Optical information device, optical storage medium, optical storage medium inspection device, and optical storage inspection method
a technology of optical information and inspection device, which is applied in the direction of digital signal error detection/correction, instruments, recording signal processing, etc., can solve the problems of power fluctuation that cannot be ignored, recorded signal quality can deteriorate, playback signal quality drops, etc., to reduce the effect of increased jitter, and reduce the effect of jitter
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
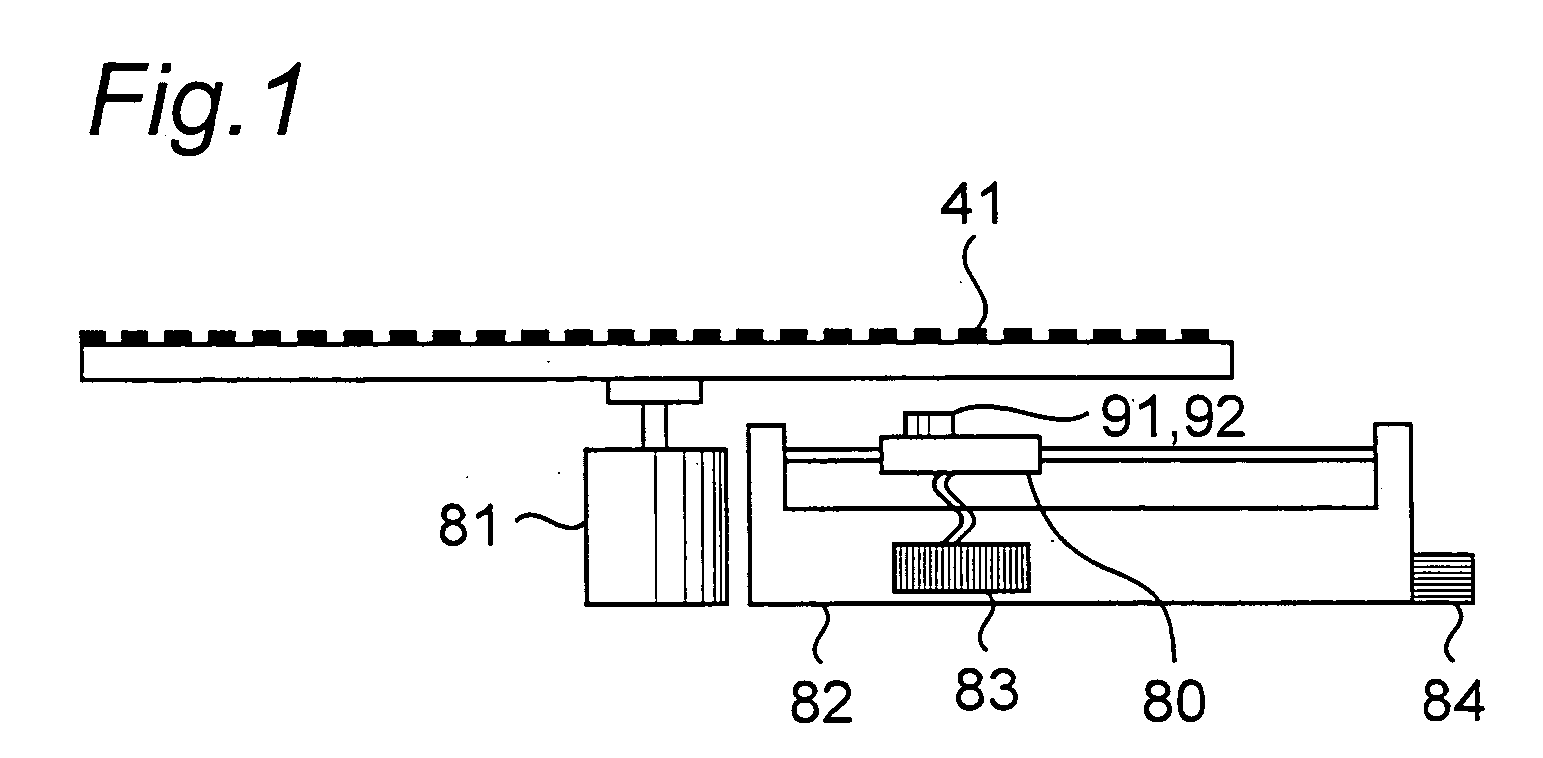
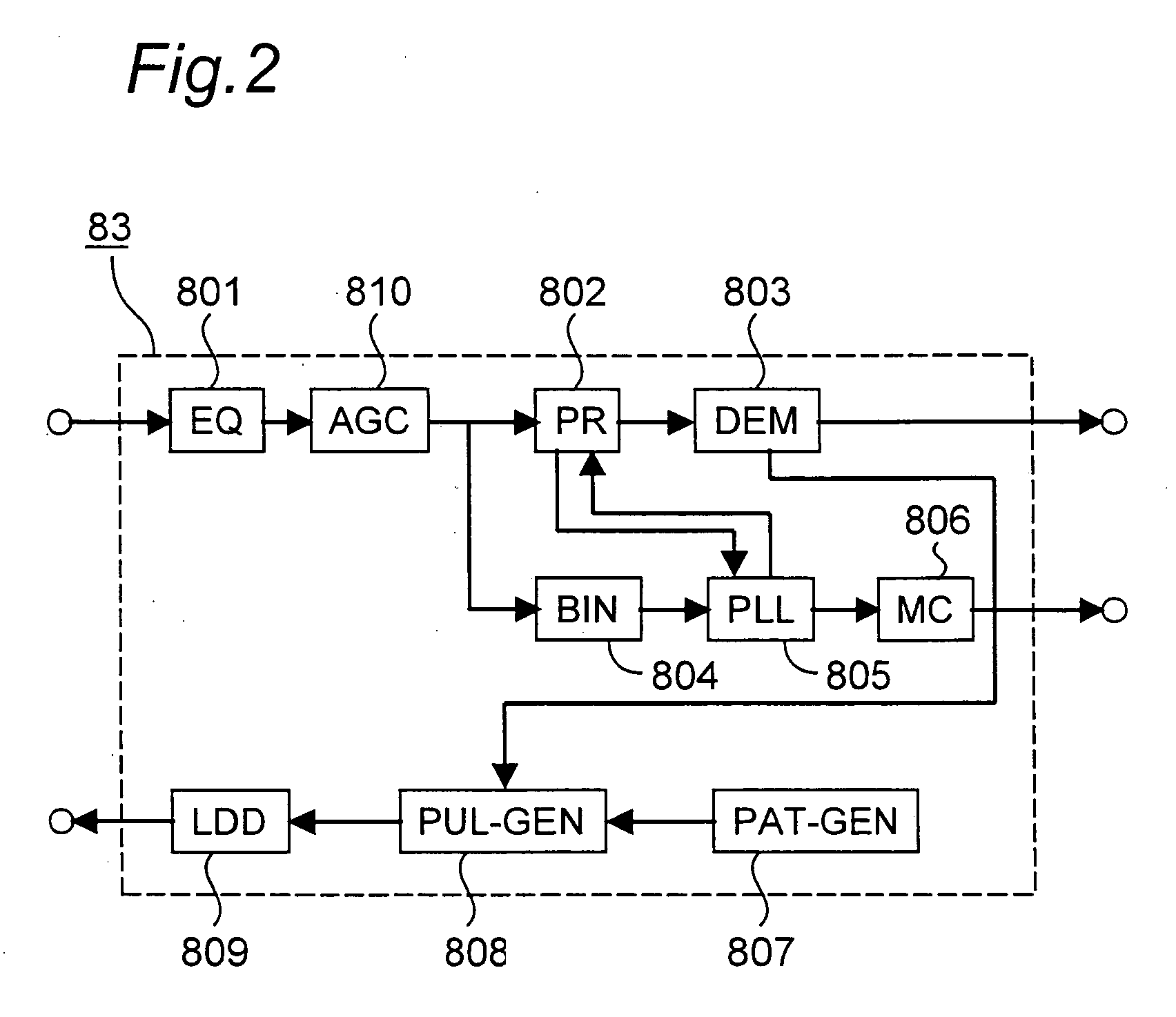
[0146]FIG. 1 shows an example of the configuration of an optical disc drive according to a first embodiment of the present invention. This optical disc drive has an optical pickup head 80, optical disc drive unit 81, optical pickup head drive unit 82, signal processing unit 83, and power supply unit 84. A configuration having a power supply unit 84 is shown in the figure, but a configuration in which a connection terminal (not shown) to an external power supply (not shown) is provided instead of power supply unit 84 and power is supplied by connecting the external power supply and connection terminal could be used. Furthermore, the configuration of the optical pickup head 80 is in no way limited, and the optical pickup head of this embodiment is identical to the conventional configuration shown in FIG. 9.
