Heat exchanger and fluid reservoir
a technology of fluid reservoir and heat exchanger, which is applied in the direction of indirect heat exchangers, lighting and heating apparatus, laminated elements, etc., can solve the problems of poor thermal exchange efficiency, large unswept or “dead” volumes, poor tasting liquid and/or microbial contamination of the liquid, etc., and achieve high thermal exchange efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
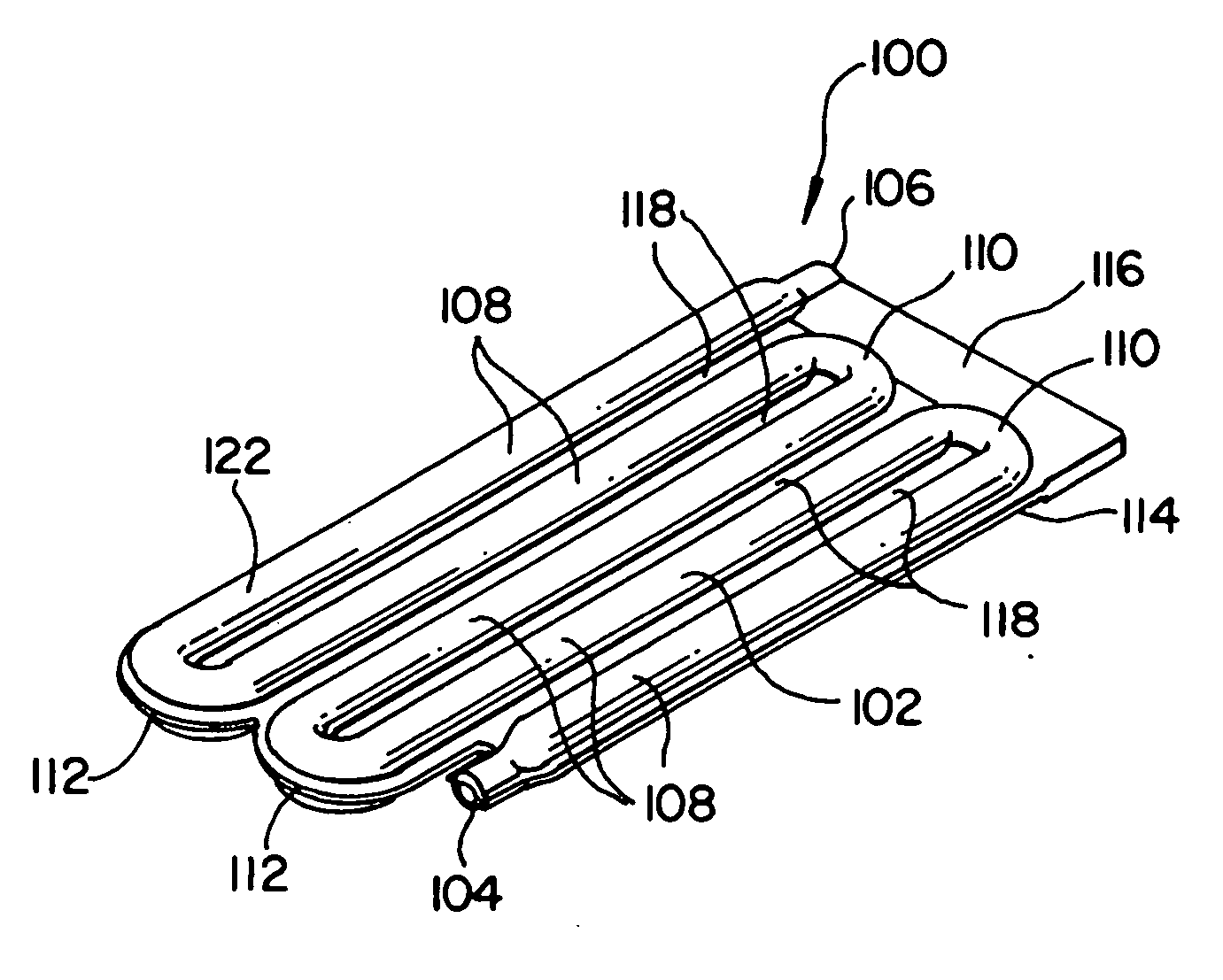
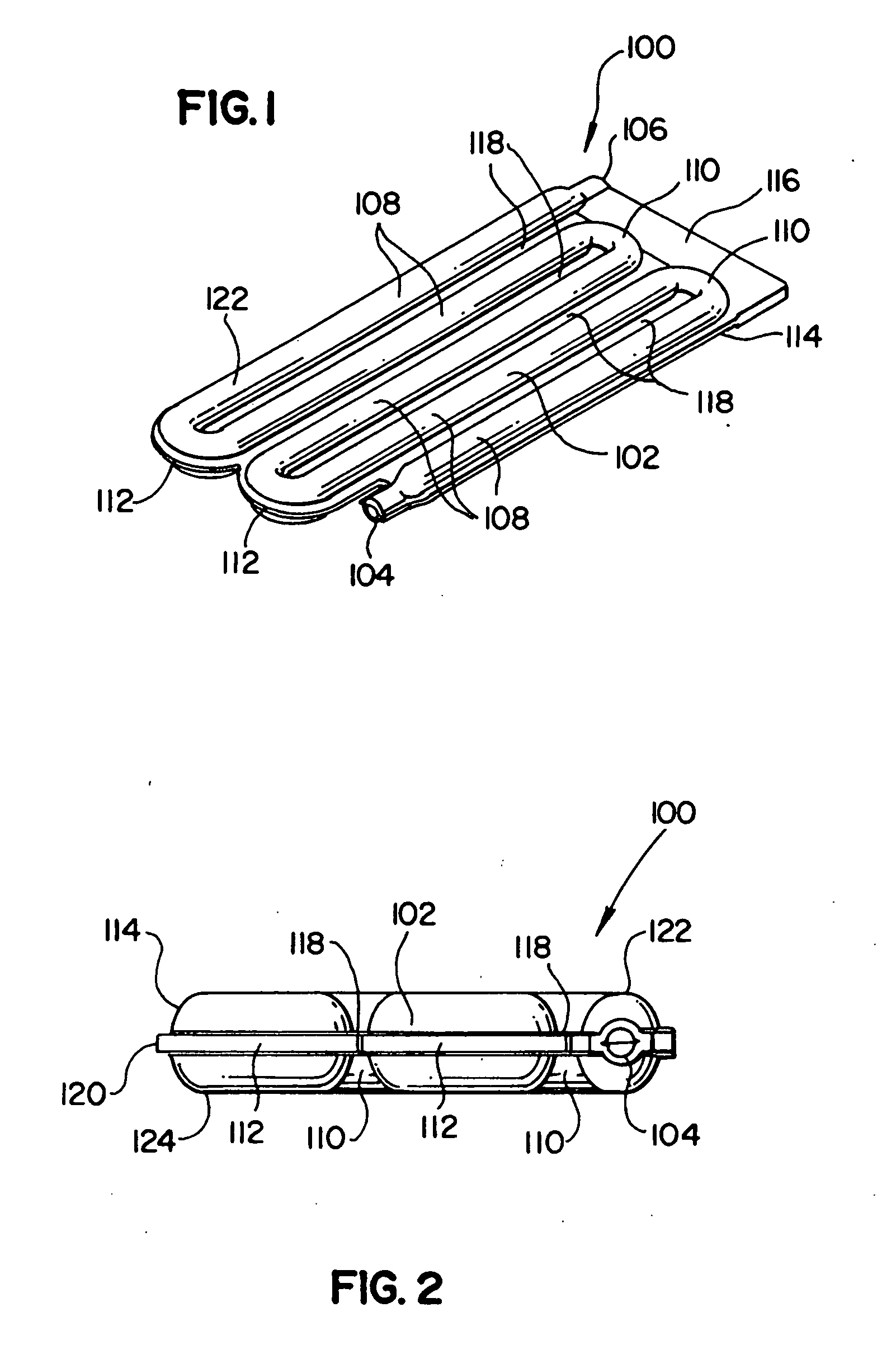
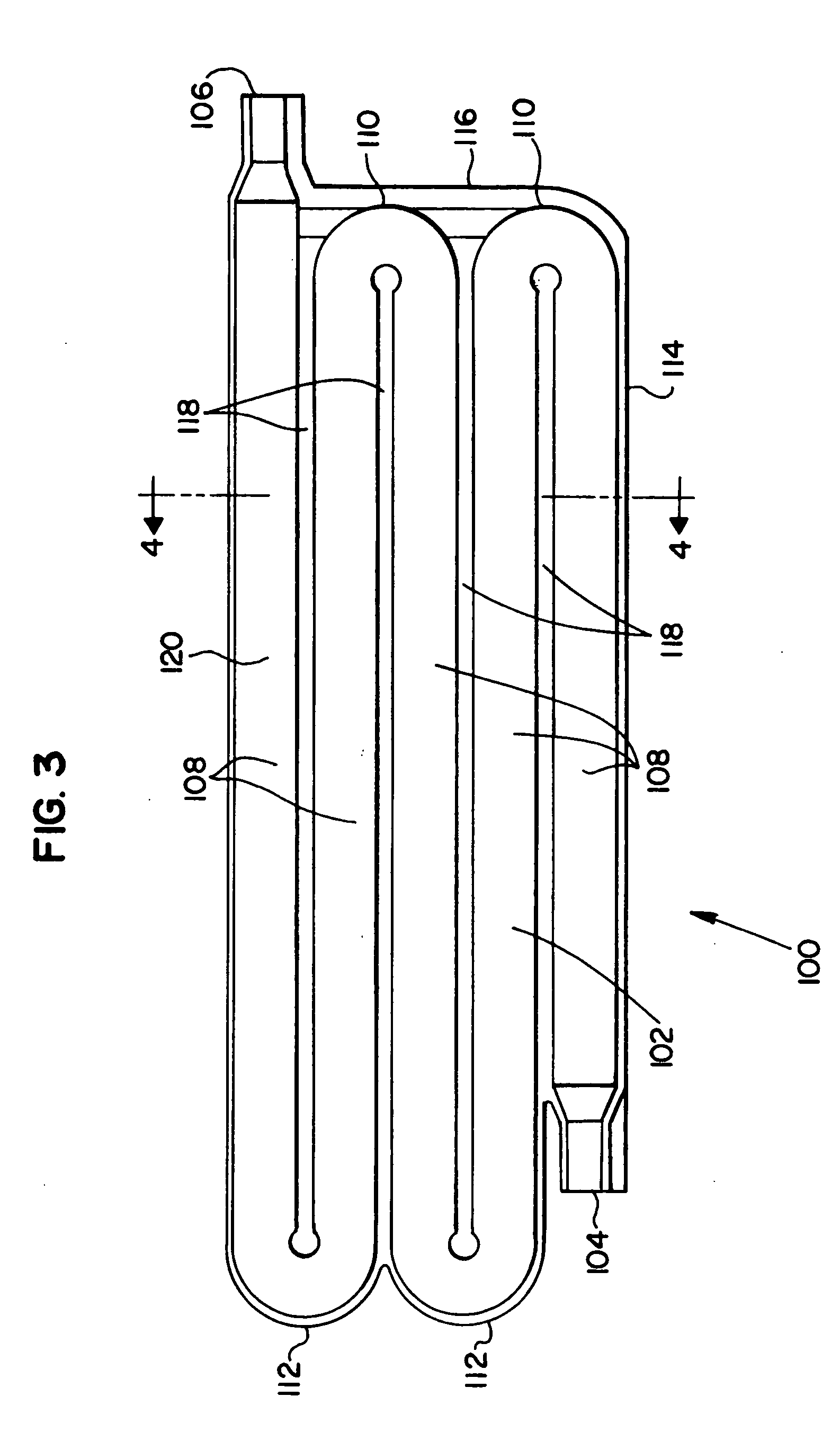
[0042] Improved fluid reservoirs described herein combine features of coiled tubes and tank fluid reservoirs to achieve desirable features of both types while exhibiting fewer drawbacks that are representative of each. New, improved, desirable processing approaches have made these previously commercially impractical fluid reservoirs practical on a commercial scale. In some presently preferred representative embodiments, the fluid reservoirs are designed to have flow that provides first in-first out flow without low flow or dead volume areas that can lead to stale liquid. At the same time, some presently preferred representative embodiments of fluid reservoirs can have a larger flow passage cross section than conventional coiled tubes so that less material is used and the pressure drop is less for a given tank volume. In some representative embodiments, the fluid reservoirs are in the form of a monolithic structure with a curved flow path and adjacent flow channels separated with a s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Reynolds number | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Reynolds number | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Reynolds number | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com