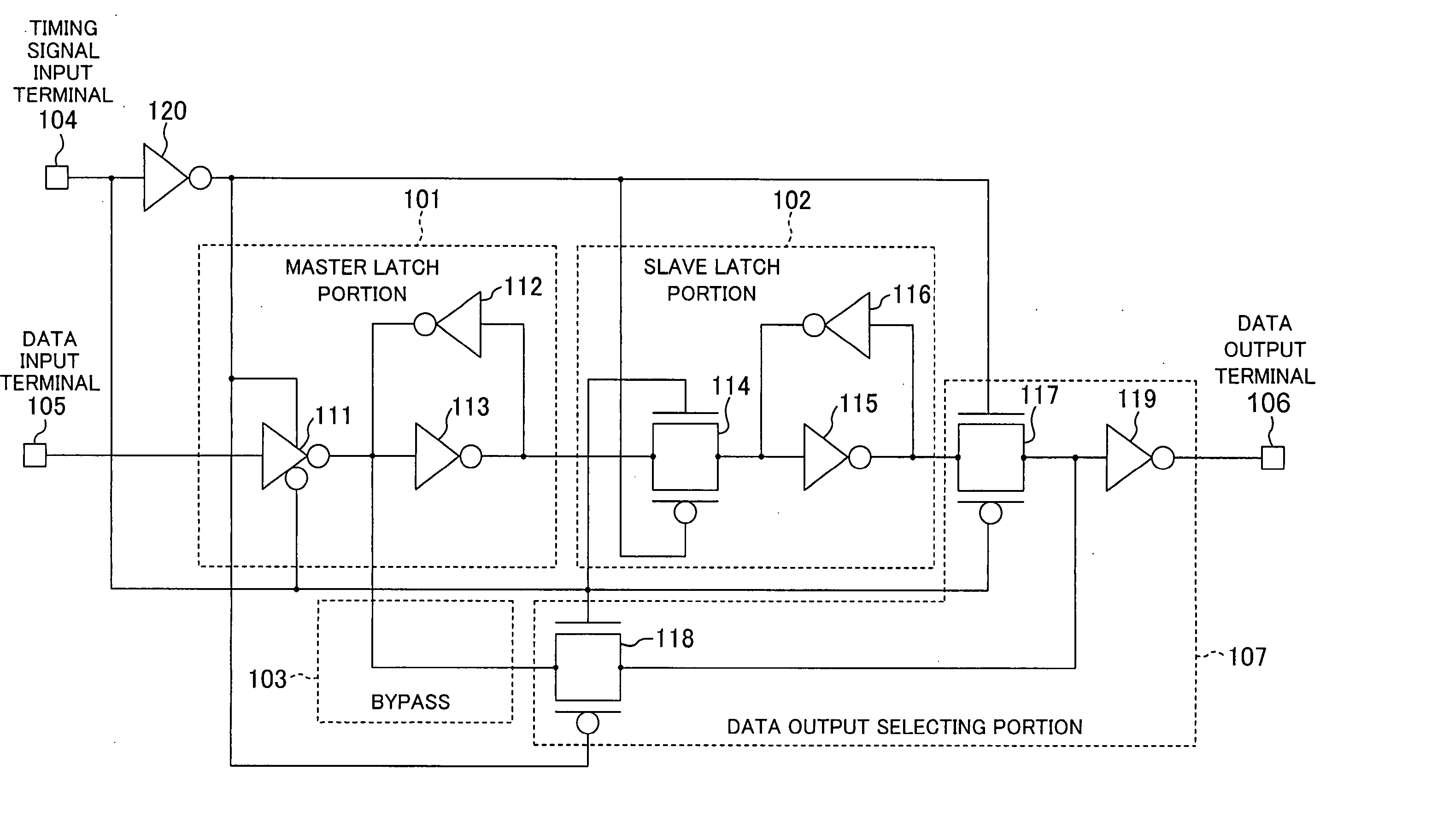
[0030]FIG. 1 is a circuit diagram illustrating a flip-flop circuit according to a first embodiment of the present invention.
[0031] A master latch portion 101 includes: a tri-state inverter 111; an inverter 112; and an inverter 113. The master latch portion 101 performs latch operation for allowing data to be written therein when a timing signal input from a timing signal input terminal 104 is “0” (e.g., at an L level) and holding data when the timing signal is “1” (e.g., at an H level). The inverter 112 has a driving capability lower than that of the tri-state inverter 111.
[0032] A slave latch portion 102 includes: a pass gate 114; an inverter 115; and an inverter 116. The slave latch portion 102 holds data when the timing signal is “0” and allows data to be written therein when the timing signal is “1”. The inverter 116 has a driving capability lower than that of the tri-state inverter 113 connected thereto via the pass gate 114.