[0147] The function of each of these components is described next. The optical disc drive unit 81 spins the optical disc 41. The optical pickup head 80 sends a signal corresponding...
embodiment 2
[0185] The configuration of an optical storage medium according to another embodiment of the present invention is shown in FIG. 7. This optical disc 41 has a transparent protective layer 41a and two recording layers 41b, 41c. This optical disc 41 differs from optical storage medium 40 in that data recording layer 41c is a recording layer that can be rewritten multiple times, and data recording layer 41b is a read-only recording layer. Marks are formed in data recording layer 41b by embossing. The shortest marks and spaces are also 2 T. The transmittance of data recording layer 41b is also greater than 50%, and in this preferred embodiment is 80%. Because it is read-only, the transmittance of data recording layer 41b is substantially constant throughout the entire layer. Furthermore, because data recording layer 41b, which is a read-only recording layer, is on the light incidence side of data recording layer 41c, the power of the beam emitted to data recording layer 41c is stable bec...
embodiment 3
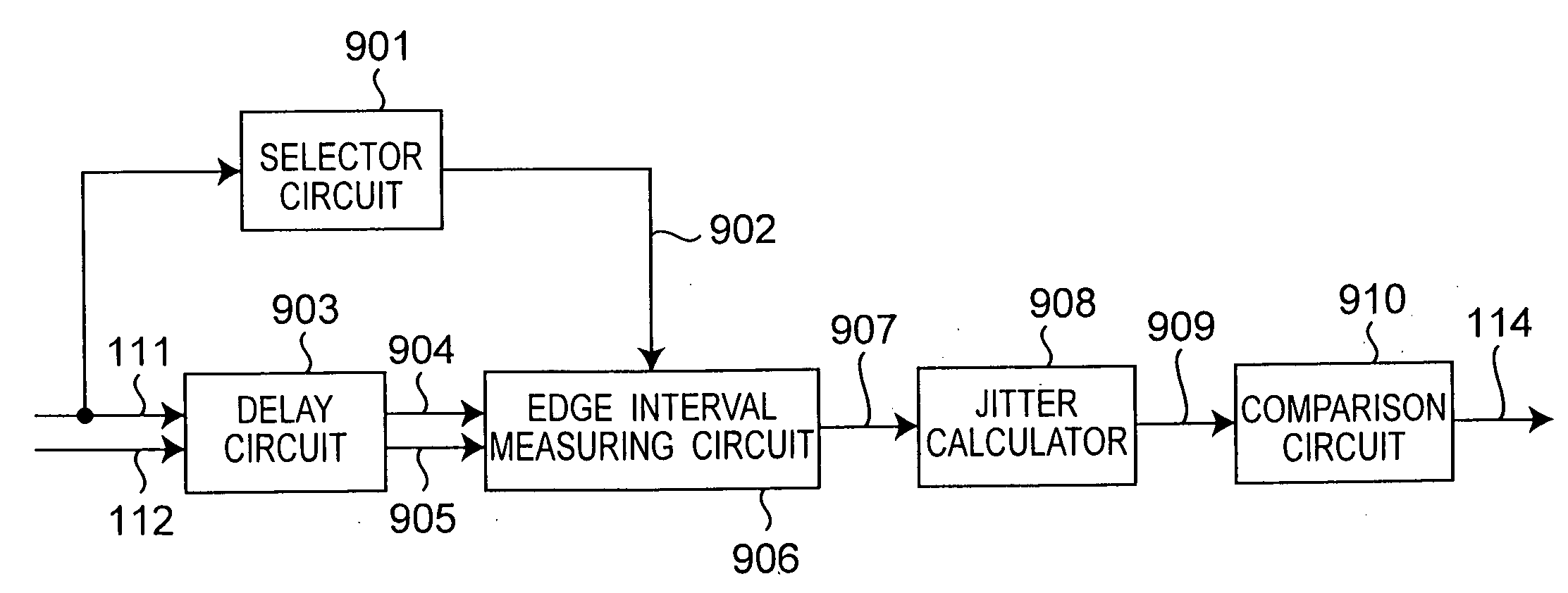
[0191] As another example of an optical disc drive according to the present invention, FIG. 8 shows the configuration of an optical disc drive that generates a TE signal using a phase difference method (also known as a DPD (differential phase detection) method) from an optical storage medium on which 2 T marks and spaces are formed as the shortest marks and spaces.
[0192] An optical storage medium having a recording layer on which embossed marks are formed as described with optical disc 41 according to the second embodiment can be used as the optical storage medium in this embodiment. The optical disc drive can use any type of optical pickup head insofar as the optical pickup head splits the beam in the far field region, detects the reflections with a photodetector, and can output signals enabling phase comparison. This embodiment is described using most common optical pickup head as shown in FIG. 9.
[0193] (a) Signals output from receptors 32a to 32d of photodetector 32 are input t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| oscillation wavelength λ1 | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| focal length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| focal length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com