[0033] A bypass 103 is a signal line for outputtin...
embodiment 2
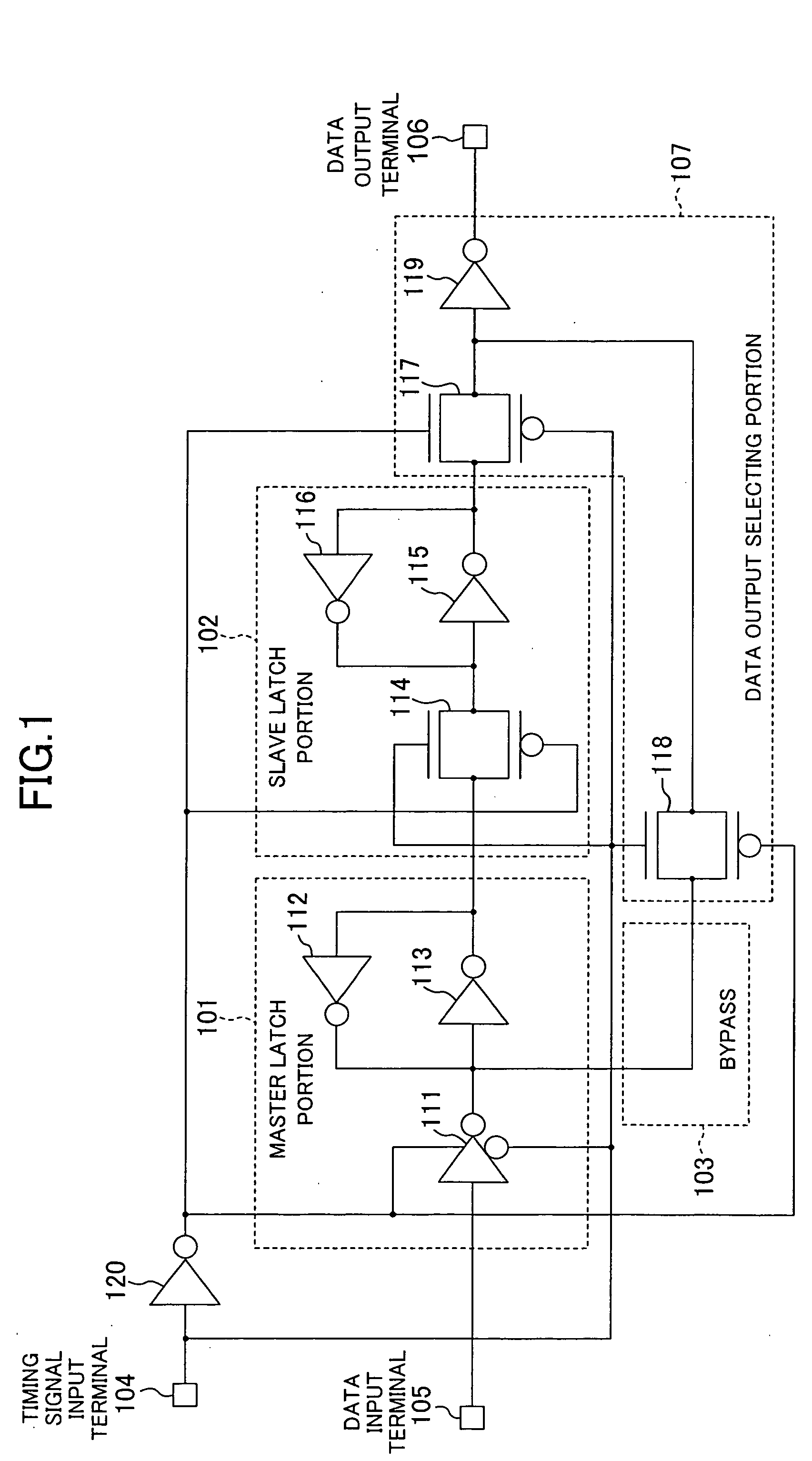
[0047] Instead of the master latch portion 101 and the slave latch portion 102 including the inverters 112 and 116, respectively, of the first embodiment, a master latch portion 201 and a slave latch portion 202 including tri-state inverters 212 and 216, respectively, may be used as shown in FIG. 2.
[0048] The tri-state inverters 212 and a tri-state inverter 111 operate at different states of a timing signal, and the tri-state inverter 216 and a pass gate 114 also operate at different states of the timing signal. Accordingly, the outputs of the tri-state inverter 212 and the tri-state inverter 111 do not conflict with each other, and the outputs of the tri-state inverter 216 and the pass gate 114 do not conflict with each other.
[0049] With this configuration, holding operation of input data itself is also the same as that in the conventional flip-flop circuit, as described in the first embodiment.
[0050] In addition, irrespective of the state of the timing signal, only the gate ter...
embodiment 3
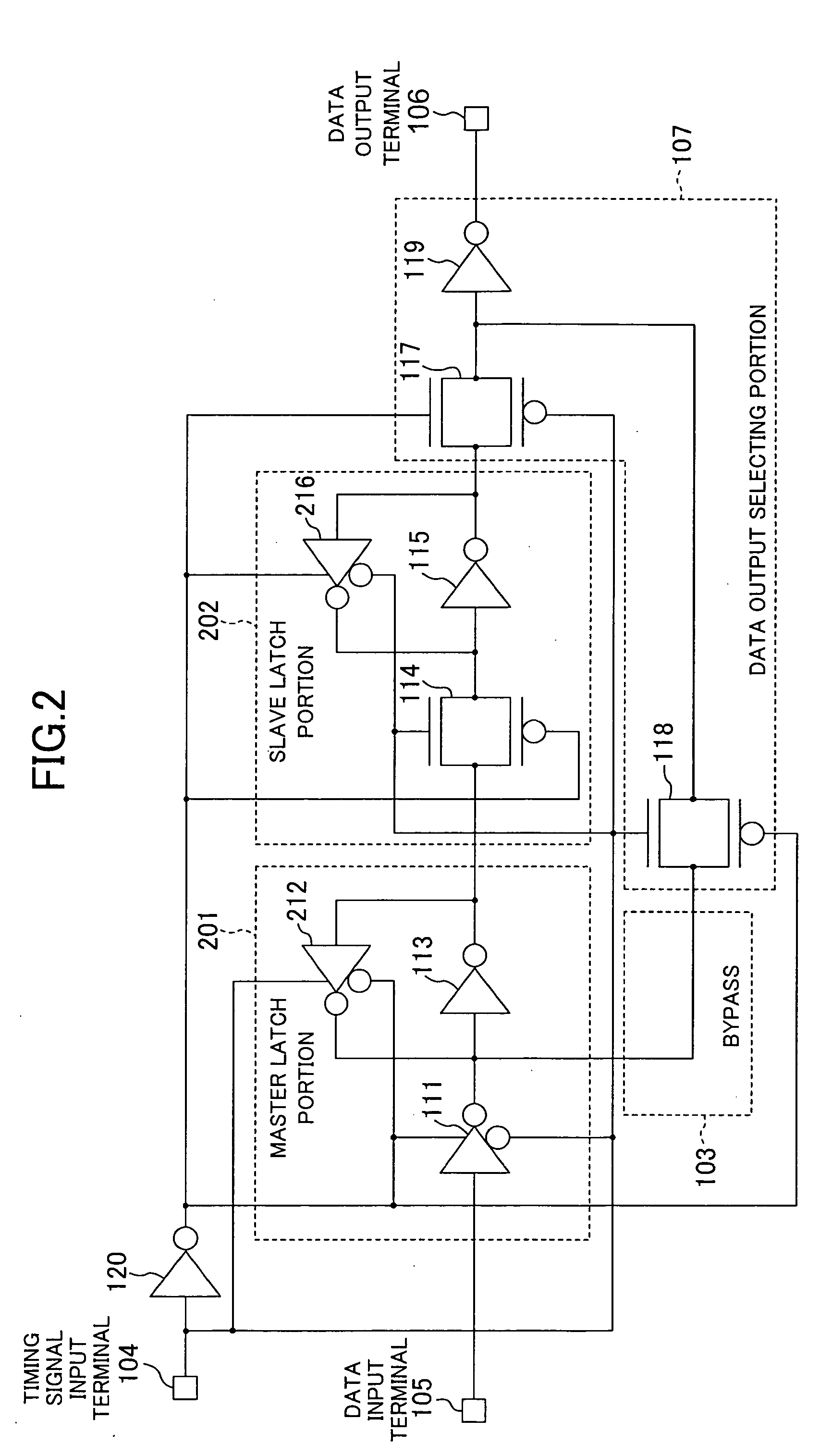
[0051] Instead of the data output selecting portion 107 of the first embodiment, a data output selecting portion 307 including tri-state inverters 317 and 318 may be provided as shown in FIG. 3. When the value of a timing signal is “0”, the tri-state inverters 317 and 318 select the output of a slave latch portion 102 (i.e., the tri-state inverter 317 is active and the tri-state inverter 318 is in a high-impedance state). On the other hand, when the value of the timing signal is “1”, the tri-state inverters 317 and 318 select the output from a bypass 103 (i.e., the tri-state inverter 317 is in a high-impedance state and the tri-state inverter 318 is active).
[0052] In this embodiment, the tri-state inverters 317 and 318 have the same driving capability (physical characteristic). Specifically, elements (transistors) constituting these inverters are designed to have the same size and shape, for example. That is, the driving capability of the tri-state inverter 317 does not affect the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com